Bolivia: A Landlocked Jewel in the Heart of South America
Related Articles: Bolivia: A Landlocked Jewel in the Heart of South America
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Bolivia: A Landlocked Jewel in the Heart of South America. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Bolivia: A Landlocked Jewel in the Heart of South America

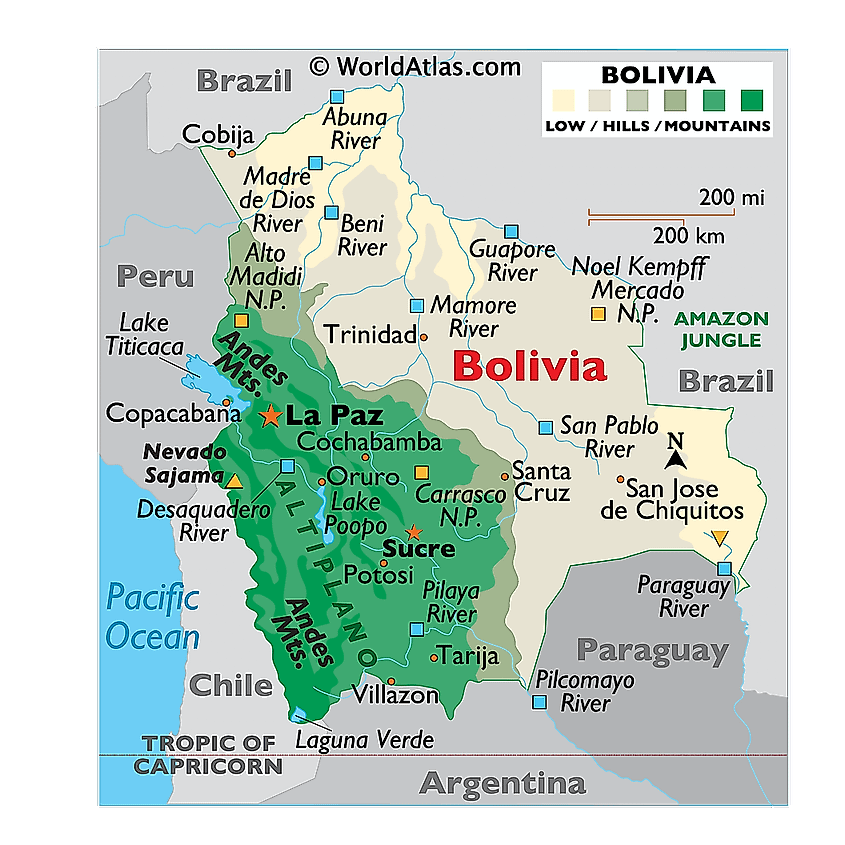
Bolivia, nestled in the heart of South America, is a landlocked country brimming with diverse landscapes, rich cultural heritage, and a vibrant history. Understanding its geography through a map provides invaluable insight into the country’s unique character and the challenges and opportunities it faces.
Geographical Features:
Bolivia’s geographical position and physical features are crucial to understanding its identity. The country is bordered by five nations: Brazil to the north and east, Peru to the northwest, Chile to the southwest, Argentina to the south, and Paraguay to the southeast. This landlocked position presents both challenges and opportunities, influencing the country’s economic development and cultural exchanges.
The map of Bolivia reveals a stunning tapestry of diverse landscapes. The Andes Mountains, a defining feature of South America, traverse the country, forming the Western Cordillera and the Eastern Cordillera, creating dramatic valleys and high plateaus. The Western Cordillera hosts the highest peaks in Bolivia, including the majestic Mount Sajama, reaching over 6,500 meters. These mountainous regions, home to ancient cultures and vibrant indigenous communities, are also rich in mineral resources, playing a crucial role in the country’s economy.
East of the Andes, the map reveals the vast plains of the Gran Chaco, a semi-arid region characterized by grasslands, savannas, and forests. This region, home to diverse flora and fauna, is a vital source of agricultural production, particularly for cattle ranching and soybean cultivation.
The eastern lowlands also encompass the Amazon Basin, a region renowned for its biodiversity and lush rainforests. This region, home to indigenous communities and a rich array of plant and animal species, is a key contributor to Bolivia’s environmental wealth.
Climate and Biodiversity:
Bolivia’s diverse landscapes create a range of microclimates, from the frigid heights of the Andes to the humid warmth of the Amazon. The high altitudes of the Andes experience a cold, dry climate, while the lowlands experience a tropical climate with high humidity and rainfall. The Gran Chaco, characterized by a semi-arid climate, experiences distinct wet and dry seasons.
This diverse climate supports a remarkable array of flora and fauna. The Andes are home to unique alpine plants, while the Amazon Basin boasts an unparalleled diversity of plant and animal life, including jaguars, macaws, and a vast array of insects. The Gran Chaco, with its grasslands and savannas, is home to diverse wildlife, including pumas, armadillos, and various bird species.
Cultural and Historical Significance:
The map of Bolivia reveals a country with a rich cultural heritage, influenced by its diverse indigenous communities and colonial past. The Andean highlands are home to the Aymara and Quechua peoples, whose traditions and languages remain vibrant and influential in contemporary Bolivia. The lowlands are home to diverse indigenous groups, each with unique cultural practices and languages.
The Spanish colonial period left a lasting mark on Bolivia’s culture and landscape. The country’s colonial cities, such as Sucre, the constitutional capital, and Potosí, a former silver mining center, showcase the architectural legacy of the Spanish Empire.
Economic and Development Challenges:
The map of Bolivia highlights the country’s economic challenges, particularly its landlocked status. Access to international markets is a significant hurdle, influencing the country’s trade and development. The reliance on primary exports, such as minerals and agricultural products, makes Bolivia vulnerable to global market fluctuations.
Despite these challenges, Bolivia has experienced significant economic growth in recent years, driven by increased mining and agricultural production. The country is also actively investing in infrastructure development, including roads, railways, and energy projects, to improve connectivity and boost economic growth.
Environmental Considerations:
Bolivia’s vast and diverse landscapes are a source of both opportunity and concern. The country is rich in natural resources, including minerals, forests, and water resources, but these resources are under increasing pressure due to deforestation, mining activities, and climate change.
The Amazon rainforest, a vital carbon sink and home to immense biodiversity, faces threats from deforestation and illegal logging. The high Andean regions are vulnerable to glacial melt and climate change, impacting water resources and agricultural production.
FAQs about Bolivia’s Geography:
-
What are the major geographical features of Bolivia?
Bolivia is characterized by the Andes Mountains, the Gran Chaco plains, and the Amazon Basin. -
What are the major cities in Bolivia?
Bolivia’s major cities include La Paz (the administrative capital), Sucre (the constitutional capital), Santa Cruz, Cochabamba, and Potosí. -
What is the climate like in Bolivia?
Bolivia’s climate varies significantly, ranging from the cold, dry climate of the Andes to the humid, tropical climate of the Amazon Basin. -
What are the major industries in Bolivia?
Bolivia’s major industries include mining, agriculture, and tourism. -
What are the major environmental challenges facing Bolivia?
Bolivia faces significant environmental challenges, including deforestation, mining pollution, and climate change.
Tips for Travelers Exploring Bolivia:
- Plan your trip carefully: Research the different regions of Bolivia and choose destinations that align with your interests.
- Be prepared for altitude: The high altitudes of the Andes can cause altitude sickness.
- Respect local customs: Bolivia has a rich cultural heritage, and it’s essential to be respectful of local customs and traditions.
- Learn some basic Spanish: While English is spoken in some tourist areas, learning basic Spanish will enhance your travel experience.
- Consider hiring a guide: A local guide can provide valuable insights into Bolivia’s history, culture, and natural beauty.
Conclusion:
The map of Bolivia reveals a country of immense beauty, cultural diversity, and economic potential. Its landlocked position presents challenges, but it also fosters a unique sense of identity and resilience. Understanding Bolivia’s geography is crucial to appreciating its rich history, diverse landscapes, and the challenges and opportunities it faces in the 21st century. Through its diverse cultures, stunning landscapes, and vibrant traditions, Bolivia offers a captivating journey into the heart of South America.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Bolivia: A Landlocked Jewel in the Heart of South America. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!