A Continental Tapestry: Understanding the Interconnectedness of Europe, Asia, and Africa
Related Articles: A Continental Tapestry: Understanding the Interconnectedness of Europe, Asia, and Africa
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Continental Tapestry: Understanding the Interconnectedness of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Continental Tapestry: Understanding the Interconnectedness of Europe, Asia, and Africa

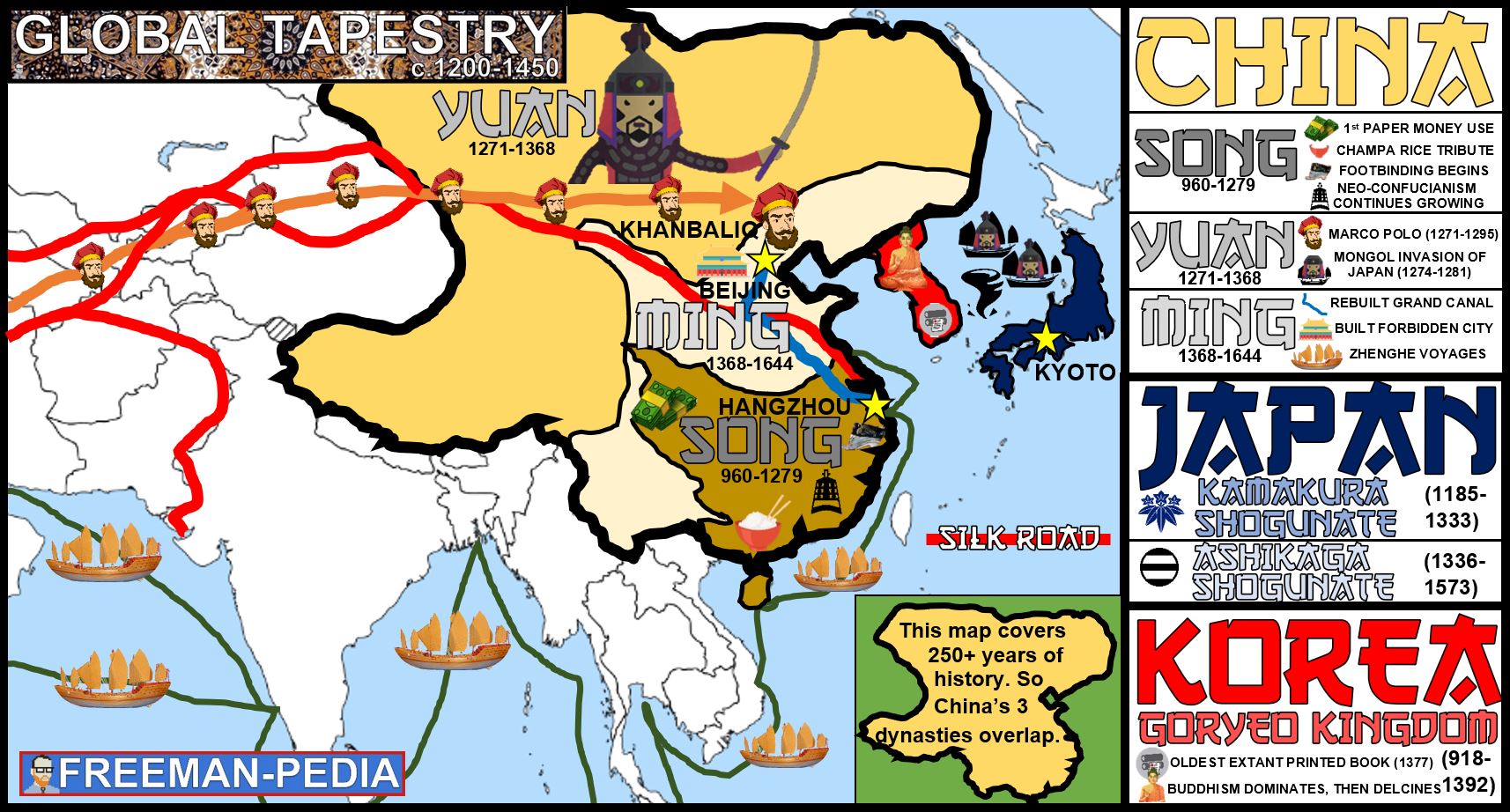
The Earth’s surface is a mosaic of continents, each with its own unique characteristics and history. However, the landmasses of Europe, Asia, and Africa, while distinct, are intricately interwoven, forming a tapestry of shared histories, cultural exchanges, and interconnected destinies. Understanding this interconnectedness requires a comprehensive approach, delving into the geographical, historical, and cultural nuances that bind these continents.
A Geographic Perspective:
Europe, Asia, and Africa are often considered separate continents due to their distinct geographical features. Europe, the westernmost of the three, is a peninsula extending westward from Asia, separated by the Ural Mountains and the Caucasus. Asia, the largest continent, encompasses the easternmost portion of the Eurasian landmass, stretching from the Mediterranean Sea to the Pacific Ocean. Africa, the second-largest continent, sits south of Europe and is connected to Asia by the Suez Canal.
This geographical arrangement has played a crucial role in shaping the history and culture of these continents. The proximity of Europe to Asia facilitated trade routes, cultural exchanges, and migrations, leading to the development of shared traditions and influences. The geographical barriers of the Mediterranean Sea, the Sahara Desert, and the Ural Mountains, while presenting challenges, also contributed to the distinct identities of these continents.
Historical Intertwining:
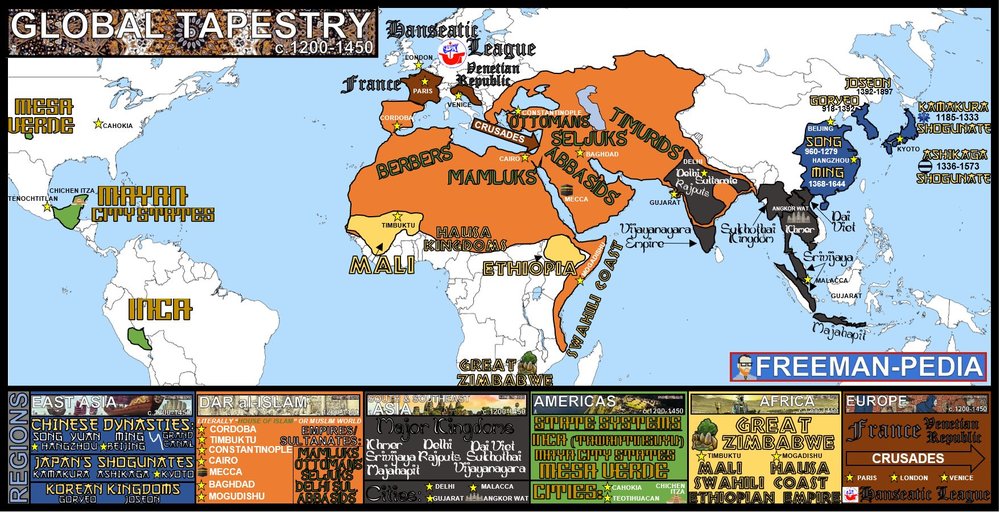
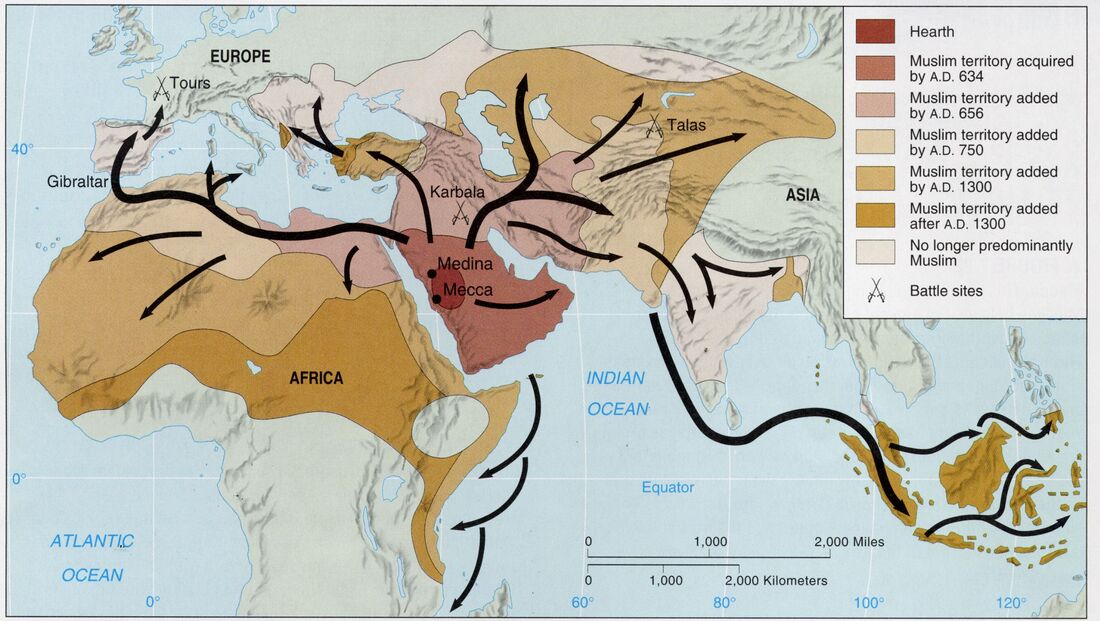
The history of Europe, Asia, and Africa is a complex tapestry woven with threads of conflict, cooperation, and cultural exchange. From the ancient Silk Road, connecting the East and West, to the colonial era, where European powers exerted influence over vast swathes of Asia and Africa, the interconnectedness of these continents has been evident throughout history.
The Roman Empire, spanning both Europe and North Africa, left a lasting legacy on the cultural landscape of the region. The spread of Christianity, originating in the Middle East, further cemented the religious ties between Europe and Asia. The Islamic conquests, originating in the Arabian Peninsula, expanded into North Africa and parts of Europe, leaving an indelible mark on the cultural and religious makeup of the region.
Cultural Crossroads:
The geographical and historical connections between Europe, Asia, and Africa have fostered a rich tapestry of cultural exchange. The Silk Road, for instance, facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and artistic influences, connecting civilizations across continents. The spread of languages, religions, and artistic styles further solidified the cultural interconnectedness of these regions.
From the vibrant bazaars of Istanbul, blending Eastern and Western influences, to the intricate architecture of the Taj Mahal, inspired by Persian and Mughal styles, the cultural landscape of Europe, Asia, and Africa is a testament to the centuries of exchange and interaction.
The Importance of Understanding the Interconnectedness:
Understanding the interconnectedness of Europe, Asia, and Africa is essential for comprehending the complexities of the contemporary world. The challenges of globalization, migration, and climate change transcend national borders, requiring collaborative solutions that acknowledge the shared interests and vulnerabilities of these continents.
FAQs:
1. What are the key geographical features that define the relationship between Europe, Asia, and Africa?
The key geographical features include the Ural Mountains, the Caucasus, the Mediterranean Sea, the Sahara Desert, and the Suez Canal. These features have shaped the historical interactions and cultural exchanges between these continents.
2. How has the Silk Road influenced the cultural landscape of Europe, Asia, and Africa?
The Silk Road facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and artistic influences, connecting civilizations across continents. It led to the spread of languages, religions, and artistic styles, contributing to the cultural interconnectedness of the region.
3. What are the contemporary challenges that necessitate a deeper understanding of the interconnectedness of these continents?
Challenges such as globalization, migration, and climate change transcend national borders, requiring collaborative solutions that acknowledge the shared interests and vulnerabilities of these continents.
Tips:
1. Utilize maps and atlases to visualize the geographical relationships between Europe, Asia, and Africa.
2. Explore historical accounts and documentaries to gain insights into the historical interactions and cultural exchanges between these continents.
3. Engage with diverse cultural perspectives to appreciate the richness and complexity of the cultural landscape of Europe, Asia, and Africa.
Conclusion:
The interconnectedness of Europe, Asia, and Africa is a powerful reminder of the interconnectedness of the world. Understanding this complex relationship is crucial for navigating the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century. By recognizing the shared history, cultural exchanges, and intertwined destinies of these continents, we can foster greater cooperation, understanding, and progress for the benefit of all humanity.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Continental Tapestry: Understanding the Interconnectedness of Europe, Asia, and Africa. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!