Hamas: A Geographical and Political Analysis
Related Articles: Hamas: A Geographical and Political Analysis
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Hamas: A Geographical and Political Analysis. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Hamas: A Geographical and Political Analysis
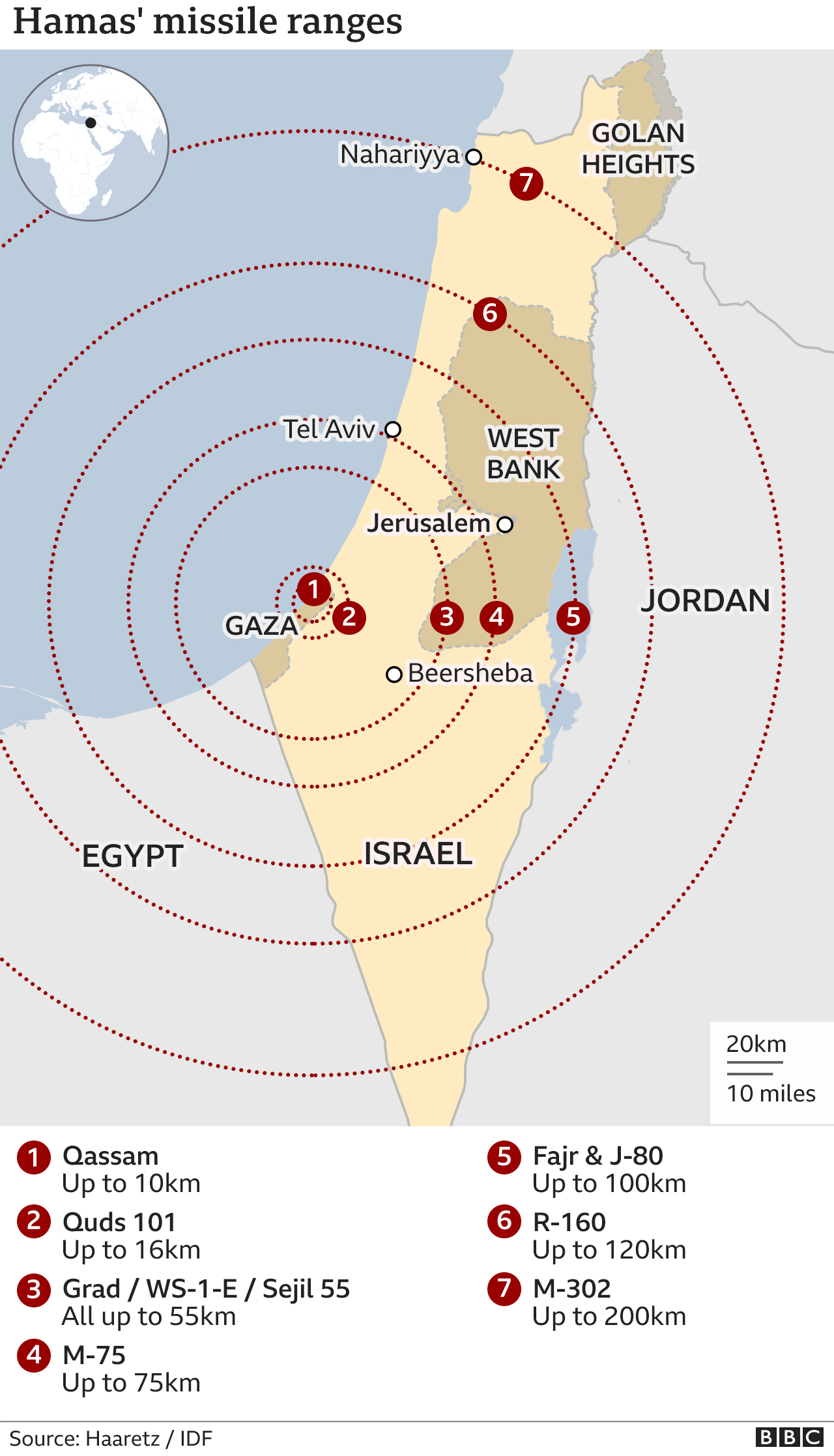
Hamas, an acronym for the Islamic Resistance Movement, is a Palestinian political and militant organization with a complex history and a significant presence in the Middle East. Understanding its geographical location and political context is crucial for comprehending the ongoing conflict in the region.
The Gaza Strip: A Geopolitical Hub
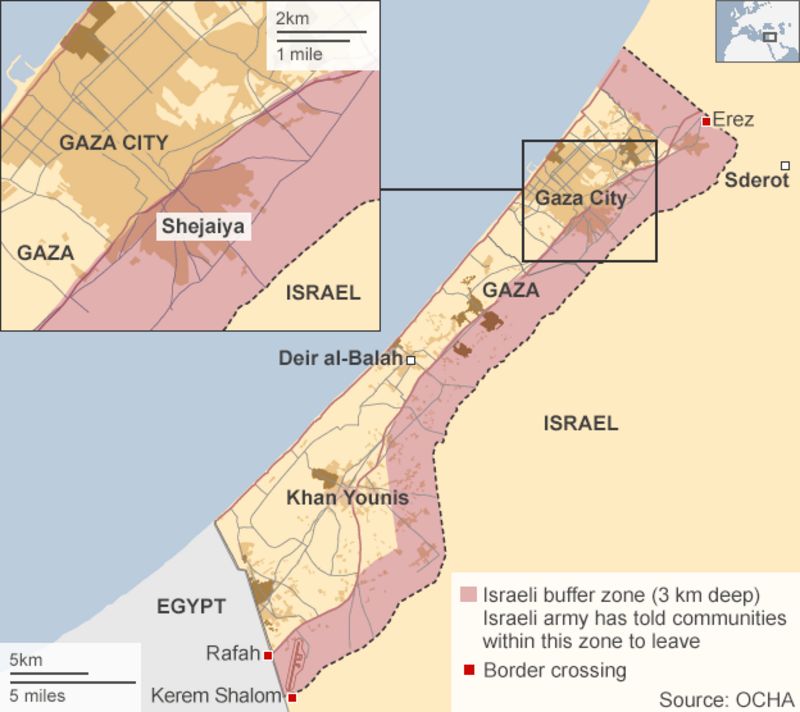
Hamas is primarily located in the Gaza Strip, a narrow coastal territory bordering Egypt to the south and Israel to the east and north. The Gaza Strip is a densely populated area, with over two million Palestinians residing within its 365 square kilometers. This territory, despite its small size, holds immense strategic significance, acting as a focal point for Palestinian nationalism and resistance.
A Map of Influence: Hamas’s Reach Beyond Gaza
While Hamas’s core operational area is the Gaza Strip, its influence extends beyond these borders. The organization maintains a presence in the West Bank, where it competes with the Palestinian Authority for political dominance. Hamas has also established branches in various countries, including Lebanon, Syria, and Turkey, where it maintains connections with like-minded groups and individuals.
The Significance of Hamas’s Location
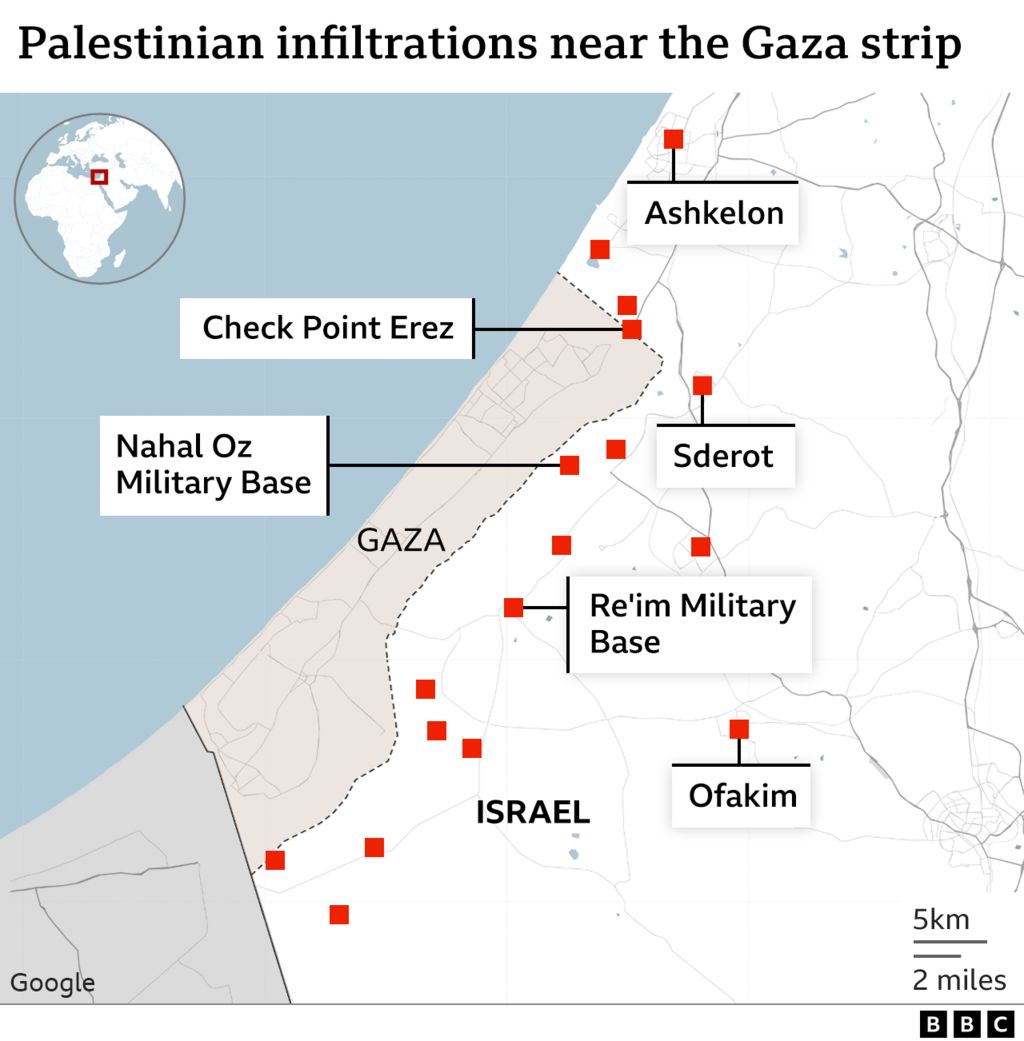
Hamas’s location in the Gaza Strip provides it with a unique set of advantages and disadvantages. The territory’s proximity to Israel allows Hamas to launch attacks against Israeli targets with relative ease. However, it also makes Gaza vulnerable to Israeli military operations, which have resulted in significant civilian casualties and humanitarian crises.
Understanding the Context: Historical and Political Factors
The location of Hamas is inextricably linked to the broader context of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. The Gaza Strip, once part of Mandatory Palestine, was occupied by Israel during the 1967 Six-Day War. Following the 1993 Oslo Accords, Israel withdrew its forces from the Gaza Strip, leaving it under the control of the Palestinian Authority. However, Hamas’s victory in the 2006 Palestinian legislative elections led to a power struggle with the Palestinian Authority, culminating in Hamas’s takeover of the Gaza Strip in 2007.
The Geopolitical Landscape: Challenges and Opportunities
Hamas’s location in the Gaza Strip presents a complex geopolitical landscape. The organization faces a multitude of challenges, including:
- Israeli Blockade: The Israeli government maintains a strict blockade on the Gaza Strip, restricting the flow of goods and people, hindering economic development and creating a humanitarian crisis.
- Internal Divisions: Hamas’s relationship with the Palestinian Authority remains strained, with ongoing power struggles and political disagreements.
- International Isolation: Hamas is designated as a terrorist organization by many countries, including the United States and the European Union, which limits its access to international funding and support.
Despite these challenges, Hamas continues to operate in the Gaza Strip, leveraging its political and military influence to pursue its objectives. The organization’s ability to withstand Israeli pressure and maintain control of the Gaza Strip underscores its resilience and adaptability.
FAQs
Q: Why is Hamas located in the Gaza Strip?
A: Hamas’s location in the Gaza Strip is rooted in its historical origins and the broader context of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. The Gaza Strip, a densely populated territory with a long history of Palestinian resistance, became a focal point for Hamas’s political and military activities.
Q: How does Hamas’s location in the Gaza Strip affect its operations?
A: Hamas’s location in the Gaza Strip provides it with a unique set of advantages and disadvantages. Its proximity to Israel allows for easier attacks but also makes it vulnerable to Israeli military operations.
Q: What are the challenges faced by Hamas in the Gaza Strip?
A: Hamas faces numerous challenges, including the Israeli blockade, internal divisions with the Palestinian Authority, and international isolation. These factors contribute to the ongoing humanitarian crisis in the Gaza Strip.
Q: What is the future of Hamas in the Gaza Strip?
A: The future of Hamas in the Gaza Strip remains uncertain. The organization’s ability to navigate the complex geopolitical landscape and address the ongoing challenges will determine its long-term success.
Tips
- Use reliable sources: Consult reputable news organizations, academic journals, and think tanks for accurate and unbiased information about Hamas and its location.
- Consider multiple perspectives: Understand the different viewpoints on Hamas, including those of Palestinians, Israelis, and the international community.
- Stay informed about current events: Keep up-to-date on the latest developments in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, as they directly impact the situation in the Gaza Strip and Hamas’s activities.
Conclusion
Hamas’s location in the Gaza Strip is a critical factor in understanding the complex dynamics of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. The organization’s presence in this strategically important territory has shaped the region’s political landscape and continues to influence the ongoing conflict.
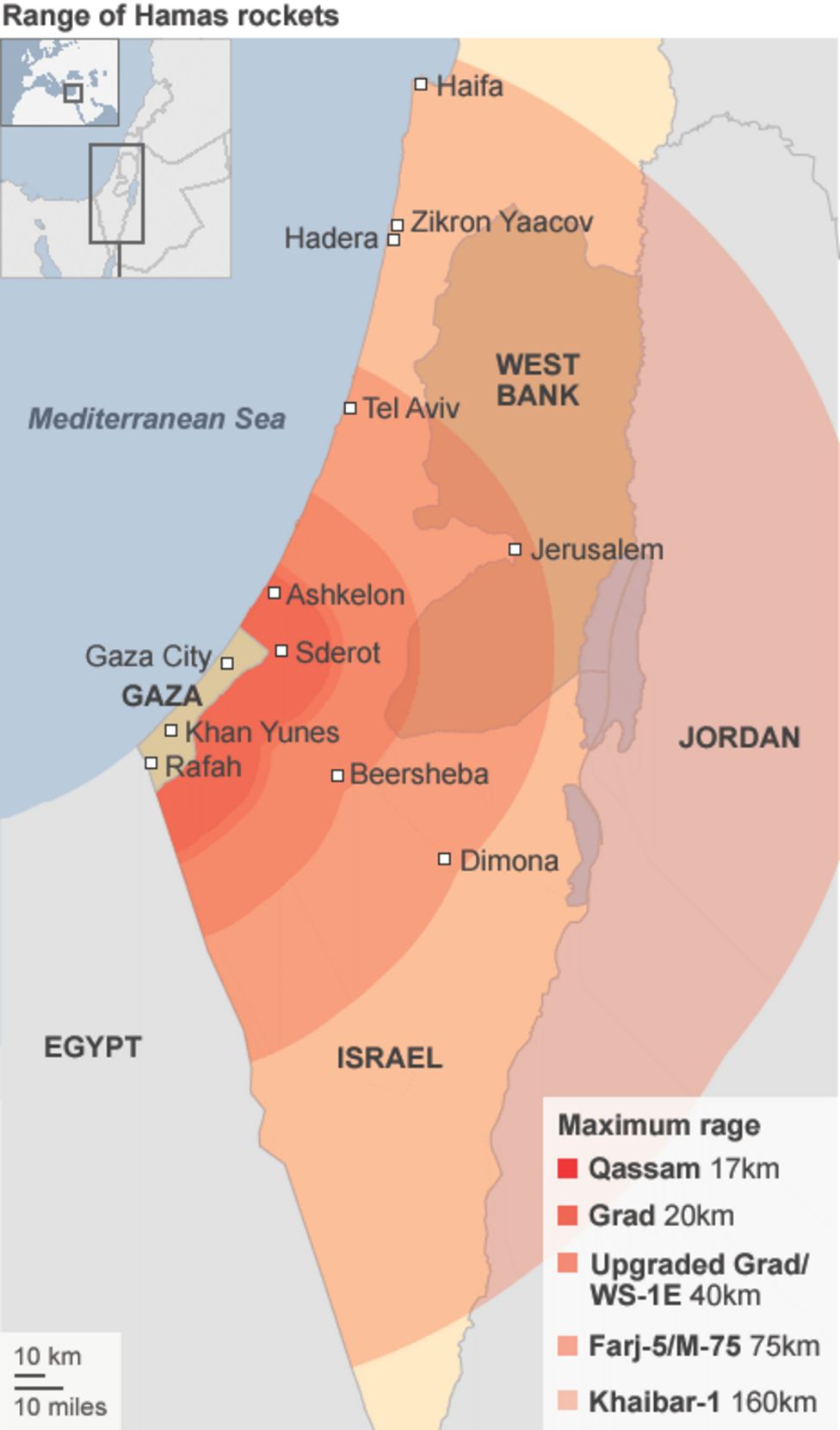
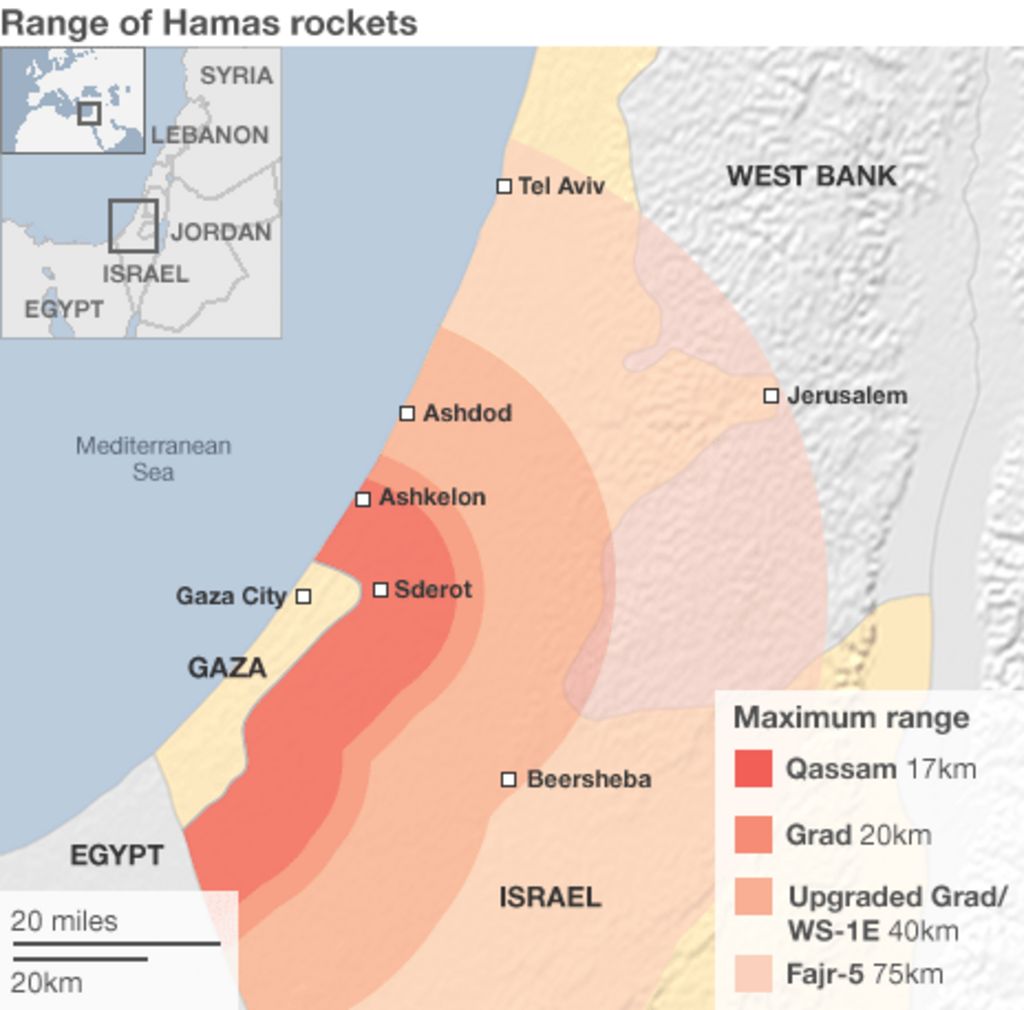



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Hamas: A Geographical and Political Analysis. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!