A Tapestry of Terrain: Unveiling the Topography of America
Related Articles: A Tapestry of Terrain: Unveiling the Topography of America
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Tapestry of Terrain: Unveiling the Topography of America. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Tapestry of Terrain: Unveiling the Topography of America

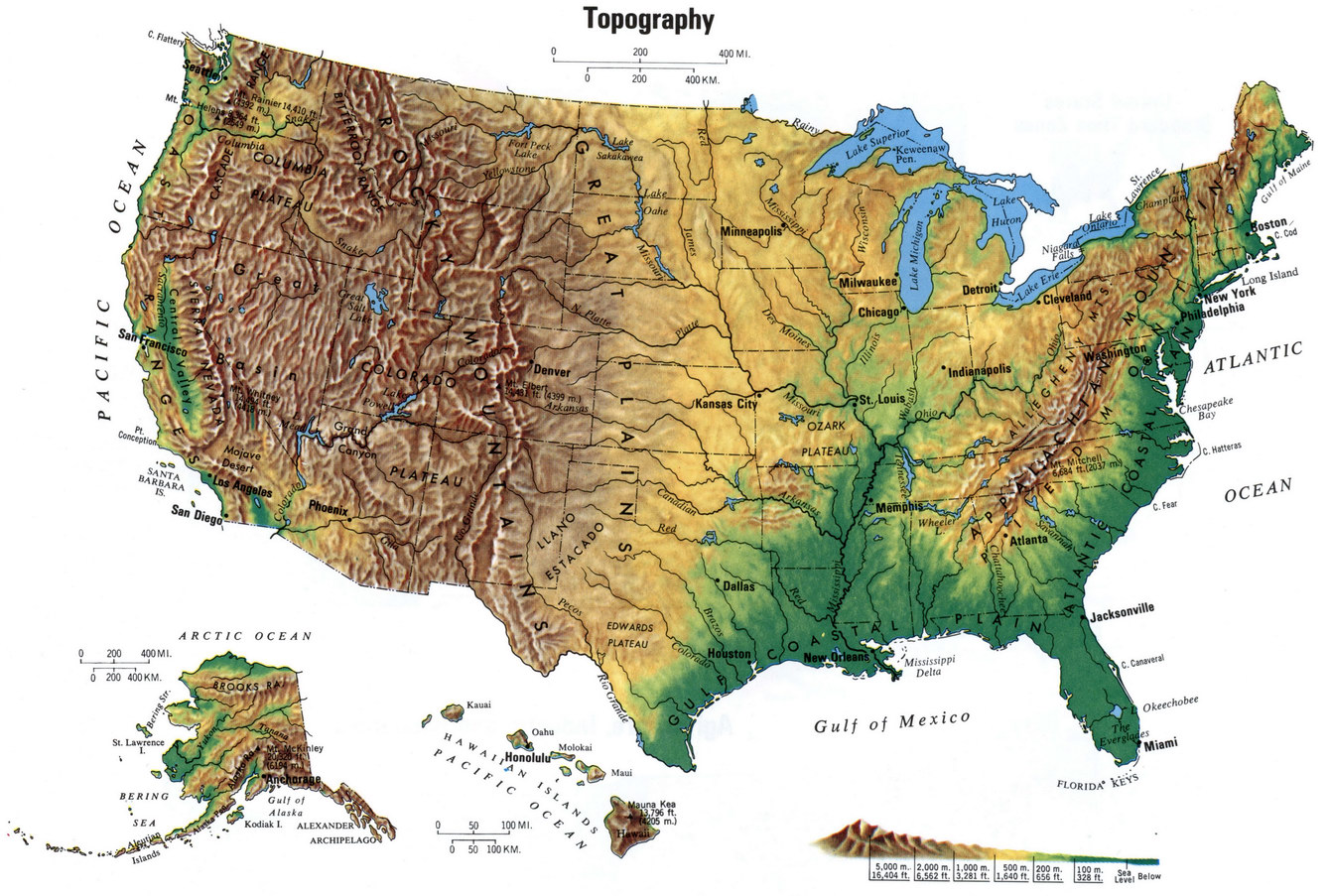
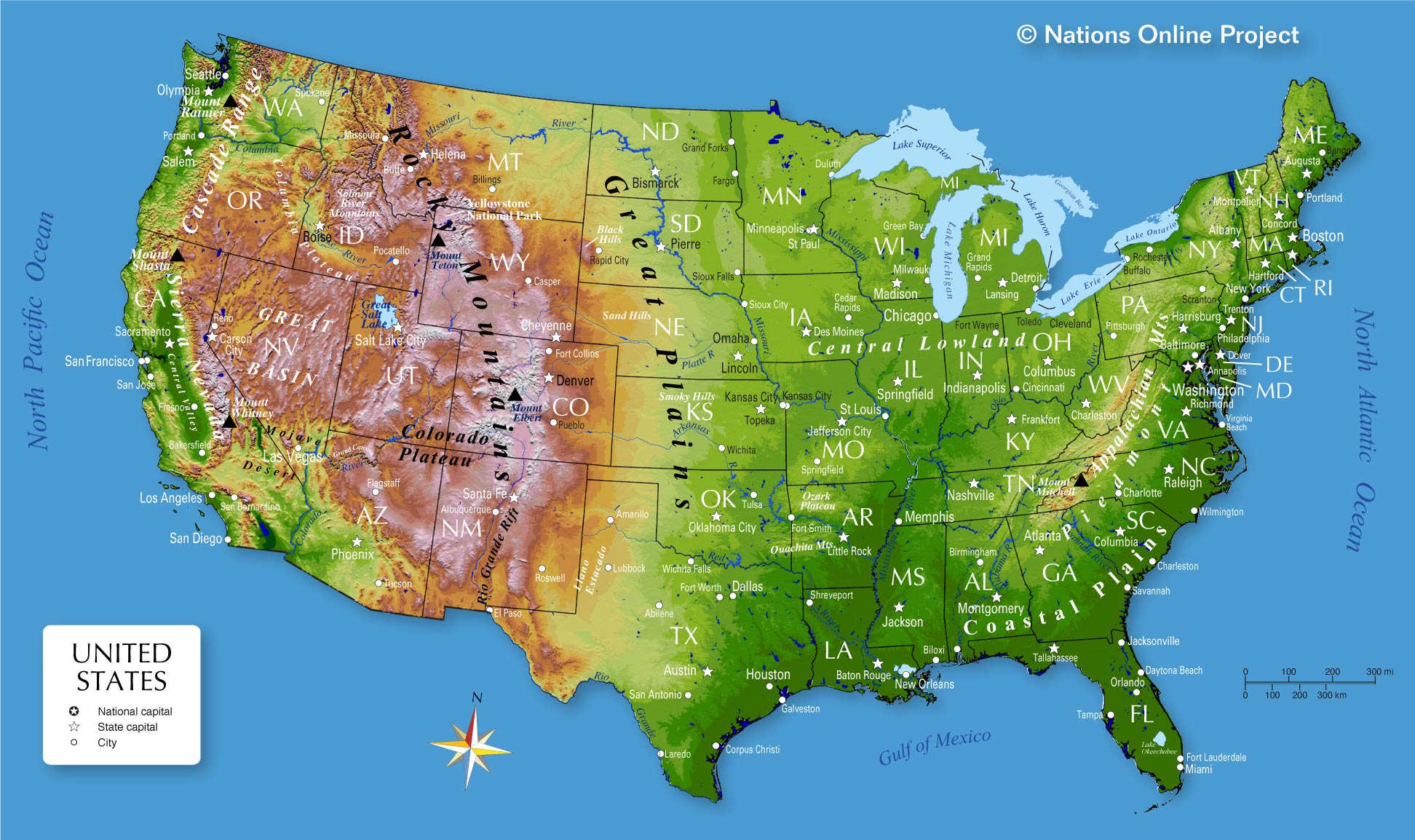
The United States, a land of vast and varied landscapes, is a testament to the dynamic forces that have shaped our planet. Its topography, a complex interplay of mountains, valleys, plains, and coastlines, is a fundamental aspect of its natural heritage. This intricate tapestry of terrain not only defines the nation’s visual identity but also profoundly influences its climate, ecosystems, and human settlements.
Mapping the Land: A Visual Representation of America’s Terrain
Topographic maps, often referred to as "topo maps," are essential tools for understanding and visualizing the three-dimensional landscape of America. They provide a detailed depiction of elevation, landforms, and geographic features, offering a comprehensive overview of the country’s diverse topography.
Understanding the Language of Topographic Maps
Topographic maps utilize specific symbols and conventions to communicate information about terrain. Contour lines, perhaps the most recognizable feature, represent lines of equal elevation. These lines, like the rings of a tree trunk, reveal the gradual rise and fall of the land. The closer the contour lines, the steeper the slope; the farther apart they are, the gentler the incline.
Other important elements on a topographic map include:
- Spot elevations: Numbers indicating the precise elevation of specific points on the map.
- Water features: Rivers, lakes, and streams are depicted with blue lines, their widths indicating the relative size of the water body.
- Cultural features: Roads, buildings, and other human-made structures are represented with symbols, providing context for the natural landscape.
- Vegetation: Different types of vegetation are often indicated by color or symbols, highlighting the diversity of plant life across the country.
The Importance of Topographic Maps: A Multifaceted Tool
Topographic maps serve a multitude of purposes, proving invaluable in various fields:
- Navigation and Recreation: Hikers, climbers, and outdoor enthusiasts rely on topo maps to navigate trails, identify potential hazards, and plan their adventures.
- Land Management and Planning: Planners and developers use topographic maps to assess the suitability of land for different uses, considering factors such as slope, elevation, and proximity to water sources.
- Engineering and Construction: Engineers and construction professionals utilize topo maps to design and build infrastructure, ensuring projects are adapted to the specific terrain.
- Environmental Studies: Scientists and researchers use topographic maps to study the distribution of ecosystems, analyze land cover changes, and understand the impacts of climate change on the landscape.
- Emergency Response: During natural disasters, topographic maps assist emergency responders in navigating affected areas, identifying potential hazards, and planning rescue efforts.
Exploring America’s Topographic Diversity: A Regional Overview
The United States boasts a remarkable range of topographic features, each region offering a unique glimpse into the nation’s geological history:
- The Appalachian Mountains: These ancient mountains, stretching from Georgia to Maine, showcase a rugged and forested landscape, with peaks reaching over 6,000 feet.
- The Great Plains: A vast expanse of flat, fertile land, the Great Plains are characterized by their gentle slopes and open horizons, providing fertile ground for agriculture.
- The Rocky Mountains: This imposing mountain range, spanning from Canada to Mexico, is a testament to tectonic forces, with towering peaks exceeding 14,000 feet.
- The Pacific Coast: This region features a dramatic coastline, characterized by steep cliffs, rugged mountains, and deep valleys, sculpted by the Pacific Ocean.
- The Great Basin: This arid region, situated between the Sierra Nevada and the Rocky Mountains, is dominated by vast deserts, salt flats, and isolated mountain ranges.
FAQs about America’s Topographic Map
Q: What is the highest point in the United States?
A: The highest point in the United States is Denali (formerly Mount McKinley) in Alaska, reaching an elevation of 20,310 feet.
Q: What is the lowest point in the United States?
A: The lowest point in the United States is Death Valley in California, reaching an elevation of -282 feet below sea level.
Q: How are topographic maps created?
A: Topographic maps are created using a combination of aerial photography, satellite imagery, and ground surveys. These data are then processed and compiled to produce a detailed map of the terrain.
Q: What are some of the challenges of mapping America’s vast and diverse topography?
A: Mapping America’s diverse landscape presents several challenges, including the vast scale of the country, the remote and inaccessible areas, and the dynamic nature of the terrain, which is constantly being shaped by natural forces.
Tips for Using Topographic Maps
- Understand the map scale: The scale of the map indicates the ratio between the map distance and the actual distance on the ground.
- Familiarize yourself with the symbols and conventions: Take the time to understand the meaning of different symbols and how they represent terrain features.
- Use a compass and altimeter: These tools are essential for accurate navigation and understanding elevation changes.
- Plan your route carefully: Before embarking on any outdoor adventure, study the topographic map thoroughly to identify potential hazards and plan a safe route.
- Be aware of weather conditions: The terrain can change dramatically with weather, so be prepared for all conditions.
Conclusion: A Window into America’s Landscape
Topographic maps serve as invaluable tools for understanding, exploring, and managing America’s diverse and dynamic landscape. They provide a visual representation of the country’s terrain, revealing the intricate interplay of mountains, valleys, plains, and coastlines that define its natural beauty and influence its human settlements. From guiding outdoor adventures to supporting scientific research, these maps play a crucial role in our understanding and appreciation of America’s topographic heritage.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Tapestry of Terrain: Unveiling the Topography of America. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!