A Comprehensive Guide to Navigating High Peak: Understanding the Map and Its Significance
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to Navigating High Peak: Understanding the Map and Its Significance
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to Navigating High Peak: Understanding the Map and Its Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to Navigating High Peak: Understanding the Map and Its Significance
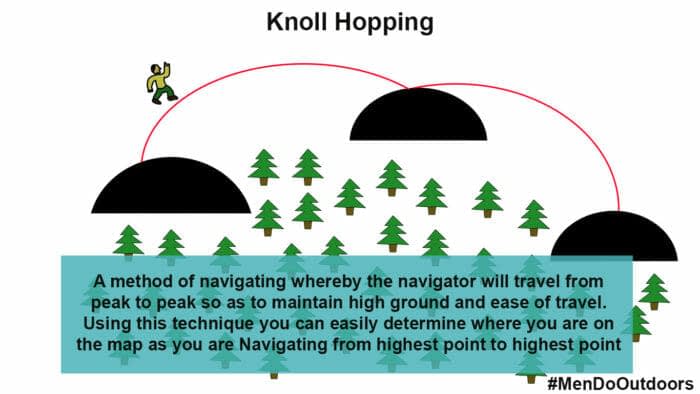
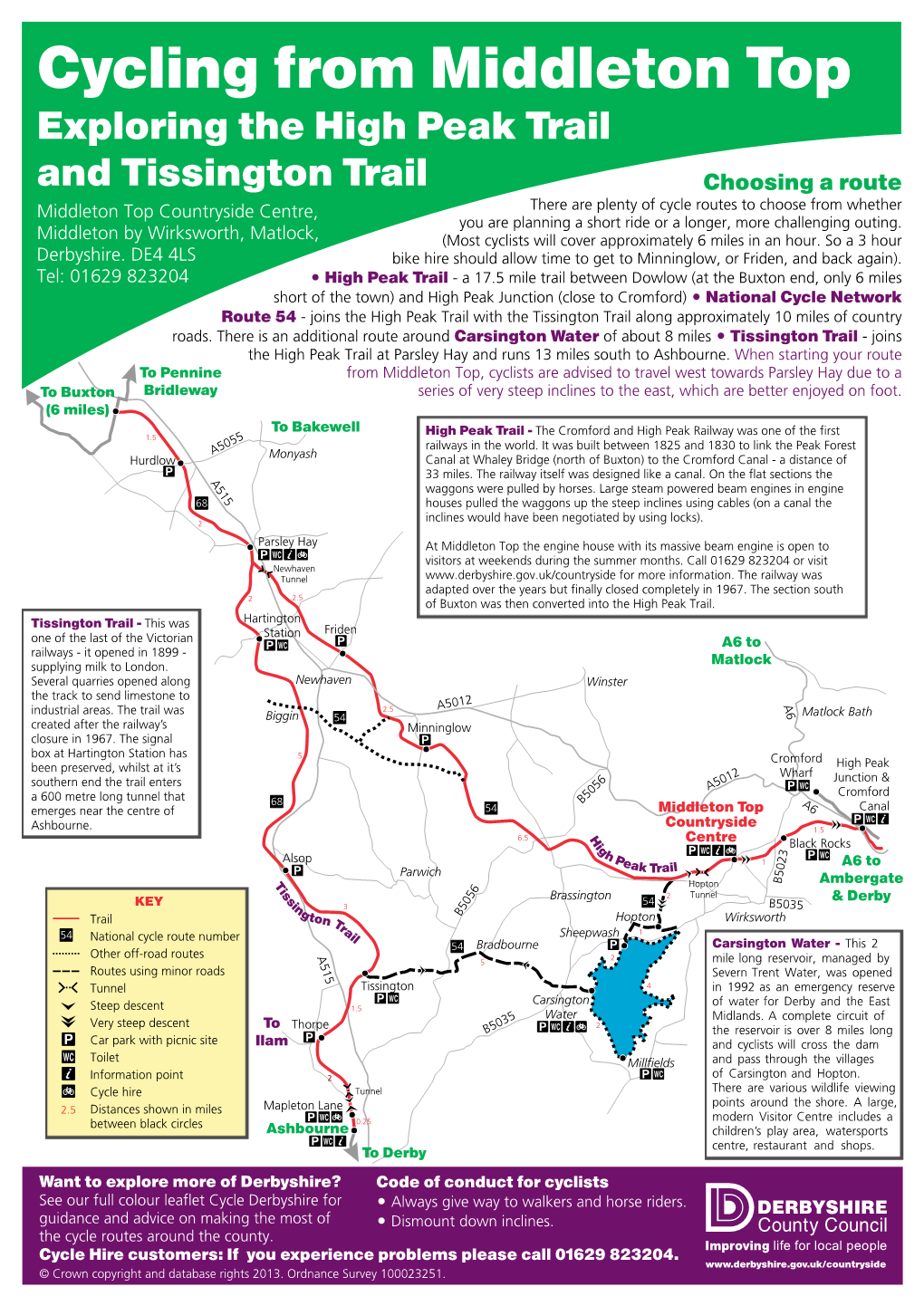
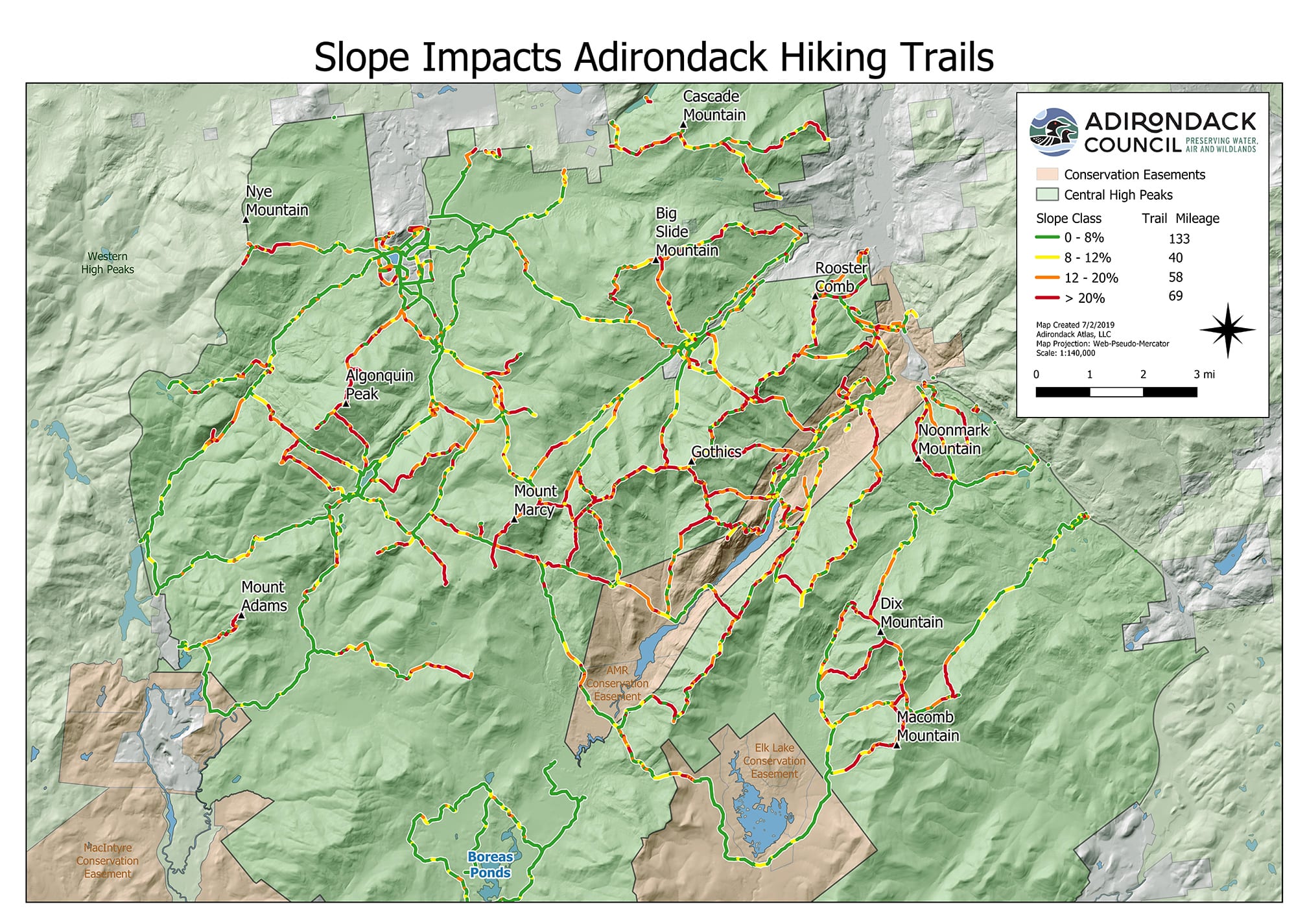
High Peak, a majestic summit often sought by adventurous hikers and climbers, requires careful planning and a thorough understanding of its terrain. A detailed map serves as an indispensable tool for safe and successful navigation, offering crucial information about trails, elevation changes, water sources, and potential hazards. This article delves into the intricacies of High Peak maps, exploring their components, benefits, and essential considerations for any aspiring climber.
Understanding the Language of High Peak Maps:
High Peak maps are typically topographic maps, showcasing the landscape’s three-dimensional features. Key elements to decipher include:
- Contour Lines: These lines connect points of equal elevation, providing a visual representation of the terrain’s slope and steepness. Closer contour lines indicate a steeper incline, while spaced-out lines signify a gentler slope.
- Elevation Points: Marked with numerical values, these points indicate specific elevations on the map, helping hikers gauge the altitude they are navigating.
- Trails: Designated paths are clearly marked, often with different colors or symbols to distinguish between hiking trails, climbing routes, and access roads.
- Water Sources: Maps often identify streams, rivers, lakes, and springs, providing vital information about water availability during the journey.
- Points of Interest: Landmarks, viewpoints, campsites, and shelters are typically marked, enhancing the overall navigation experience.
Navigating High Peak with Confidence:
A well-prepared hiker armed with a High Peak map enjoys numerous advantages:
- Route Planning: Maps allow for meticulous route planning, enabling hikers to choose the most suitable trail based on their experience, fitness level, and available time.
- Elevation Awareness: The contour lines provide a clear picture of elevation changes, allowing hikers to anticipate challenging climbs and plan for appropriate pacing.
- Hazard Identification: Maps highlight potential hazards like steep cliffs, rocky terrain, and treacherous slopes, enabling hikers to take necessary precautions.
- Emergency Preparedness: Maps can help locate the nearest trailhead, shelter, or communication point, crucial for navigating emergencies or unexpected weather changes.
- Environmental Awareness: Understanding the terrain through maps allows hikers to appreciate the natural beauty of High Peak, recognizing its delicate ecosystems and respecting its fragility.
FAQs about High Peak Maps:
Q: What type of map is best suited for High Peak?
A: Topographic maps with a scale of 1:24,000 or 1:25,000 are generally recommended for High Peak. These maps provide sufficient detail while maintaining a manageable size for carrying.
Q: Are electronic maps a viable alternative to paper maps?
A: Electronic maps, like those on GPS devices or smartphones, can be convenient, but they rely on battery power and cellular reception, which may not be reliable in remote areas. It is recommended to have a paper map as a backup.
Q: What are the essential features to look for in a High Peak map?
A: Essential features include clear contour lines, accurate trail markings, water source identification, elevation points, and information about campsites and shelters.
Q: How can I learn to read a topographic map effectively?
A: Numerous resources are available to learn map reading skills, including online tutorials, workshops, and books. The National Park Service and other organizations offer excellent resources specifically tailored to hiking and climbing.
Tips for Using High Peak Maps:
- Always study the map before embarking on your journey. Familiarize yourself with the terrain, trail markings, and potential hazards.
- Mark your planned route on the map. This helps you stay on track and allows others to understand your intended itinerary.
- Carry a compass and learn how to use it. A compass is essential for navigating in areas with limited visibility.
- Check the weather forecast before your hike. Weather conditions can significantly impact your experience and safety.
- Pack extra food, water, and warm clothing. Be prepared for unexpected delays or changes in weather.
- Inform someone about your plans and expected return time. This ensures someone knows your whereabouts in case of an emergency.
Conclusion:
A well-prepared hiker understands the importance of a detailed map in navigating High Peak. The map serves as a vital tool for route planning, elevation awareness, hazard identification, emergency preparedness, and environmental appreciation. By mastering the language of maps and utilizing them responsibly, hikers can unlock the wonders of High Peak, ensuring a safe and enriching journey.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to Navigating High Peak: Understanding the Map and Its Significance. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!