A Divided City: Understanding the Berlin Cold War Map
Related Articles: A Divided City: Understanding the Berlin Cold War Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Divided City: Understanding the Berlin Cold War Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Divided City: Understanding the Berlin Cold War Map

The Berlin Cold War map stands as a potent visual representation of the Cold War’s stark reality. This map, depicting a city physically split by an ideological divide, encapsulates the tension and geopolitical complexities of the era. Understanding its intricacies offers a unique lens through which to analyze the Cold War’s impact on Germany, Europe, and the world.
The Birth of a Divided City:
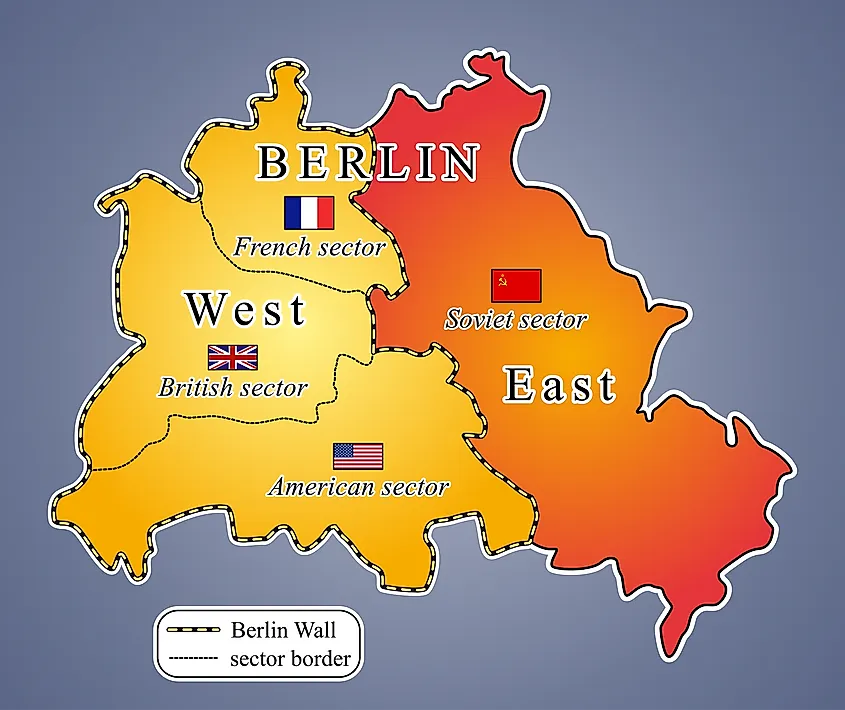
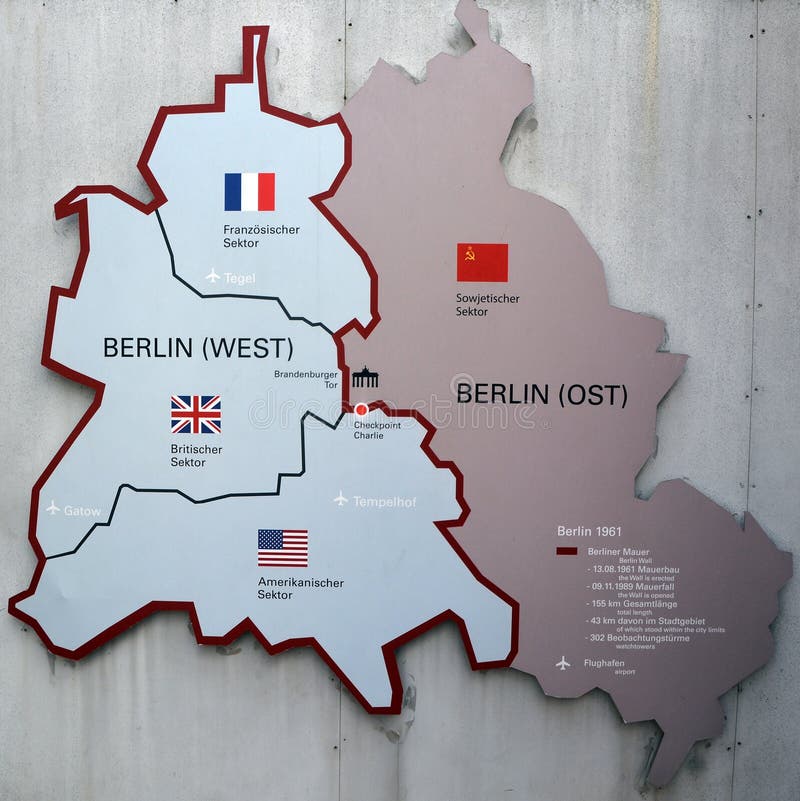
Following World War II, Germany was divided into four occupation zones, controlled by the Allied powers: the United States, the United Kingdom, the Soviet Union, and France. Berlin, situated within the Soviet zone, was also divided into four sectors, mirroring the occupation zones. While the Western Allies combined their sectors into West Berlin, the Soviet Union maintained control over East Berlin.
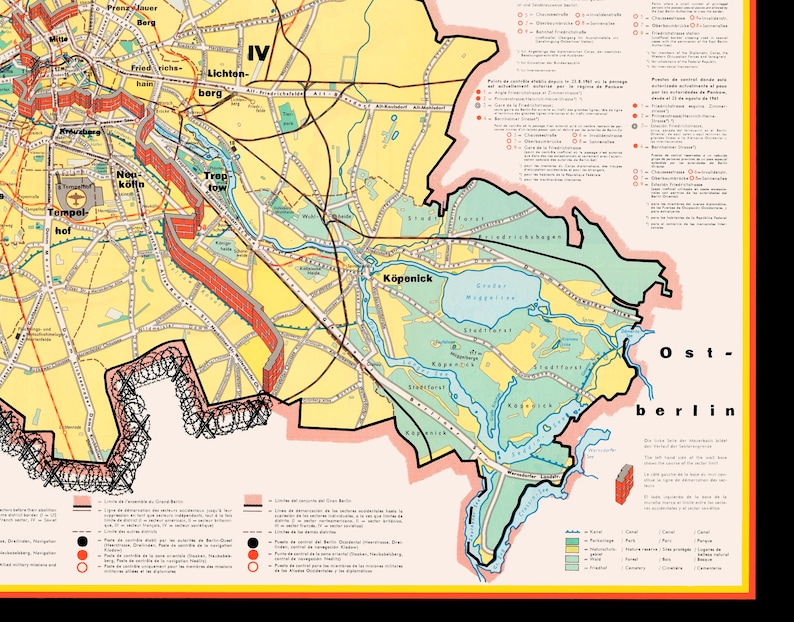
The Berlin Wall: A Tangible Symbol of Division:
In 1961, the Soviet Union erected the Berlin Wall, a physical barrier separating East and West Berlin. This act, intended to prevent the exodus of East German citizens to the West, transformed the Berlin Cold War map into a powerful symbol of the Cold War’s ideological divide. The Wall, with its watchtowers, barbed wire, and heavily armed guards, became a stark reminder of the Iron Curtain that separated East and West Europe.
The Berlin Cold War Map: A Geopolitical Puzzle:
The Berlin Cold War map highlights the complex geopolitical situation within the city. While West Berlin, surrounded by East Germany, functioned as a Western enclave within Soviet-controlled territory, it also served as a symbol of freedom and opportunity. The map demonstrates the strategic importance of Berlin, which became a focal point for Cold War tensions and a stage for numerous confrontations.
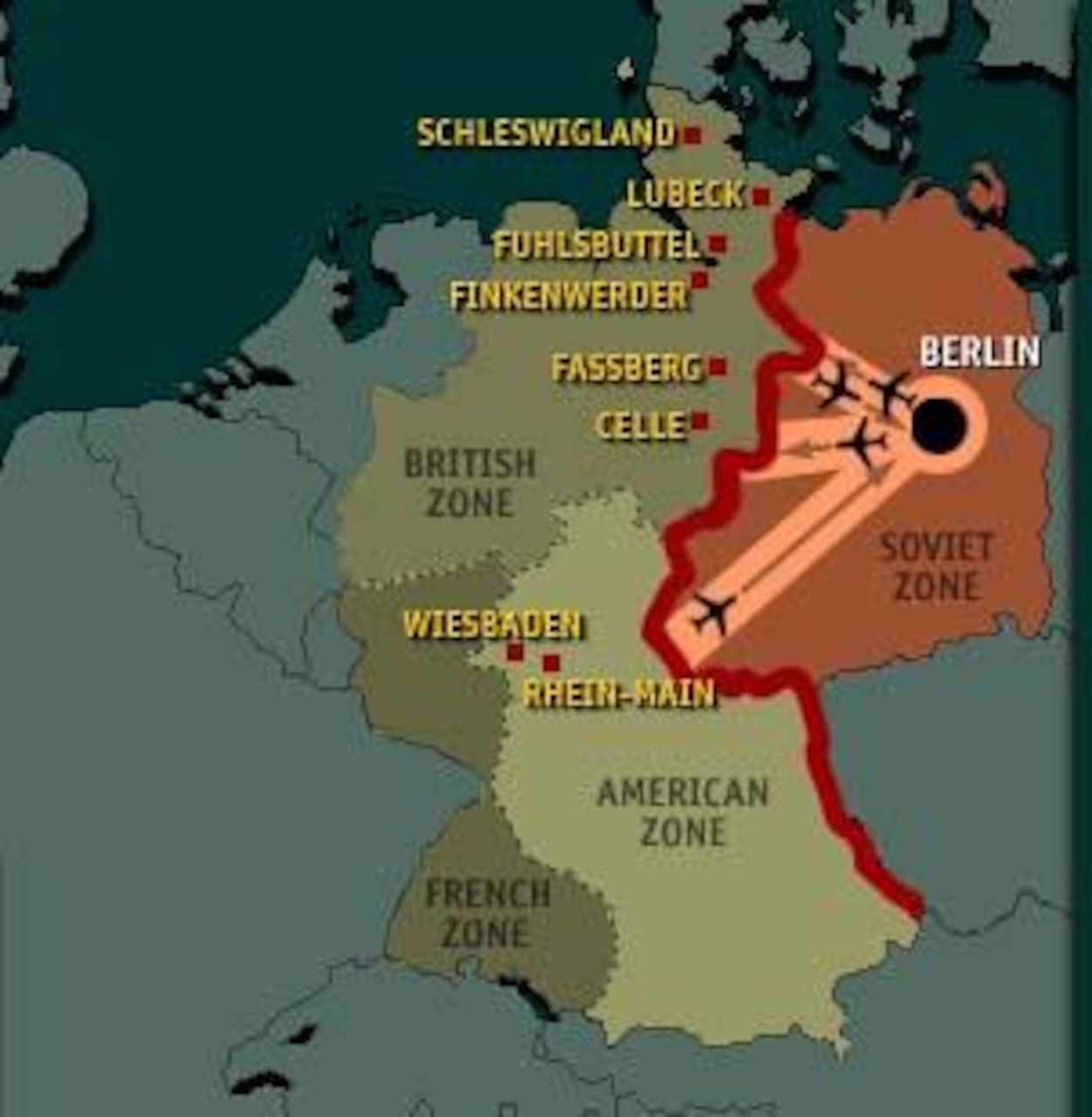
The Berlin Airlift: A Test of Will:
The Soviet Union’s 1948 blockade of West Berlin aimed to force the Western Allies to relinquish control. In response, the Western powers initiated the Berlin Airlift, a massive operation to supply West Berliners with food, fuel, and other necessities. This aerial lifeline, lasting for over a year, showcased the Western Allies’ determination and challenged the Soviet Union’s control over the city.
The Berlin Crisis of 1961:
The construction of the Berlin Wall, a response to the growing exodus from East Germany, marked a significant escalation of Cold War tensions. The crisis, fueled by fear of Soviet aggression, brought the world to the brink of war. The Berlin Cold War map became a visual representation of this perilous situation, highlighting the potential for conflict.
The Berlin Cold War Map: A Window into History:
The Berlin Cold War map serves as a valuable historical resource, offering insights into the Cold War’s impact on Germany and Europe. It provides a visual understanding of the division, the tensions, and the geopolitical complexities of the era. The map also serves as a reminder of the Cold War’s legacy, highlighting the enduring impact of the ideological divide and the importance of diplomacy and cooperation.
FAQs about the Berlin Cold War Map:
Q: Why was Berlin divided?
A: Following World War II, Germany was divided into four occupation zones, with Berlin, located within the Soviet zone, also divided into four sectors. The Western Allies combined their sectors into West Berlin, while the Soviet Union maintained control over East Berlin.
Q: Why was the Berlin Wall built?
A: The Berlin Wall was erected in 1961 by the Soviet Union to prevent the exodus of East German citizens to the West. The wall became a symbol of the Cold War’s ideological divide.
Q: What was the Berlin Airlift?
A: The Berlin Airlift was a massive operation undertaken by the Western Allies to supply West Berlin with food, fuel, and other necessities after the Soviet Union imposed a blockade in 1948.
Q: What was the significance of the Berlin Crisis of 1961?
A: The Berlin Crisis of 1961, triggered by the construction of the Berlin Wall, brought the world to the brink of war. The crisis highlighted the potential for conflict and the fragility of peace during the Cold War.
Tips for Understanding the Berlin Cold War Map:
- Focus on the key geographical features: Pay attention to the location of the Berlin Wall, the division of the city into East and West, and the surrounding East German territory.
- Consider the historical context: Understand the events leading up to the division of Berlin, including World War II and the Allied occupation.
- Analyze the symbolism: Recognize the Berlin Wall as a symbol of division and the Berlin Airlift as a symbol of Western determination.
- Explore the impact on the people: Consider the experiences of those living in both East and West Berlin during the Cold War.
Conclusion:
The Berlin Cold War map is a powerful visual representation of the Cold War’s impact on Germany and Europe. It highlights the division, the tensions, and the geopolitical complexities of the era. Studying this map offers a unique opportunity to understand the Cold War’s legacy and the importance of diplomacy and cooperation in maintaining peace.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Divided City: Understanding the Berlin Cold War Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!