A Tangible Landscape: Exploring the Art and Science of Wooden Topographic Maps
Related Articles: A Tangible Landscape: Exploring the Art and Science of Wooden Topographic Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Tangible Landscape: Exploring the Art and Science of Wooden Topographic Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Tangible Landscape: Exploring the Art and Science of Wooden Topographic Maps

The world around us is a tapestry of peaks and valleys, plains and plateaus, a dynamic landscape sculpted by geological forces over millennia. Capturing this intricate beauty and complexity is a task undertaken by cartographers, who translate the earth’s contours into maps. While traditional paper maps serve a vital function, a new wave of artistry is emerging, one that blends the scientific precision of cartography with the tactile warmth of wood. Wooden topographic maps, crafted with meticulous detail and a deep appreciation for the natural world, offer a unique and captivating way to experience the terrain.
The Art of Wood and Elevation:
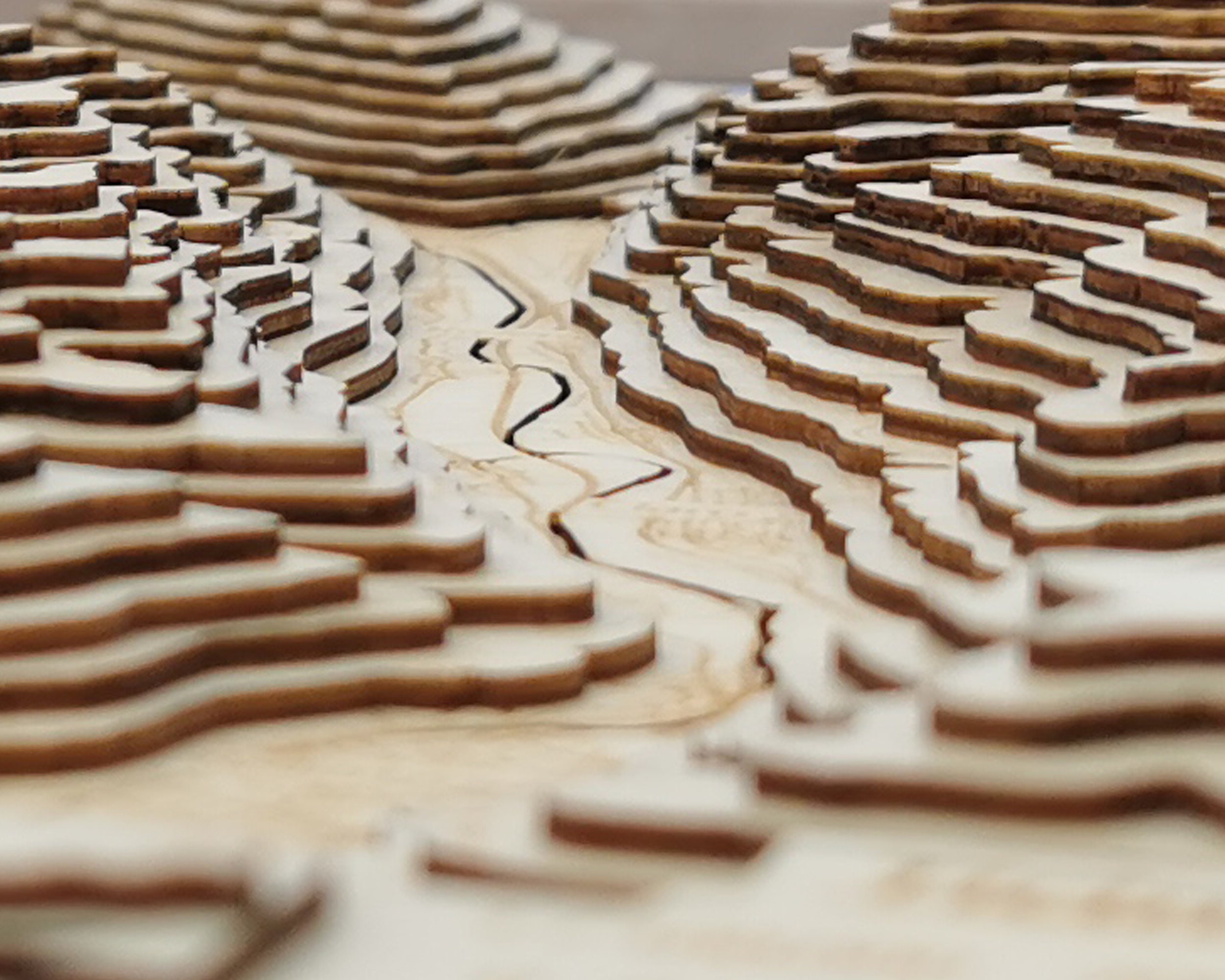
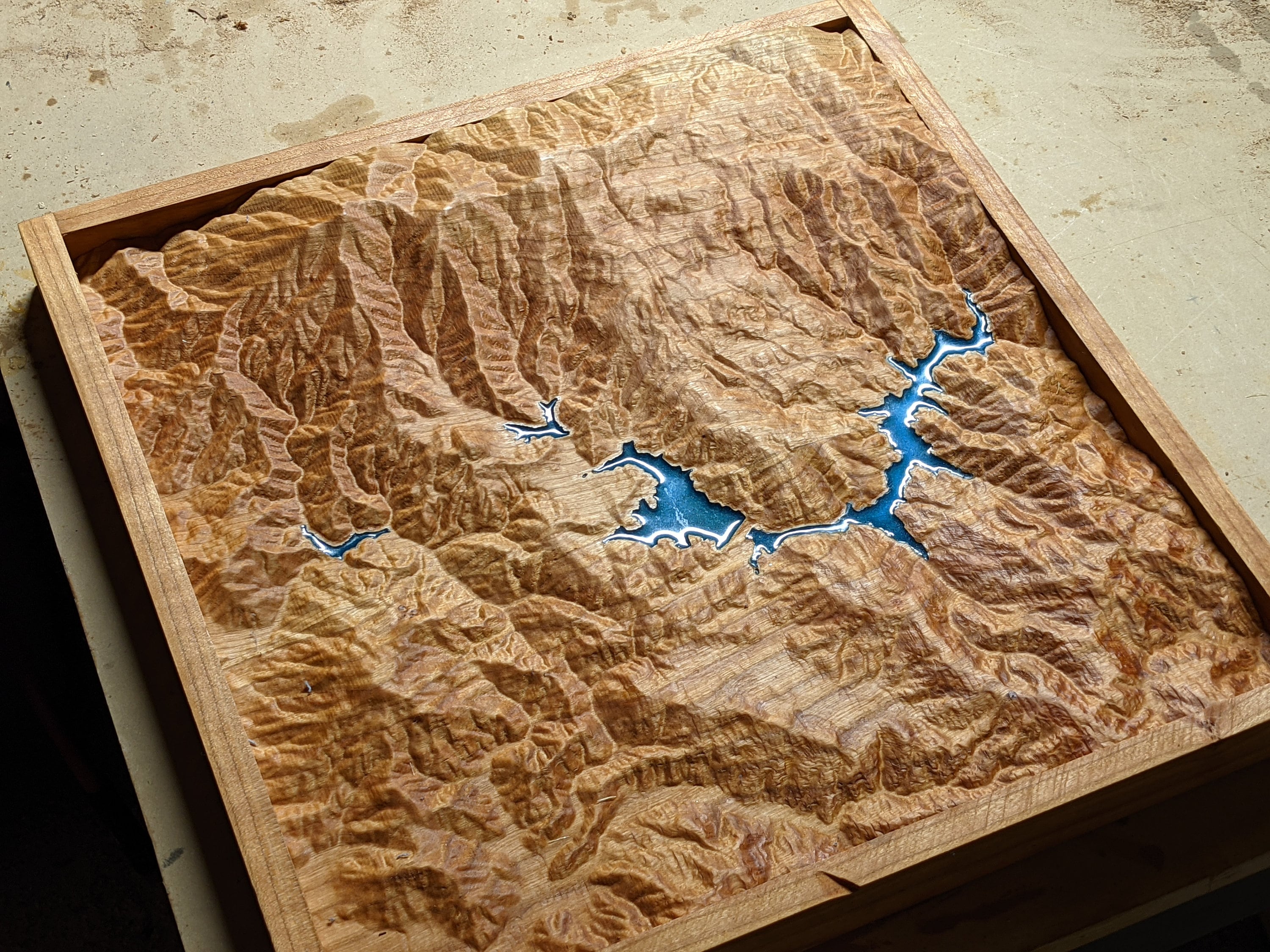
Wooden topographic maps are not merely representations of landforms; they are three-dimensional works of art that embody the very essence of the landscape they depict. Each peak, valley, and slope is meticulously sculpted from wood, often using techniques borrowed from woodworking traditions. The resulting maps are not only visually striking but also offer a tactile experience, allowing users to physically trace the contours of the land with their fingertips.
The Science of Topography:
The creation of a wooden topographic map begins with a meticulous process of data acquisition. Cartographers use sophisticated surveying techniques, aerial photography, and digital elevation models (DEMs) to gather precise data on the terrain’s elevation and features. This data is then translated into a digital model, forming the blueprint for the wooden map.
Crafting the Map:
The process of transforming the digital model into a tangible wooden map is a testament to the skill and artistry of woodworkers. Skilled artisans carefully select wood species based on their aesthetic qualities, durability, and suitability for carving. The wood is then meticulously cut and shaped using a combination of traditional hand tools and modern CNC machinery.
Beyond the Surface:
The beauty of wooden topographic maps extends beyond their visual appeal. These maps offer a multi-sensory experience, inviting users to explore the terrain not only visually but also through touch. The texture of the wood, the subtle variations in height, and the interplay of light and shadow all contribute to a more immersive understanding of the landscape.
Benefits of Wooden Topographic Maps:
- Enhanced Understanding of Terrain: The three-dimensional nature of these maps provides a more intuitive and engaging way to comprehend the topography of a region.
- Educational Value: Wooden topographic maps serve as valuable teaching tools, particularly for geography, geology, and environmental studies. They provide a tangible and interactive representation of the Earth’s surface.
- Artistic Expression: The meticulous craftsmanship and attention to detail make wooden topographic maps unique works of art, capable of capturing the beauty and complexity of the natural world.
- Personalized Gifts: These maps can be personalized with specific locations, making them ideal gifts for nature enthusiasts, travelers, and anyone seeking a unique and meaningful keepsake.
Beyond the Traditional:
The potential of wooden topographic maps extends beyond traditional representations of landforms. Artists and designers are exploring innovative ways to integrate these maps into furniture, sculptures, and architectural elements. This fusion of art, science, and craftsmanship creates a unique and captivating aesthetic that bridges the gap between the natural world and the human-made environment.
FAQs:
Q: What types of wood are typically used for wooden topographic maps?
A: The choice of wood depends on the desired aesthetic and the specific needs of the project. Common choices include hardwoods like maple, cherry, walnut, and oak, known for their durability, grain patterns, and color variations. Softwoods like pine and cedar can also be used, offering a lighter and more rustic look.
Q: How are the details of the terrain captured in the wooden map?
A: The details of the terrain are captured through a process of data acquisition and translation. Cartographers use sophisticated surveying techniques, aerial photography, and digital elevation models (DEMs) to gather precise data on the terrain’s elevation and features. This data is then transformed into a digital model, which serves as the blueprint for the wooden map.
Q: What are the typical sizes and scales of wooden topographic maps?
A: The size and scale of wooden topographic maps can vary significantly depending on the region being depicted and the intended use. Some maps are small and compact, suitable for desk displays or personal collections. Others are large and elaborate, designed for exhibition or educational purposes.
Q: How can I create a custom wooden topographic map?
A: Many artisans and companies offer custom wooden topographic map services. You can provide them with a specific location, desired scale, and any personalization requests. They will then use the data to create a unique and personalized map tailored to your needs.
Tips for Creating a Wooden Topographic Map:
- Choose a suitable wood species: Consider the desired aesthetic, durability, and availability of different wood species.
- Use precise data: Ensure the data used for the map is accurate and up-to-date.
- Invest in quality tools: Using quality hand tools and machinery will ensure the map is crafted to the highest standards.
- Pay attention to detail: The success of a wooden topographic map lies in the meticulous attention to detail given to each contour and feature.
- Experiment with finishes: Explore different finishes like oil, wax, or lacquer to enhance the beauty and durability of the map.
Conclusion:
Wooden topographic maps offer a unique and captivating way to experience the world’s landscapes. They blend the scientific precision of cartography with the tactile warmth and artistry of wood, creating tangible representations of the Earth’s intricate terrain. These maps not only enhance our understanding of the natural world but also serve as beautiful and enduring works of art. As technology continues to evolve, the potential of wooden topographic maps to bridge the gap between science, art, and craftsmanship will continue to grow, offering new ways to explore and appreciate the beauty of our planet.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Tangible Landscape: Exploring the Art and Science of Wooden Topographic Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!