Mapping Indigenous Heritage: Understanding the Tapestry of Diversity
Related Articles: Mapping Indigenous Heritage: Understanding the Tapestry of Diversity
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Mapping Indigenous Heritage: Understanding the Tapestry of Diversity. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping Indigenous Heritage: Understanding the Tapestry of Diversity
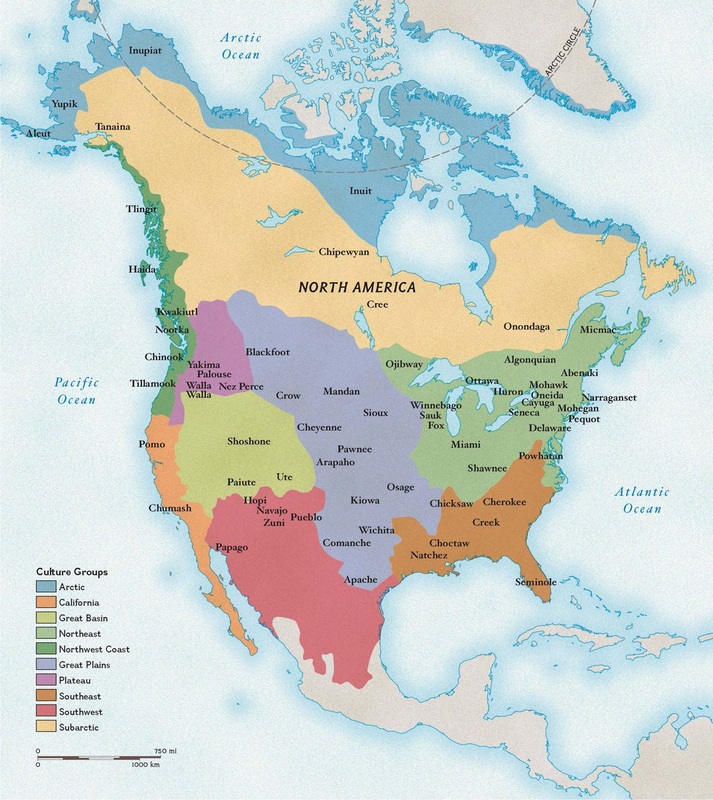
An indigenous tribes map is a powerful tool for visualizing and understanding the diverse tapestry of cultures, languages, and traditions that have thrived across the globe for millennia. These maps offer a unique window into the rich history of indigenous peoples, revealing their ancestral territories, cultural practices, and ongoing struggles for recognition and self-determination.
The Importance of Indigenous Tribes Maps:
1. Recognizing and Honoring Indigenous Sovereignty:
Indigenous tribes maps serve as a vital reminder of the historical and ongoing presence of indigenous peoples on their ancestral lands. They visually demonstrate the interconnectedness of indigenous communities with their environments and highlight the importance of recognizing and respecting their sovereignty over their territories.
2. Preserving Cultural Heritage:
Indigenous tribes maps are essential tools for preserving and promoting cultural heritage. They provide a framework for understanding the intricate relationships between language, land, and culture, fostering a deeper appreciation for the diverse traditions and knowledge systems that have been passed down through generations.
3. Promoting Reconciliation and Understanding:
By showcasing the historical and contemporary realities of indigenous peoples, these maps contribute to fostering reconciliation and understanding between indigenous communities and dominant societies. They provide a platform for dialogue, education, and the recognition of past injustices, promoting a more inclusive and equitable future.
4. Supporting Indigenous Rights and Self-Determination:
Indigenous tribes maps are valuable resources for advocating for indigenous rights and self-determination. They serve as a powerful visual representation of the land claims and resource rights of indigenous communities, providing a strong basis for advocating for policies and programs that support their well-being and cultural survival.
5. Fostering Environmental Stewardship:
Indigenous peoples have long been recognized as stewards of their environments, possessing deep knowledge and sustainable practices that have preserved ecosystems for generations. Indigenous tribes maps can highlight the vital role that indigenous communities play in protecting biodiversity and promoting sustainable development.
Types of Indigenous Tribes Maps:
There are various types of indigenous tribes maps, each serving a specific purpose and reflecting different perspectives:
1. Ethnolinguistic Maps: These maps depict the distribution of different indigenous languages and cultures across a region, highlighting the linguistic diversity and cultural richness of indigenous peoples.
2. Territorial Maps: These maps showcase the traditional territories and ancestral lands of indigenous communities, providing a visual representation of their historical and ongoing claims to land and resources.
3. Resource Maps: These maps highlight the natural resources found within indigenous territories, emphasizing the importance of indigenous knowledge and sustainable practices in managing these resources.
4. Historical Maps: These maps trace the historical movements and migrations of indigenous peoples, revealing their resilience and adaptability in the face of changing circumstances.
5. Contemporary Maps: These maps showcase the current distribution and demographics of indigenous communities, highlighting their ongoing presence and struggles for recognition and self-determination.
Challenges and Considerations:
While indigenous tribes maps offer valuable insights, it’s essential to acknowledge certain challenges and considerations:
1. Accuracy and Representation: Ensuring the accuracy and inclusivity of these maps is crucial. Collaboration with indigenous communities is vital to ensure that their perspectives and knowledge are accurately reflected.
2. Historical Context: Understanding the historical context surrounding the development of indigenous tribes maps is essential. Recognizing the potential for colonial biases and inaccuracies is crucial for interpreting these maps critically.
3. Ongoing Change: Indigenous communities are dynamic entities, constantly adapting and evolving. Recognizing the fluidity of tribal boundaries and cultural practices is essential for developing accurate and up-to-date maps.
4. Respect and Consent: It is paramount to respect the sovereignty of indigenous communities and obtain their consent before using or sharing information about their territories and cultural practices.
FAQs about Indigenous Tribes Maps:
1. What is the purpose of an indigenous tribes map?
Indigenous tribes maps serve to visualize and understand the diverse cultures, languages, and traditions of indigenous peoples, honoring their sovereignty, preserving their heritage, and advocating for their rights.
2. How are these maps created?
Indigenous tribes maps are often created through collaboration between indigenous communities, researchers, and cartographers, drawing upon historical knowledge, oral traditions, and contemporary data.
3. What are the limitations of these maps?
Indigenous tribes maps are subject to limitations due to ongoing changes in tribal boundaries, cultural practices, and historical inaccuracies.
4. How can I access these maps?
Indigenous tribes maps are available through various sources, including academic institutions, government agencies, and indigenous organizations.
5. How can I use these maps responsibly?
It is crucial to use indigenous tribes maps responsibly, recognizing the historical context, respecting indigenous sovereignty, and acknowledging the ongoing struggles for recognition and self-determination.
Tips for Understanding Indigenous Tribes Maps:
1. Context is Key: Always consider the historical context and potential biases present in these maps.
2. Collaboration is Essential: Seek input from indigenous communities to ensure accurate and inclusive representation.
3. Respect Indigenous Perspectives: Acknowledge the diverse perspectives and knowledge systems of indigenous peoples.
4. Recognize Ongoing Change: Understand that indigenous communities are dynamic entities subject to ongoing change.
5. Promote Dialogue and Education: Utilize these maps to foster dialogue, education, and understanding about indigenous cultures and histories.
Conclusion:
Indigenous tribes maps are invaluable tools for understanding and honoring the rich diversity and resilience of indigenous peoples worldwide. They serve as a powerful reminder of the interconnectedness of land, culture, and identity, highlighting the importance of recognizing indigenous sovereignty, preserving cultural heritage, and advocating for self-determination. By engaging with these maps thoughtfully and responsibly, we can contribute to a more just and equitable future for all.
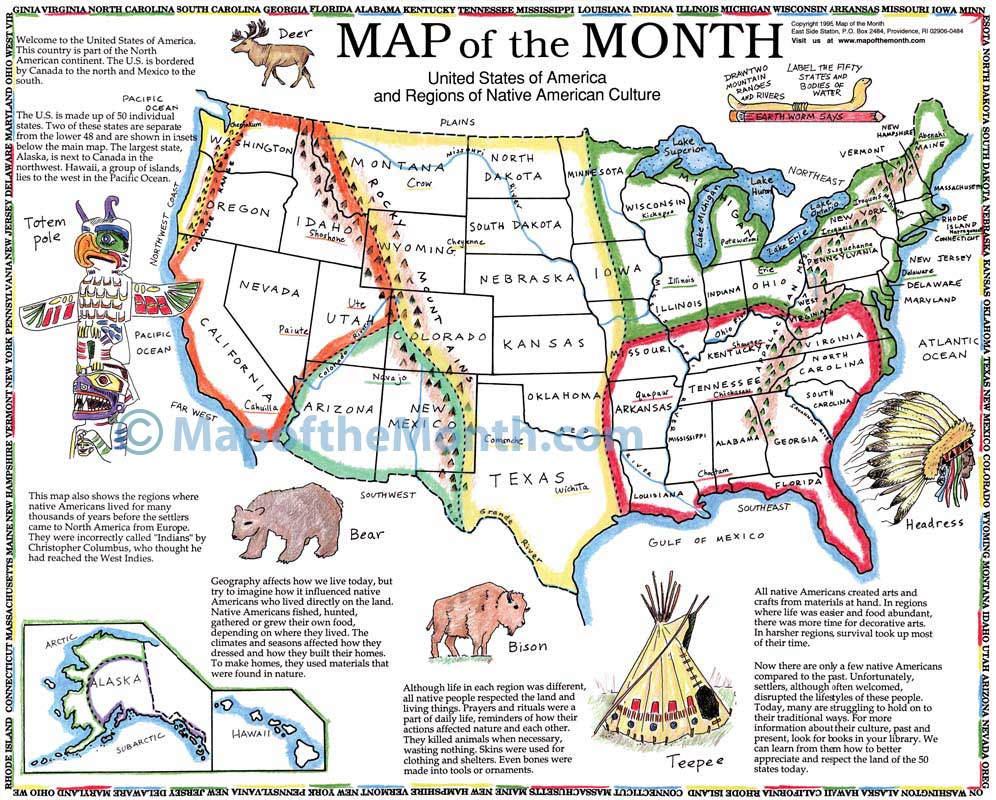






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping Indigenous Heritage: Understanding the Tapestry of Diversity. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!