Deciphering the Landscape: Understanding Election Map Results
Related Articles: Deciphering the Landscape: Understanding Election Map Results
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Landscape: Understanding Election Map Results. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the Landscape: Understanding Election Map Results

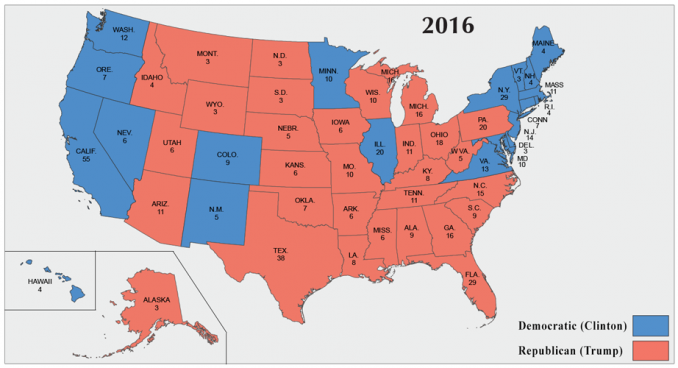
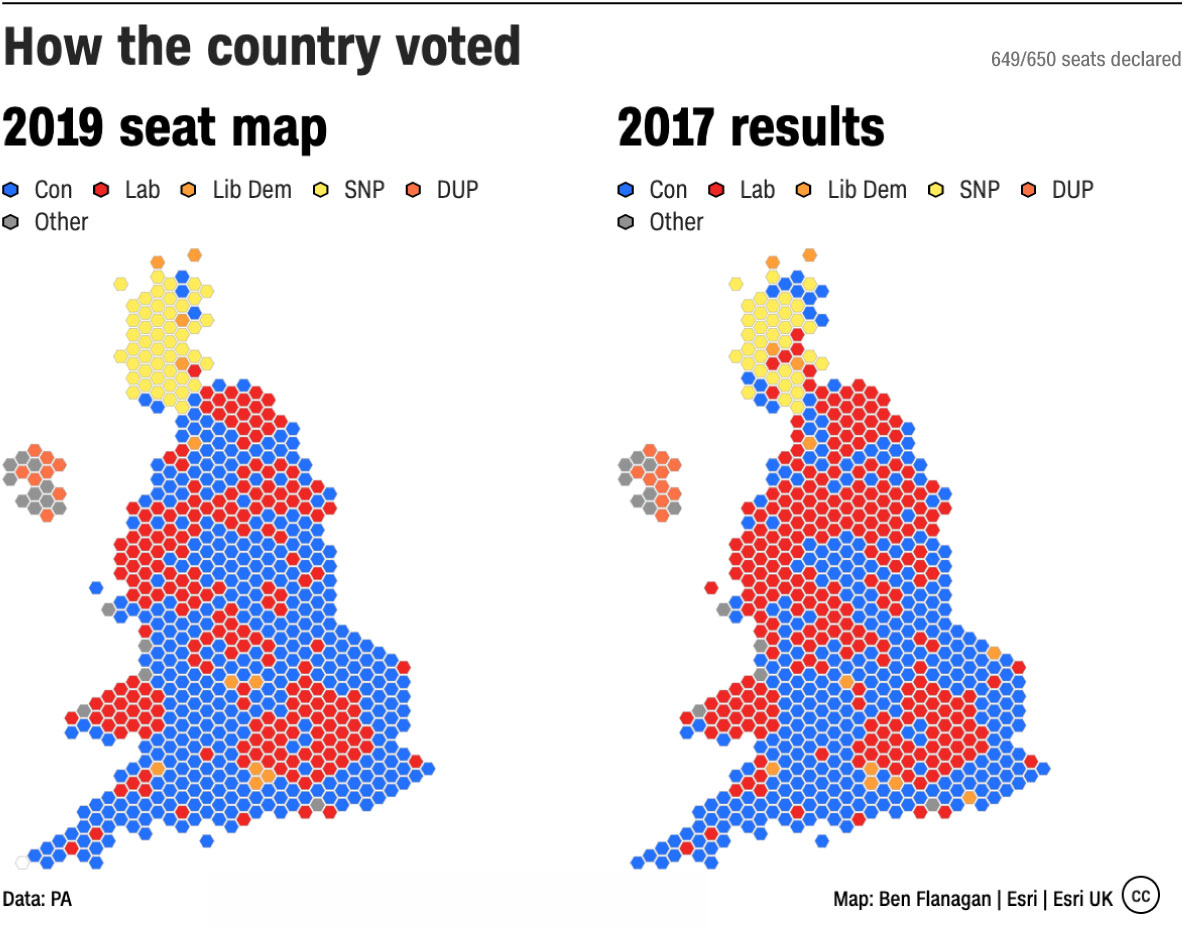
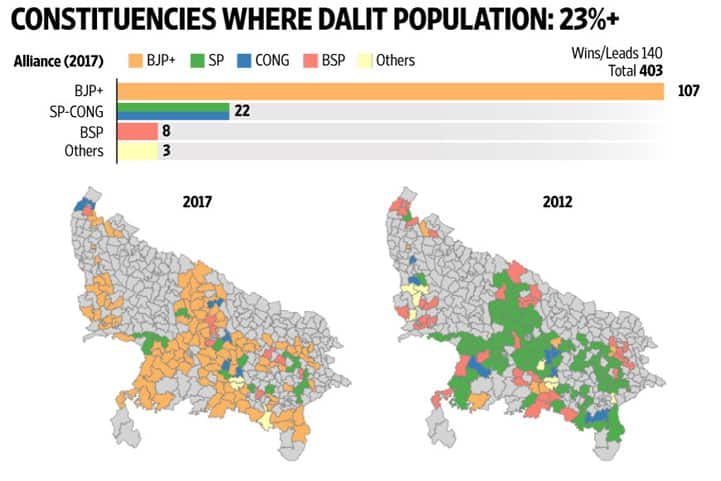
Election maps, those vibrant, geographically-segmented displays of electoral outcomes, offer a powerful visual representation of political trends and voter preferences. Beyond their aesthetic appeal, these maps serve as crucial tools for understanding the dynamics of an election, revealing insights into regional variations, demographic shifts, and the strategies employed by candidates and parties.
The Anatomy of an Election Map
Election maps typically depict a geographical area, often a country, state, or district, divided into smaller units, such as counties, congressional districts, or voting precincts. Each unit is colored according to the winning candidate or party, with different colors representing distinct political affiliations. The intensity of the color can often reflect the margin of victory, with darker shades indicating a more decisive win.
Interpreting the Data: Beyond the Colors
While the visual impact of an election map is undeniable, its true value lies in the data it conveys. Understanding the nuances of the map requires considering several key factors:
- Candidate Performance: A map can reveal the geographical strengths and weaknesses of individual candidates. A candidate who wins a large number of counties or districts, even with narrow margins, demonstrates broad appeal across various regions. Conversely, a candidate who wins a small number of areas with overwhelming majorities might indicate a more concentrated base of support.
- Party Strength: The distribution of colors across the map can indicate the relative strength of political parties in different regions. For instance, a map dominated by one party’s color might suggest a strong partisan divide, while a more balanced map indicates a closer contest.
- Demographic Trends: Election maps can shed light on the influence of demographic factors on voting patterns. By overlaying demographic data, such as population density, ethnicity, or income levels, analysts can identify correlations between these factors and voting preferences.
- Electoral Strategies: Maps can provide insights into the strategic choices made by candidates and parties. For instance, a candidate who focuses resources on a particular region might be targeting a key demographic group or aiming to secure a specific number of electoral votes.
The Importance of Context
It is crucial to remember that election maps are snapshots of a specific moment in time. They reflect the outcome of a single election and do not necessarily predict future results. Furthermore, the interpretation of a map should always be considered within the context of the broader political landscape, including historical trends, current events, and the specific issues at stake in the election.
Frequently Asked Questions about Election Maps
Q: What are the limitations of election maps?
A: Election maps can be misleading if not interpreted with caution. They can oversimplify complex political realities, potentially obscuring nuances in voter preferences and the influence of factors not captured by the map. Additionally, maps can be subject to manipulation or misrepresentation, leading to biased or inaccurate interpretations.
Q: How can election maps be used to predict future elections?
A: While election maps can provide insights into historical trends, they are not reliable predictors of future outcomes. Elections are influenced by a multitude of factors, including the political climate, candidate performance, and unexpected events, which can significantly alter the electoral landscape.
Q: Are election maps useful for understanding public opinion?
A: Election maps can provide a general sense of public opinion, but they are not a substitute for rigorous public opinion polling. Maps reflect voting outcomes, which are influenced by a range of factors, including voter turnout, electoral systems, and the specific issues at stake in the election.
Tips for Interpreting Election Maps Effectively
- Consider the scale: The level of detail on an election map is crucial. Maps showing national results might obscure regional variations, while highly detailed maps might focus on specific areas at the expense of broader trends.
- Pay attention to margins of victory: A map with a uniform color might appear to represent a clear mandate, but the margin of victory in each area can reveal different levels of support.
- Look for patterns and anomalies: Analyzing the distribution of colors and margins of victory can help identify geographic patterns and areas where voting patterns deviate from the overall trend.
- Compare maps across different elections: Comparing maps from different elections can reveal long-term trends, shifts in voter preferences, and the impact of specific events on the political landscape.
Conclusion: Election Maps as a Tool for Political Understanding
Election maps offer a compelling visual representation of electoral outcomes, providing valuable insights into regional variations, demographic trends, and the dynamics of political competition. While they are not without limitations, when interpreted with caution and within the context of the broader political landscape, election maps can serve as a powerful tool for understanding the complex interplay of factors that shape political outcomes. By analyzing these maps, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the nuances of electoral politics and the diverse perspectives of voters across different regions.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Landscape: Understanding Election Map Results. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!