Fracking in Pennsylvania: A Detailed Exploration of the Marcellus Shale
Related Articles: Fracking in Pennsylvania: A Detailed Exploration of the Marcellus Shale
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Fracking in Pennsylvania: A Detailed Exploration of the Marcellus Shale. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Fracking in Pennsylvania: A Detailed Exploration of the Marcellus Shale
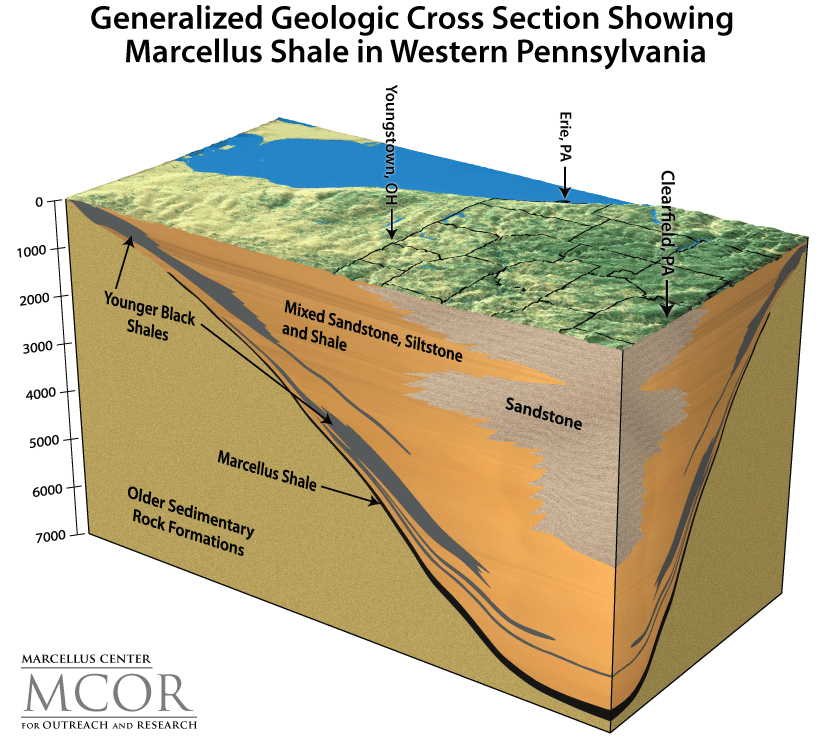
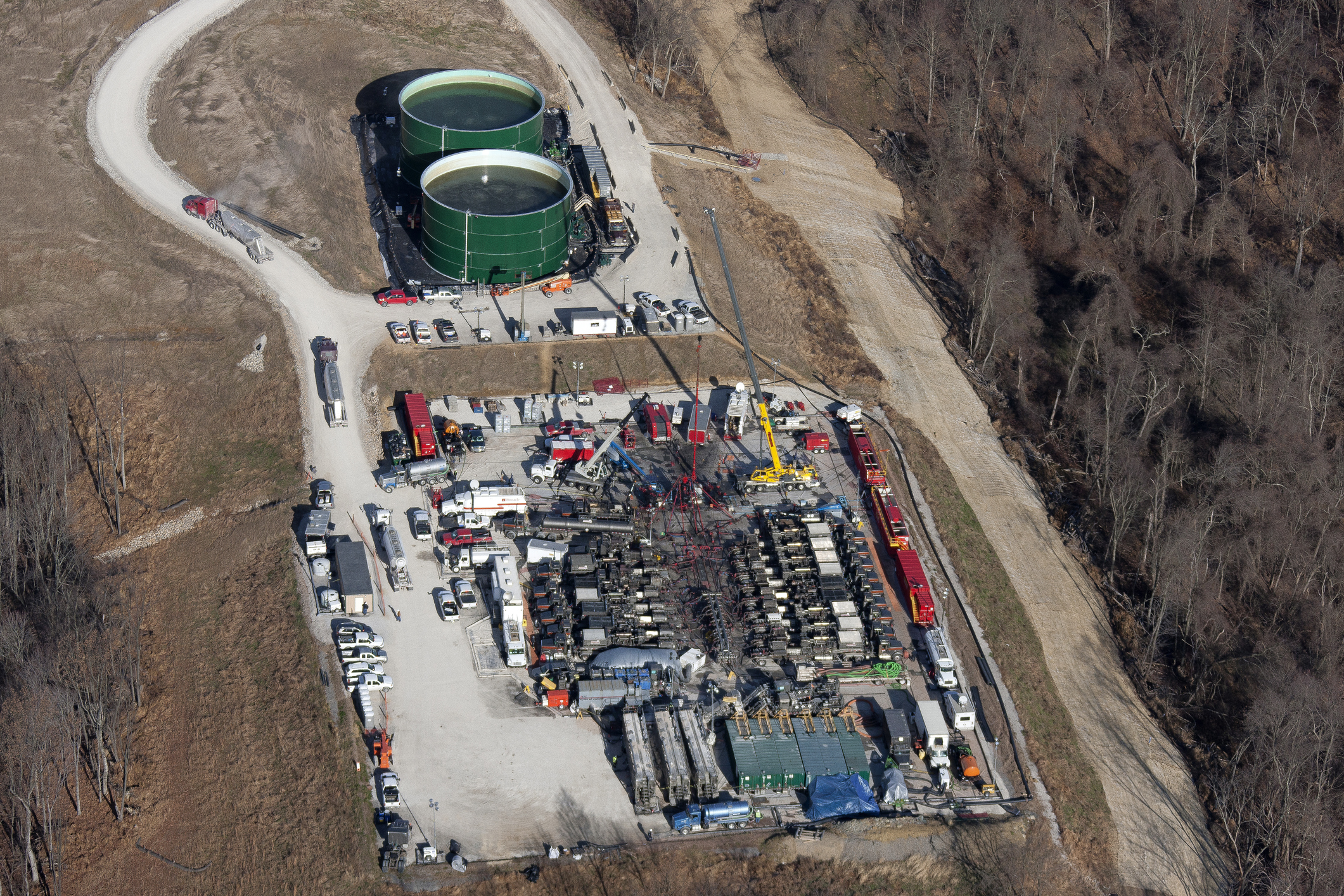
Pennsylvania, with its vast deposits of natural gas locked within the Marcellus Shale formation, has become a focal point for hydraulic fracturing, commonly known as fracking. This controversial practice has sparked intense debate, pitting economic growth and energy independence against environmental concerns. Understanding the intricacies of fracking in Pennsylvania requires a nuanced perspective, examining its impact on the state’s economy, environment, and communities.
The Marcellus Shale: A Reservoir of Natural Gas
The Marcellus Shale, a layer of sedimentary rock spanning parts of Pennsylvania, New York, West Virginia, and Ohio, holds vast reserves of natural gas. This shale formation is known for its tight, impermeable nature, making traditional drilling methods ineffective. Fracking, however, offers a solution by injecting a high-pressure mixture of water, sand, and chemicals into the shale, creating fissures and releasing the trapped gas.
Economic Implications: A Boon or a Burden?
Fracking has had a significant impact on Pennsylvania’s economy, creating jobs, boosting tax revenue, and revitalizing rural communities. The industry has generated thousands of direct and indirect jobs, from drilling and extraction to manufacturing and transportation. Moreover, the increased natural gas production has led to lower energy prices for consumers and businesses, stimulating economic activity across various sectors.
However, the economic benefits are not universally distributed. While some communities have experienced a surge in economic activity, others have faced challenges such as increased traffic, noise pollution, and water contamination. The long-term economic viability of fracking remains a subject of debate, with concerns about the potential for job losses as natural gas production peaks and the environmental costs associated with the industry.
Environmental Concerns: Navigating the Trade-offs
The environmental impacts of fracking are a major area of concern. The process involves the use of large quantities of water, raising concerns about water scarcity and potential contamination. The chemicals used in fracking fluids have also raised concerns about their impact on groundwater and surface water quality. Additionally, the release of methane, a potent greenhouse gas, during fracking and natural gas production contributes to climate change.
While the industry has made strides in improving its environmental practices, concerns persist about the long-term consequences of fracking on air and water quality. The potential for seismic activity induced by fracking operations is another significant concern, especially in areas prone to earthquakes.
Community Impacts: Balancing Development and Quality of Life
Fracking has had a profound impact on communities across Pennsylvania. While some residents have welcomed the economic benefits, others have expressed concerns about the environmental and social consequences. The influx of workers and industrial activity has led to changes in local demographics, housing costs, and social dynamics.
The issue of community engagement and transparency in decision-making processes related to fracking has been a source of tension. Concerns about the lack of public input and the potential for environmental harm have fueled community activism and legal challenges.
Navigating the Complexities: A Need for Responsible Development
The debate surrounding fracking in Pennsylvania highlights the complex trade-offs between economic growth, environmental protection, and community well-being. Striking a balance between these competing interests requires a comprehensive approach that addresses the concerns of all stakeholders.
This approach necessitates:
- Rigorous environmental regulations: Implementing stringent regulations to minimize the environmental impacts of fracking, including water and air pollution, methane emissions, and seismic activity.
- Transparent decision-making: Fostering open communication and public participation in decision-making processes related to fracking, ensuring that communities have a voice in shaping the industry’s development.
- Sustainable development practices: Promoting environmentally responsible fracking practices, such as minimizing water usage, recycling fracking fluids, and utilizing renewable energy sources.
- Community engagement and support: Investing in community development initiatives to address the social and economic impacts of fracking, ensuring that benefits are shared equitably.
FAQs about Fracking in Pennsylvania
1. What are the main benefits of fracking in Pennsylvania?
Fracking has contributed to economic growth in Pennsylvania by creating jobs, boosting tax revenue, and lowering energy prices. The increased availability of natural gas has also led to the development of new industries and businesses.
2. What are the environmental concerns associated with fracking?
Fracking raises concerns about water contamination, air pollution, methane emissions, and potential seismic activity. The chemicals used in fracking fluids and the disposal of wastewater have also been subjects of debate.
3. How does fracking impact communities in Pennsylvania?
Fracking can lead to changes in local demographics, housing costs, and social dynamics. It has also sparked debates about community engagement, transparency, and the potential for environmental harm.
4. What are the regulations governing fracking in Pennsylvania?
Pennsylvania has a comprehensive regulatory framework for fracking, covering aspects such as well construction, water usage, waste disposal, and air emissions. However, the effectiveness of these regulations remains a subject of ongoing debate.
5. What is the future of fracking in Pennsylvania?
The future of fracking in Pennsylvania depends on various factors, including technological advancements, environmental regulations, and public opinion. The industry faces challenges related to environmental concerns, community resistance, and the potential for market volatility.
Tips for Understanding Fracking in Pennsylvania
- Consult reliable sources: Refer to reputable organizations and publications for accurate information about fracking, such as the Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection, the Environmental Protection Agency, and academic research institutions.
- Engage in critical thinking: Examine the arguments presented by proponents and opponents of fracking, evaluating the evidence and considering potential biases.
- Attend public meetings and hearings: Participate in community discussions and decision-making processes related to fracking, voicing your concerns and perspectives.
- Stay informed about ongoing developments: Keep abreast of legislative changes, regulatory updates, and scientific research related to fracking.
Conclusion
Fracking in Pennsylvania remains a complex and controversial issue, raising questions about economic development, environmental protection, and social equity. The industry has brought economic benefits but also significant environmental and social challenges. Striking a balance between these competing interests requires a thoughtful approach that prioritizes transparency, environmental protection, and community well-being. The future of fracking in Pennsylvania will depend on the ability of policymakers, industry stakeholders, and communities to navigate these complex issues and forge a path toward sustainable development.







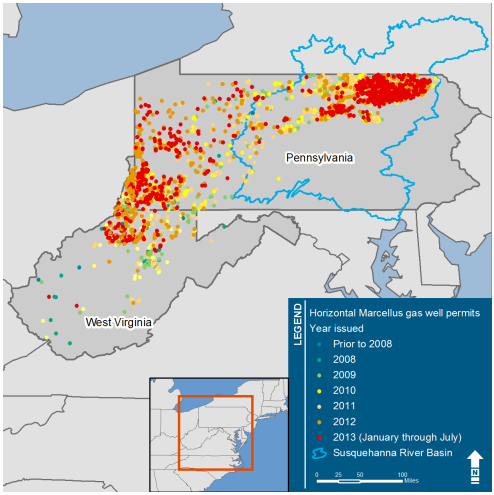
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Fracking in Pennsylvania: A Detailed Exploration of the Marcellus Shale. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!