Navigating North America: A Comprehensive Look at Latitude Lines and Their Significance
Related Articles: Navigating North America: A Comprehensive Look at Latitude Lines and Their Significance
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating North America: A Comprehensive Look at Latitude Lines and Their Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating North America: A Comprehensive Look at Latitude Lines and Their Significance
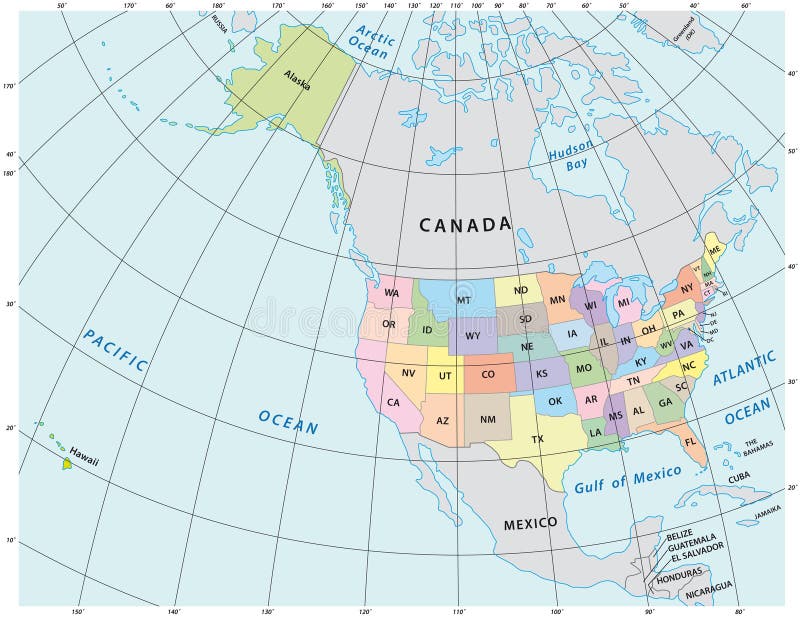
North America, a vast and diverse continent, stretches from the icy Arctic to the tropical Caribbean, encompassing a wide range of climates, ecosystems, and cultures. Understanding the continent’s geography, particularly its latitude lines, provides crucial insights into its diverse landscapes and the interplay of natural forces that shape its environment.
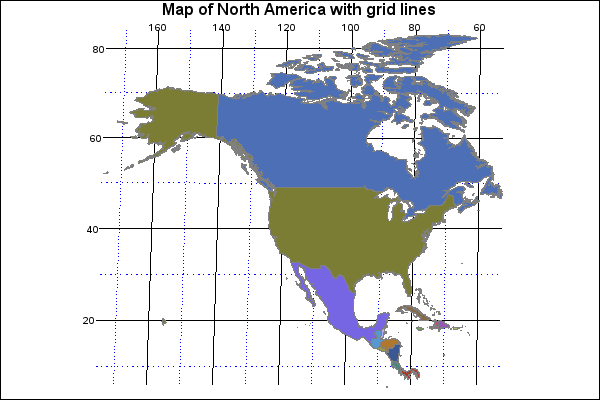
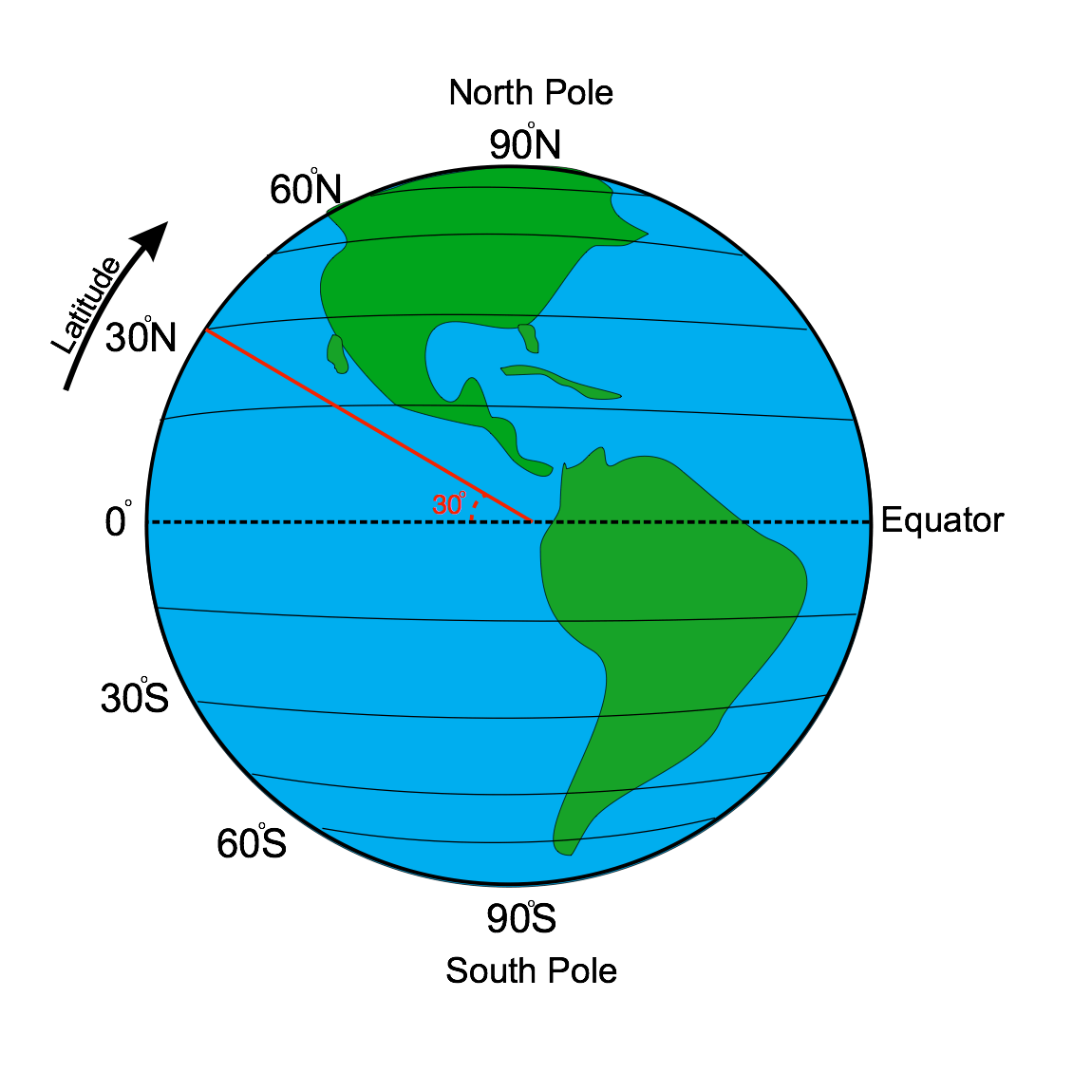
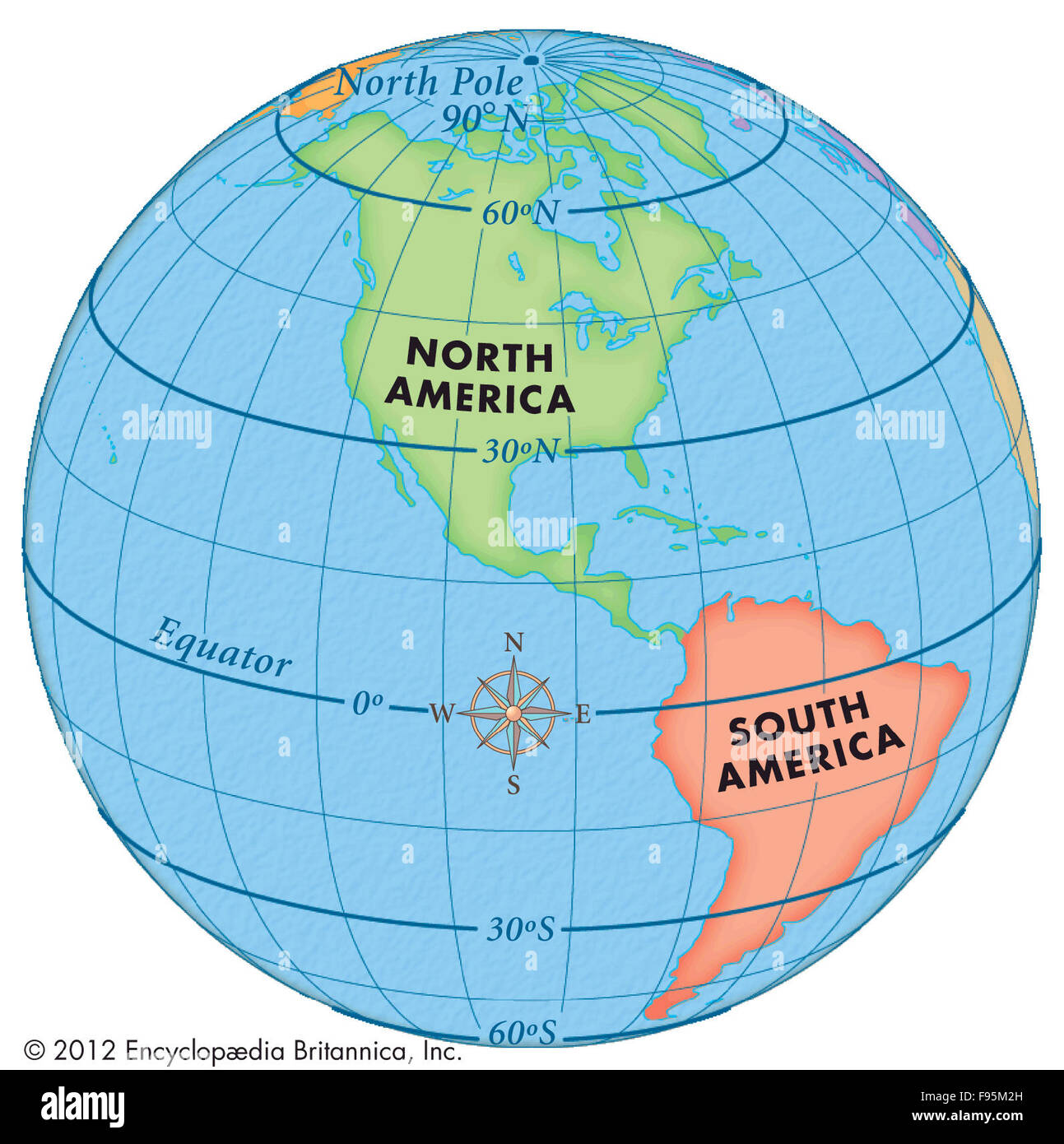
Latitude Lines: Defining North America’s Geography
Latitude lines, also known as parallels, are imaginary circles drawn around the Earth parallel to the equator. They are measured in degrees, with the equator being 0 degrees and the North and South Poles at 90 degrees. These lines play a fundamental role in understanding North America’s geographical features, climate patterns, and cultural diversity.
Key Latitude Lines and Their Impact on North America
-
Equator (0°): While the equator does not directly intersect North America, its influence is felt in the southernmost regions. The Caribbean islands, located near the equator, experience tropical climates with high temperatures and humidity.
-
Tropic of Cancer (23.5° North): This line marks the northernmost point where the sun can be directly overhead at noon. It passes through Mexico, the Bahamas, and parts of the United States, including Florida and Hawaii. Regions south of the Tropic of Cancer are generally characterized by warm temperatures and abundant rainfall.
-
Arctic Circle (66.5° North): This line marks the southernmost point where the sun does not set for 24 hours during the summer solstice and does not rise for 24 hours during the winter solstice. It passes through northern Canada, Alaska, and Greenland, marking the transition from temperate to polar climates.
-
North Pole (90° North): The North Pole is the northernmost point on Earth and is located in the Arctic Ocean. It experiences extreme cold and long periods of darkness during the winter and continuous daylight during the summer.
The Influence of Latitude on Climate and Ecosystems
Latitude plays a crucial role in determining a region’s climate and the types of ecosystems that thrive there. Regions closer to the equator receive more direct sunlight and experience warmer temperatures and higher humidity. As one moves northward, the angle of the sun decreases, leading to cooler temperatures, shorter growing seasons, and a greater variation in seasonal weather patterns.
Impact on Human Geography and Culture
Latitude influences not only the physical landscape but also the development of human settlements and cultures. Coastal regions with access to navigable waterways and moderate climates have historically been centers of trade and population density. Regions further north, with harsher climates and limited resources, have developed unique adaptations and cultures tailored to their environment.
Navigating North America’s Diverse Landscapes
By understanding the significance of latitude lines, we gain a deeper appreciation for the diverse landscapes and ecosystems that make up North America. From the lush rainforests of the Pacific Northwest to the arid deserts of the Southwest, from the bustling cities of the East Coast to the remote villages of the Arctic, each region is shaped by its unique geographical location and the latitude lines that define it.
FAQs about Latitude and North America
Q: How do latitude lines influence the length of days and nights?
A: Latitude determines the angle at which sunlight strikes the Earth. Areas closer to the equator receive more direct sunlight, leading to longer days and shorter nights. As one moves towards the poles, the angle of the sun decreases, resulting in shorter days and longer nights.
Q: What are the main climate zones in North America?
A: North America is home to a variety of climate zones, including:
- Tropical: Characterized by high temperatures and humidity, found in the Caribbean and parts of Florida.
- Subtropical: With warm temperatures and distinct wet and dry seasons, found in the southeastern United States and parts of Mexico.
- Temperate: Experiencing moderate temperatures and four distinct seasons, found in much of the eastern and western United States and Canada.
- Continental: With extreme temperature variations between seasons, found in the interior of North America.
- Polar: Characterized by extremely cold temperatures and long periods of darkness during the winter, found in northern Canada, Alaska, and Greenland.
Q: How does latitude impact plant and animal life in North America?
A: Latitude plays a major role in determining the types of plants and animals that can thrive in a particular region. Tropical regions support a wide diversity of plant and animal life due to their warm temperatures and abundant rainfall. As one moves northward, the diversity of species decreases, with adaptations to colder temperatures and shorter growing seasons becoming more prominent.
Tips for Using a Latitude Map of North America
- Focus on key latitude lines: Pay attention to the equator, Tropic of Cancer, Arctic Circle, and North Pole. These lines provide a framework for understanding the continent’s diverse geographical features and climate patterns.
- Relate latitude to climate and ecosystems: Observe how latitude influences the distribution of different climate zones and the types of ecosystems that thrive in each region.
- Explore human geography: Use the map to investigate how latitude has shaped the development of human settlements, cultures, and economies across North America.
- Compare and contrast regions: Analyze the differences in climate, vegetation, and human activity between regions at different latitudes.
Conclusion
A North America latitude map serves as a valuable tool for understanding the continent’s diverse landscapes, climates, and ecosystems. It provides a framework for exploring the intricate relationship between geography and human activity, highlighting the significant influence of latitude on the continent’s physical and cultural diversity. By studying the map and its implications, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities of North America and the factors that have shaped its unique character.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating North America: A Comprehensive Look at Latitude Lines and Their Significance. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!