A Tale of Two Cities: Exploring the Maps of Sparta and Athens
Related Articles: A Tale of Two Cities: Exploring the Maps of Sparta and Athens
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Tale of Two Cities: Exploring the Maps of Sparta and Athens. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Tale of Two Cities: Exploring the Maps of Sparta and Athens

The ancient Greek city-states of Sparta and Athens, though geographically close, were worlds apart in their political, social, and cultural structures. Understanding the geographical context of these two powerful entities is crucial to appreciating their unique identities and the enduring impact they had on the course of Western civilization.
Sparta: A Fortified City-State
Sparta was located in the fertile valley of the Eurotas River in the Peloponnese region of Greece. The city itself was relatively small, with its main focus being on military training and expansion. Its geographical position, nestled between the Taygetus Mountains and the Eurotas River, provided both natural protection and access to fertile land for agriculture.
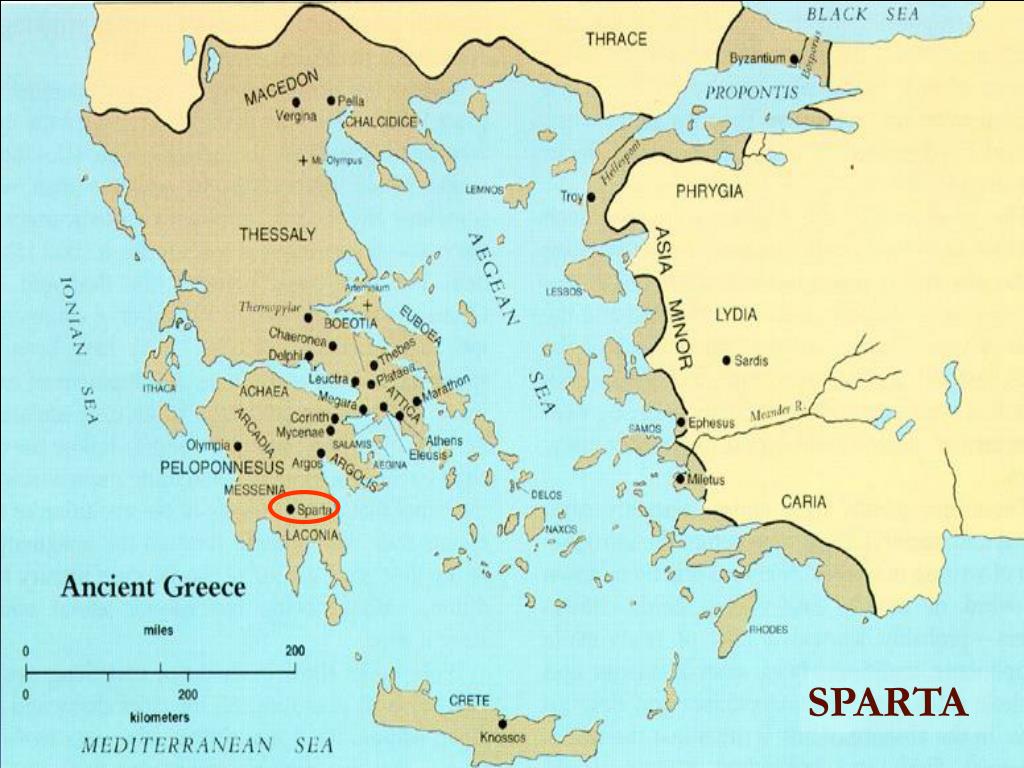
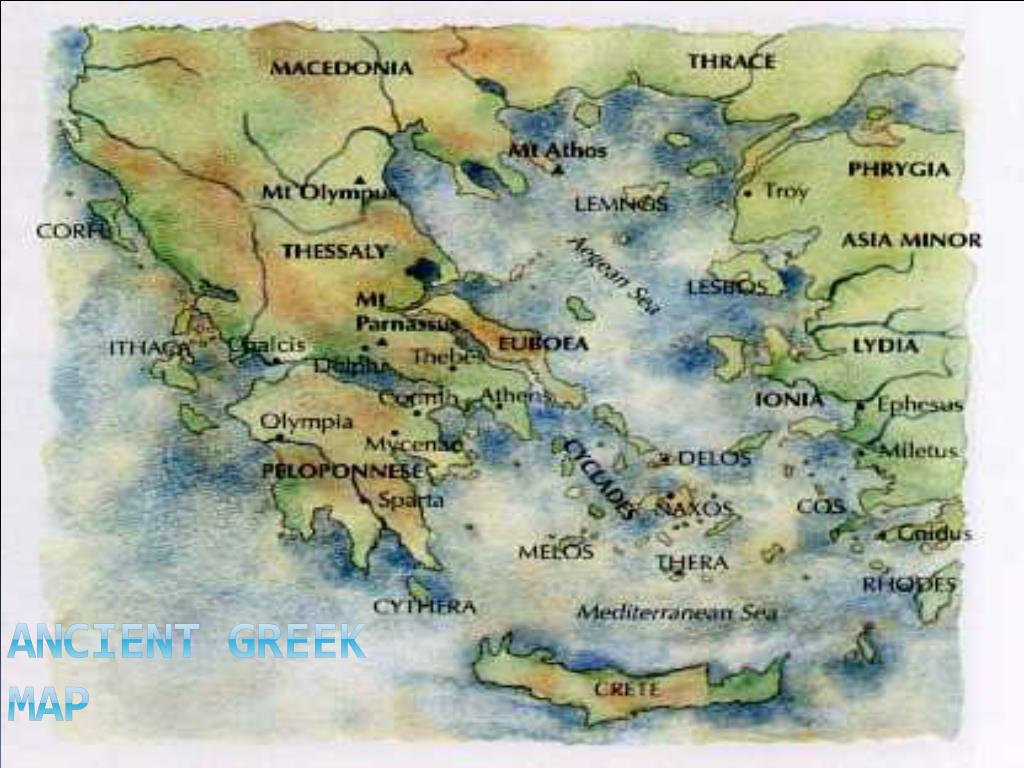
The Map of Sparta:
- Location: The city of Sparta was situated in the Laconia region, in the southeastern Peloponnese peninsula. It was strategically located near the Eurotas River, which provided water and fertile land for agriculture.
- Terrain: The terrain around Sparta was characterized by the Taygetus Mountains, which provided natural defenses against invaders. The Eurotas River valley offered fertile land for farming and allowed for easy communication within the region.
- Expansion: Sparta’s territorial expansion led to the control of the surrounding areas, including the coastal city of Gythium and the fertile region of Messenia. This expansion provided Sparta with a significant agricultural base and strategic advantages.
Athens: A Thriving City-State
Athens, on the other hand, was located in the Attic peninsula, overlooking the Aegean Sea. It was a bustling center of trade, commerce, and intellectual pursuits. The city’s strategic location, with access to the sea and fertile land, facilitated its growth and prosperity.
The Map of Athens:
- Location: Athens was situated on a peninsula in the eastern part of Attica, facing the Saronic Gulf. Its proximity to the sea made it a natural port and a hub for trade.
- Terrain: The terrain around Athens was a mix of hills and plains, offering both defensive advantages and fertile land for agriculture. The Acropolis, a hill overlooking the city, was a prominent landmark and served as a defensive stronghold.
- Expansion: Athens’ influence extended beyond its city walls, encompassing the surrounding region of Attica and several islands in the Aegean Sea. This expansion allowed Athens to control trade routes and access valuable resources.
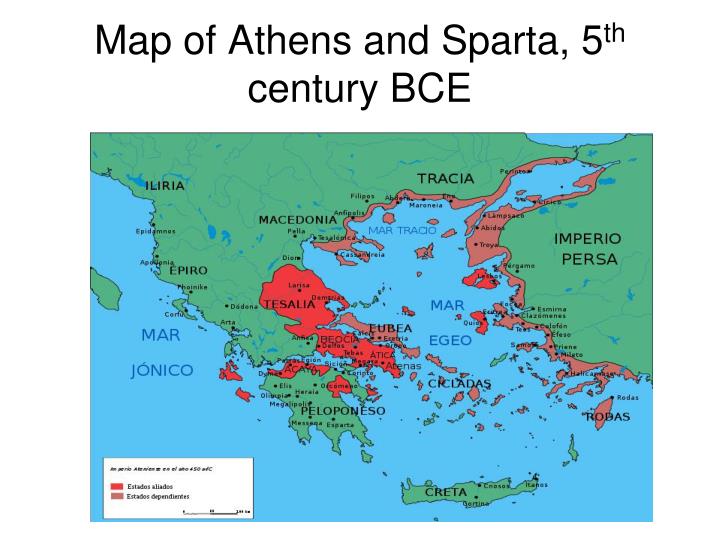
The Significance of the Maps
The maps of Sparta and Athens reveal the crucial role geography played in shaping their distinct identities. Sparta’s strategic location, with its natural defenses and access to fertile land, fostered a focus on military strength and territorial expansion. Athens’ location, with its access to the sea and fertile land, facilitated its growth as a commercial and cultural center.
The Impact of Geography on Their Societies
- Sparta: The terrain around Sparta, with its mountainous landscape and fertile valley, influenced its social structure and political system. The emphasis on military strength and discipline was directly linked to the need for defense and territorial expansion. Spartan society was highly militaristic, with a strict social hierarchy and a focus on physical training.
- Athens: The geographical advantages of Athens, with its access to the sea and fertile land, contributed to its flourishing economy and its development as a center of learning and culture. The Athenian democracy, with its emphasis on civic participation and intellectual pursuits, was a product of its unique environment.
The Maps as a Window into History
The maps of Sparta and Athens offer a valuable window into the ancient world, revealing the intricate relationship between geography, culture, and politics. They provide a visual representation of the unique characteristics of these two city-states, highlighting their strategic locations, territorial expansions, and the ways in which geography shaped their social structures and cultural values.
FAQs on Sparta and Athens Maps:
-
Q: What are the main geographical differences between Sparta and Athens?
- A: Sparta was located in the Peloponnese region, characterized by mountains and fertile valleys, while Athens was situated on a peninsula in Attica, with access to the sea and fertile land.
-
Q: How did the geography of Sparta influence its society?
- A: The mountainous terrain and the need for defense led to a highly militaristic society, with a focus on physical training and discipline.
-
Q: How did the geography of Athens influence its society?
- A: Athens’ access to the sea and fertile land facilitated its growth as a commercial and cultural center, leading to a democratic system and a flourishing intellectual life.
-
Q: What are some key geographical features on the maps of Sparta and Athens?
- A: Key features include the Taygetus Mountains and the Eurotas River in Sparta, and the Acropolis and the Saronic Gulf in Athens.
-
Q: How did the maps of Sparta and Athens contribute to our understanding of their histories?
- A: The maps provide a visual representation of the geographical context of these city-states, highlighting their strategic locations, territorial expansions, and the ways in which geography shaped their societies and cultures.
Tips for Understanding Sparta and Athens Maps:
- Focus on key geographical features: Pay attention to the location of mountains, rivers, and coastlines, as these features played a crucial role in shaping the cities’ development.
- Consider the scale: Understand the relative size and distance between the cities and their surrounding territories.
- Analyze the relationship between geography and society: Explore how the geographical features influenced the cities’ social structures, political systems, and cultural values.
- Compare and contrast: Analyze the differences in geography, society, and culture between Sparta and Athens to gain a deeper understanding of their unique identities.
Conclusion:
The maps of Sparta and Athens are not mere geographical representations. They are powerful tools for understanding the complex interplay between geography, culture, and politics in the ancient world. By studying these maps, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the unique identities of these two city-states and their enduring legacy on Western civilization. They serve as a reminder of the profound influence geography can have on the development of societies and the shaping of human history.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Tale of Two Cities: Exploring the Maps of Sparta and Athens. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!