Charting the Dutch East Indies: A Map of Colonial Power and Trade
Related Articles: Charting the Dutch East Indies: A Map of Colonial Power and Trade
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Charting the Dutch East Indies: A Map of Colonial Power and Trade. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Charting the Dutch East Indies: A Map of Colonial Power and Trade

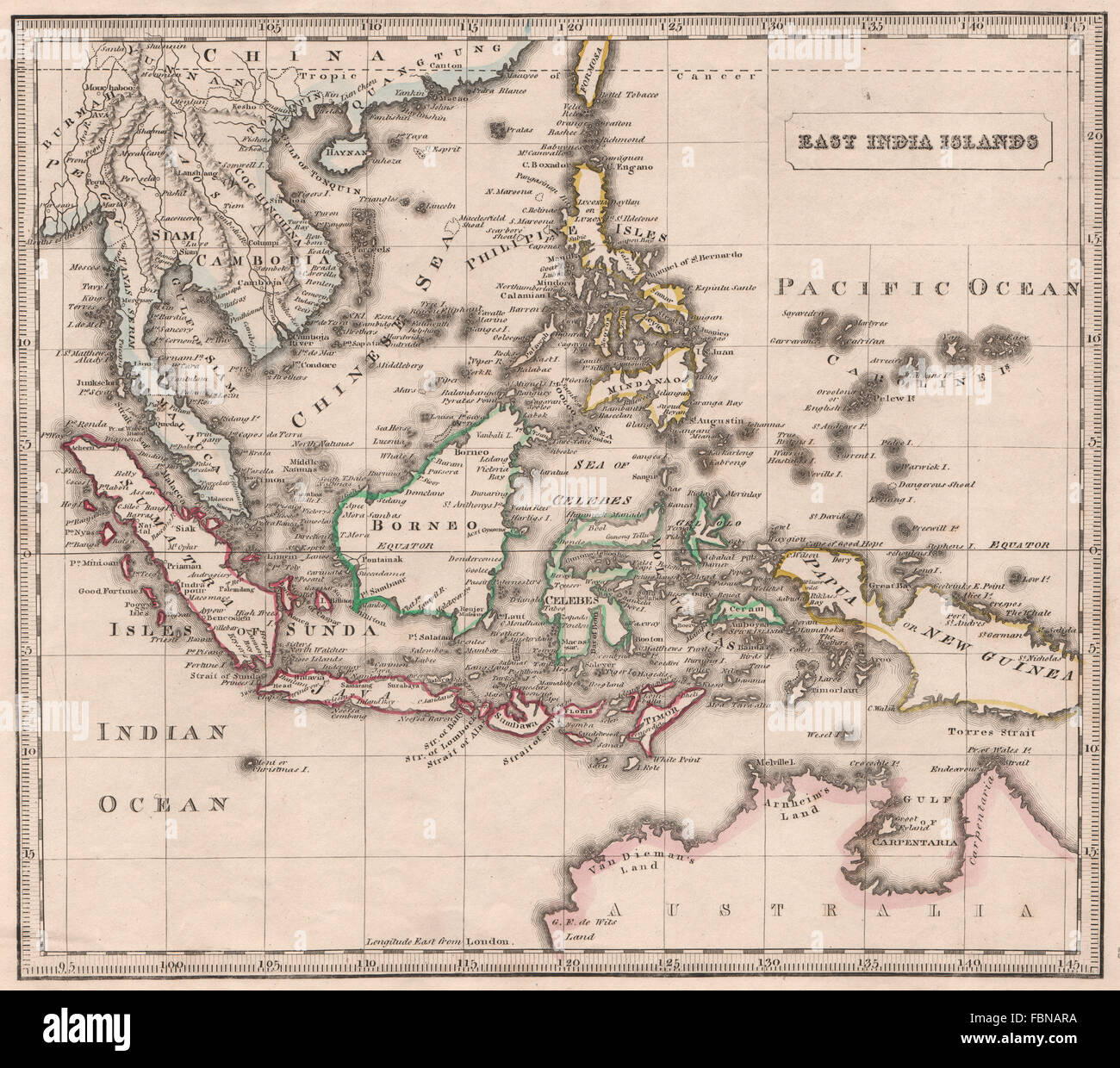
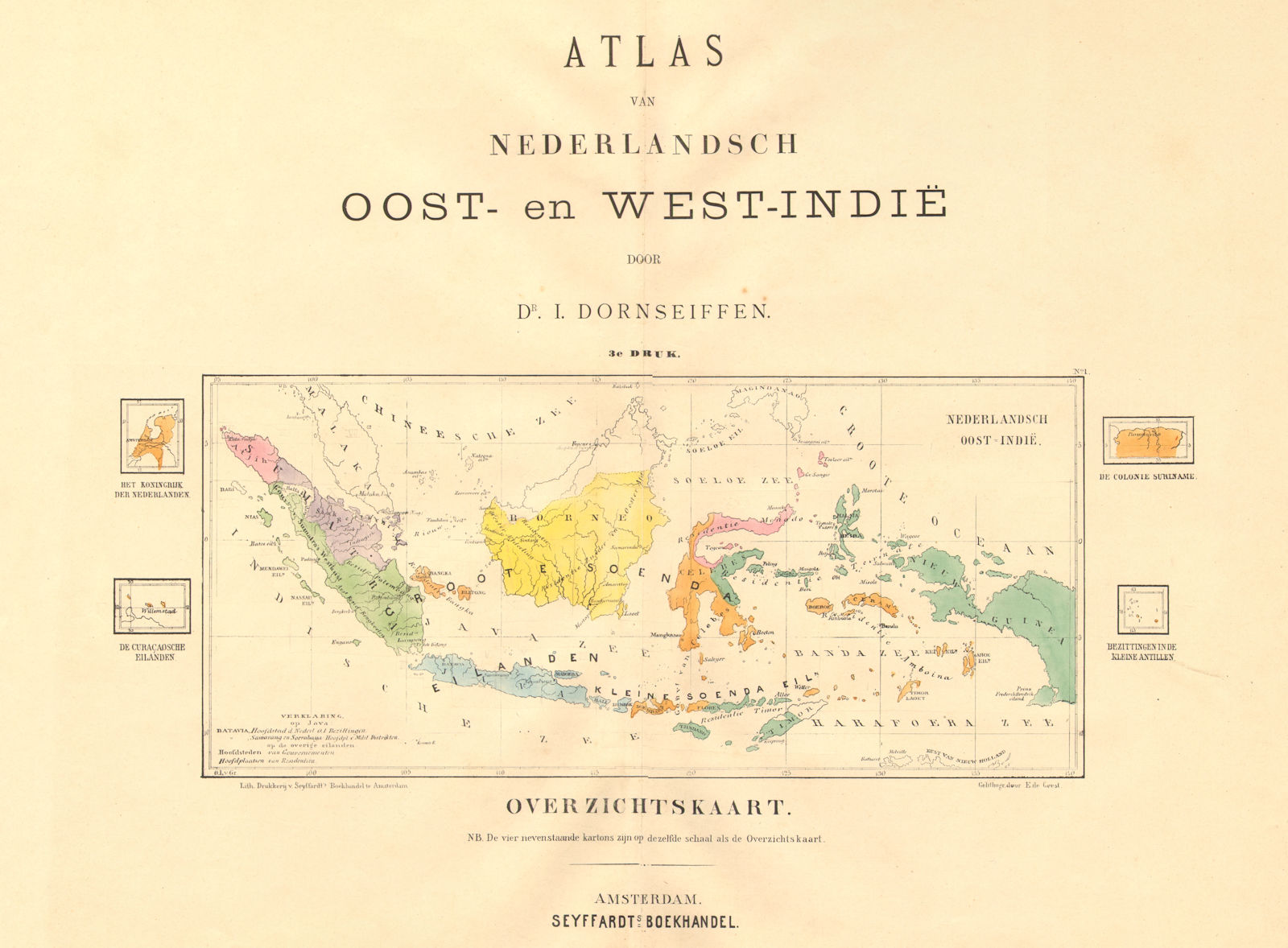
The Dutch East Indies, a sprawling archipelago encompassing modern-day Indonesia, played a pivotal role in shaping global trade and colonial history. Understanding the geographical landscape of this vast territory, as depicted on maps, is crucial for grasping the complexities of its past. This article will delve into the cartographic representations of the Dutch East Indies, analyzing the evolution of mapping techniques, the significance of these maps, and their lasting impact on our understanding of the region.
Mapping the Indies: From Exploration to Exploitation
The earliest maps of the Dutch East Indies were primarily based on European exploration and trade routes. Early Dutch cartographers, like Willem Blaeu and Johannes Vingboons, relied on accounts from voyagers and merchants to create rudimentary maps. These maps, often adorned with fantastical creatures and mythical islands, served as navigational tools and illustrated the growing interest in the region.
As Dutch influence solidified in the 17th century, maps became more detailed and accurate. The establishment of the Dutch East India Company (VOC) spurred the creation of precise maps for navigation, trade, and colonial administration. These maps, often referred to as "charts," depicted the major islands, ports, and trade routes, enabling the VOC to control and exploit the region’s resources.
The Power of Cartographic Representation
The Dutch East Indies maps served several crucial purposes:
- Navigation and Trade: Accurate maps were essential for navigating the complex waterways and islands of the archipelago. They allowed the VOC to establish efficient trade routes, maximizing profits from spices, textiles, and other valuable commodities.
- Colonial Administration: Maps were instrumental in managing the Dutch colonial presence. They provided insights into population distribution, resource availability, and potential areas for expansion. This information was vital for maintaining control and exploiting the territory’s wealth.
- Propaganda and Legitimization: Maps were also used as tools of propaganda, projecting Dutch power and dominance over the region. By depicting the islands under Dutch control, these maps reinforced the narrative of a thriving colonial enterprise.
Evolution of Mapping Techniques
Over time, mapping techniques advanced, reflecting technological advancements and the growing knowledge of the region.
- Early Maps: Early maps relied on visual representations and often lacked precise geographical coordinates. They were primarily based on eyewitness accounts and nautical observations.
- The Rise of Scientific Mapping: The Enlightenment saw the development of scientific mapping techniques. Dutch cartographers began using triangulation and other methods to determine precise locations and distances. This resulted in more accurate and detailed maps.
- The Age of Exploration: The 19th century witnessed the advent of advanced surveying techniques and the use of scientific instruments. This enabled the creation of more comprehensive and detailed maps, incorporating information on topography, vegetation, and population density.
Beyond the Physical Landscape: Maps as Instruments of Power
While maps provided valuable information about the physical landscape, they also served as powerful tools for shaping perceptions and exerting control.
- Colonial Boundaries: Maps often depicted colonial boundaries in a clear and definitive manner, reinforcing the notion of Dutch ownership and control over the territory.
- Ethnic and Cultural Divisions: Maps could also be used to highlight ethnic and cultural divisions within the archipelago, reinforcing colonial policies of divide and rule.
- Resource Exploitation: Maps played a key role in identifying and exploiting the region’s natural resources, from spices and timber to minerals and oil.
The Legacy of Dutch East Indies Maps
The maps of the Dutch East Indies offer a window into the complex history of colonialism, trade, and cultural exchange. They provide insights into the power dynamics between colonizers and colonized, the impact of European influence on the region, and the enduring legacy of this historical period.
FAQs
1. What was the primary purpose of Dutch East Indies maps?
Dutch East Indies maps served multiple purposes, including navigation, trade, colonial administration, and propaganda.
2. How did mapping techniques evolve over time?
Mapping techniques evolved from rudimentary visual representations to more accurate and detailed maps using scientific methods like triangulation and surveying.
3. What role did maps play in colonial power dynamics?
Maps reinforced colonial boundaries, highlighted ethnic divisions, and facilitated resource exploitation, contributing to the maintenance of Dutch control over the region.
4. What is the lasting impact of Dutch East Indies maps?
These maps provide valuable insights into the history of colonialism, trade, and cultural exchange, highlighting the complex power dynamics and enduring legacy of this historical period.
Tips
- Explore historical maps: Research online repositories and libraries to access digital copies of historical maps of the Dutch East Indies.
- Analyze map features: Pay attention to map features like scale, legend, and symbols to understand the information conveyed.
- Consider the context: Examine the maps within their historical context, considering the motivations of the mapmakers and the intended audience.
- Compare different maps: Compare maps from different periods to observe the evolution of cartographic techniques and the changing representation of the region.
Conclusion
The maps of the Dutch East Indies are not mere static representations of a geographical landscape; they are dynamic artifacts reflecting the complex interplay of power, trade, and cultural exchange. By understanding the history and evolution of these maps, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate relationship between cartography, colonialism, and the enduring impact of the Dutch East Indies on the world.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting the Dutch East Indies: A Map of Colonial Power and Trade. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!