Navigating the Diverse Landscape of Bolivia: A Geographic Exploration
Related Articles: Navigating the Diverse Landscape of Bolivia: A Geographic Exploration
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Diverse Landscape of Bolivia: A Geographic Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Diverse Landscape of Bolivia: A Geographic Exploration

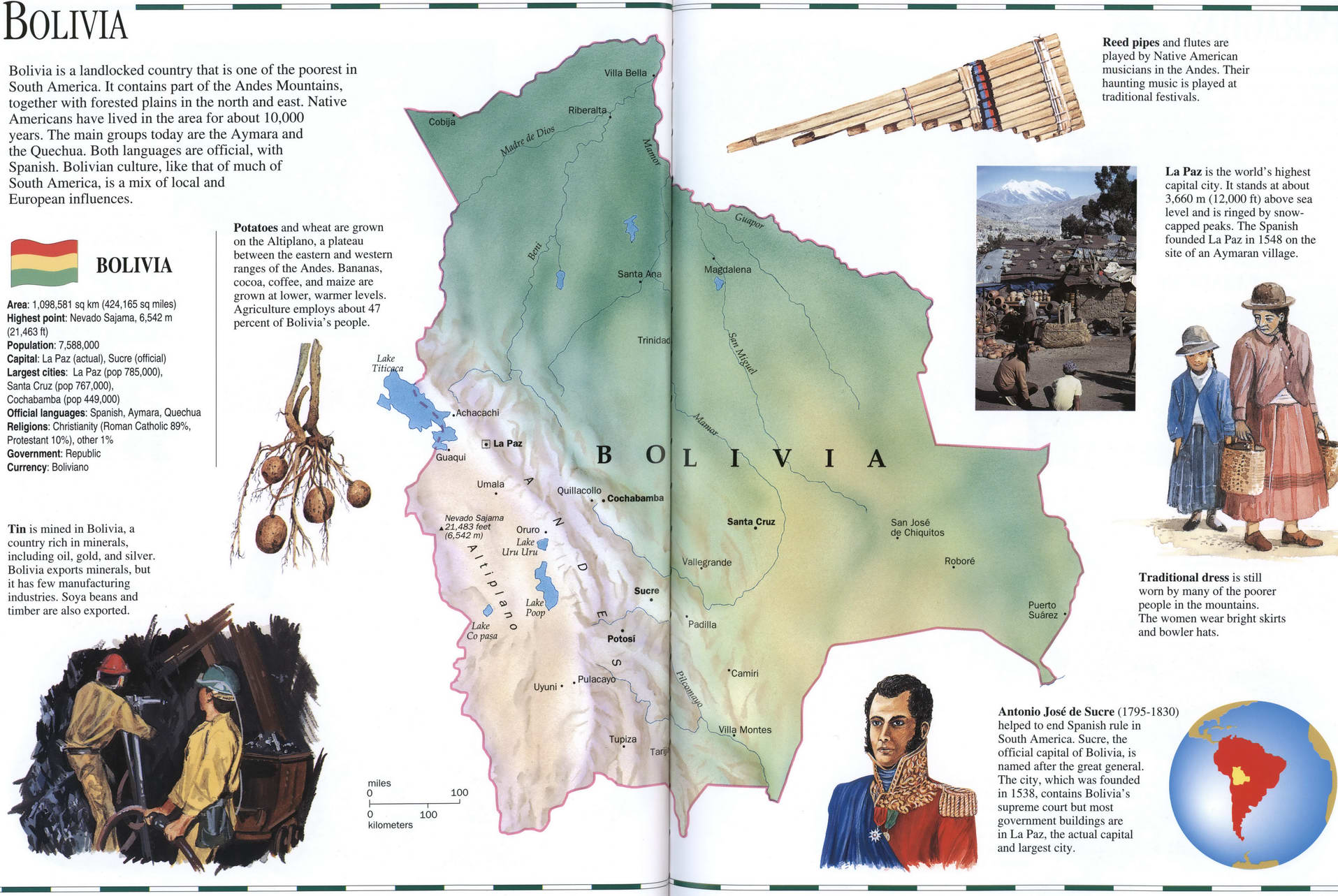
Bolivia, nestled in the heart of South America, is a land of dramatic contrasts. From the snow-capped peaks of the Andes to the vast expanse of the Amazon rainforest, its geography is a tapestry of diverse ecosystems, each with its own unique beauty and challenges. Understanding Bolivia’s geography is crucial to appreciating its rich history, culture, and economic potential.
A Land of Extremes: The Geographic Features of Bolivia
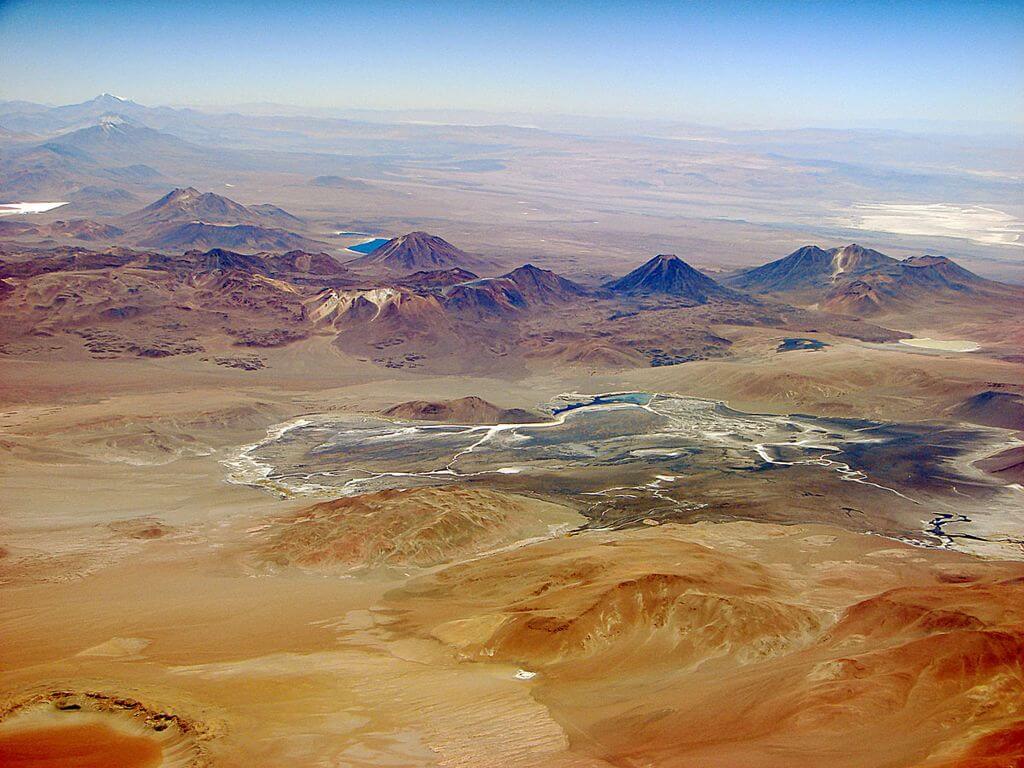
Bolivia’s landscape is defined by its elevation, with the Andes Mountains dominating the western portion of the country. This region, known as the Altiplano, is a high plateau characterized by arid plains, salt flats, and volcanic peaks. The Andes also create a natural barrier, influencing Bolivia’s climate and isolating it from the Pacific Ocean.
To the east, the Andes gradually descend into the Amazon Basin, giving way to the vast lowland plains of the Amazon rainforest. This region is characterized by dense vegetation, abundant wildlife, and a humid tropical climate.
The country can be broadly divided into four distinct geographic regions:
-
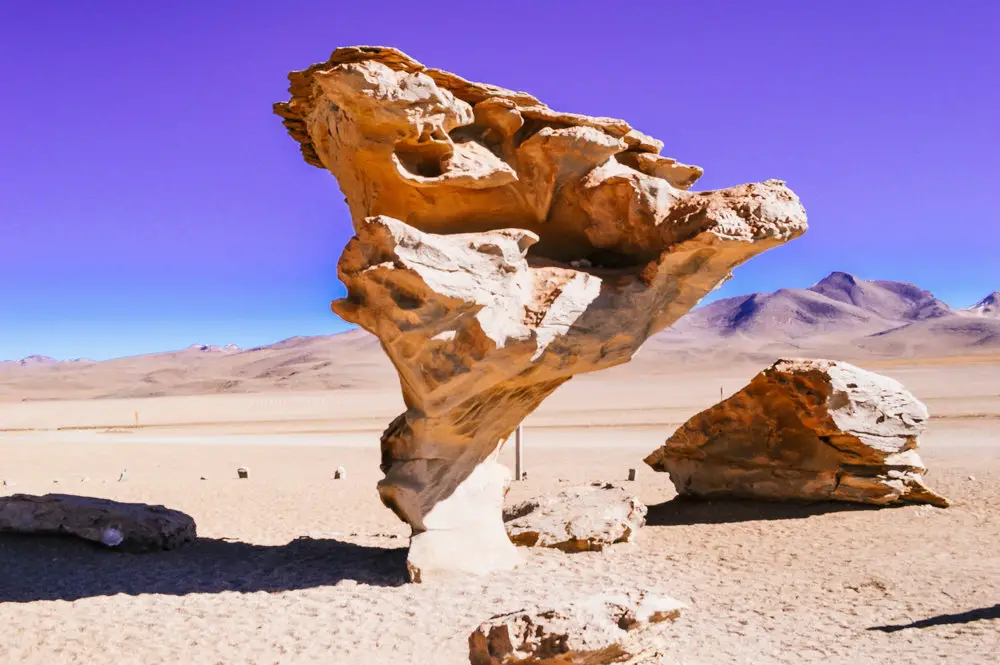
The Andes: This region encompasses the western highlands and includes the Altiplano, a high plateau that is home to iconic landmarks like Lake Titicaca and the Salar de Uyuni, the world’s largest salt flat. The Andes are also home to Bolivia’s highest peak, Mount Sajama, which reaches over 6,500 meters.
-
The Yungas: Located on the eastern slopes of the Andes, the Yungas are a transition zone between the highlands and the lowlands. This region is characterized by its lush vegetation, steep valleys, and a diverse array of ecosystems.
-
The Llanos Orientales: Also known as the Amazon Basin, this region covers the eastern lowlands of Bolivia. It is characterized by its vast expanse of rainforest, abundant wildlife, and a humid tropical climate.
-
The Chaco: Located in the southeastern part of the country, the Chaco is a semi-arid region characterized by its flat plains, sparse vegetation, and unique wildlife.
Navigating the Terrain: Understanding Bolivia’s Geography
Bolivia’s diverse geography presents both opportunities and challenges. The Andes, while providing stunning scenery, also pose significant challenges for transportation and communication. The mountainous terrain makes road construction difficult and expensive, limiting connectivity between different regions.
The Amazon rainforest, while rich in biodiversity, is also a challenging environment to navigate. Dense vegetation and limited infrastructure make access to this region difficult, posing challenges for development and conservation efforts.
Despite these challenges, Bolivia’s diverse geography is a source of immense wealth. The Altiplano is home to a wealth of mineral resources, including lithium, tin, and silver. The Amazon rainforest provides a vast array of timber and other natural resources, while the Chaco region is home to valuable oil and gas reserves.
The Importance of Geographic Knowledge in Understanding Bolivia
Understanding Bolivia’s geography is crucial for appreciating its rich history, culture, and economic potential. The country’s diverse landscape has shaped its cultural identity, influencing its art, music, and cuisine.
For example, the indigenous cultures of the Altiplano have developed unique traditions and customs adapted to the harsh conditions of the high altitude. The Amazon rainforest has also played a significant role in shaping Bolivia’s indigenous cultures, with its rich biodiversity providing a source of food, medicine, and inspiration.
Bolivia’s geography also has a profound impact on its economy. The country’s mineral resources are a major source of revenue, while its agricultural sector is heavily dependent on the availability of water and land.
Exploring Bolivia: A Journey Through its Geographic Tapestry
Bolivia’s diverse geography offers a wealth of opportunities for exploration and adventure. Visitors can experience the breathtaking beauty of the Altiplano, hike through the lush Yungas, or explore the vast Amazon rainforest.
FAQs about Bolivia’s Geography
Q: What are the major geographic features of Bolivia?
A: Bolivia’s major geographic features include the Andes Mountains, the Altiplano, the Amazon rainforest, the Yungas, the Llanos Orientales, and the Chaco.
Q: What is the highest point in Bolivia?
A: The highest point in Bolivia is Mount Sajama, which reaches over 6,500 meters.
Q: What is the largest salt flat in the world?
A: The Salar de Uyuni, located in the Altiplano, is the world’s largest salt flat.
Q: What are the major challenges posed by Bolivia’s geography?
A: Bolivia’s geography presents challenges in terms of transportation, communication, and development. The mountainous terrain makes road construction difficult and expensive, while the dense vegetation of the Amazon rainforest limits access to this region.
Q: What are the economic benefits of Bolivia’s geography?
A: Bolivia’s diverse geography provides a wealth of natural resources, including minerals, timber, and oil and gas. These resources are a major source of revenue for the country.
Tips for Exploring Bolivia’s Diverse Landscape:
- Plan your trip carefully: Bolivia’s diverse geography requires careful planning. Consider your interests, budget, and physical abilities when choosing destinations.
- Respect the environment: Bolivia’s natural beauty is fragile. Be mindful of your impact on the environment and follow responsible tourism practices.
- Learn about the local culture: Bolivia’s indigenous cultures are rich and diverse. Take the time to learn about their traditions and customs.
- Be prepared for altitude sickness: The high altitude of the Altiplano can cause altitude sickness. Be prepared by acclimatizing gradually and staying hydrated.
- Consider hiring a local guide: Local guides can provide valuable insights into Bolivia’s geography, history, and culture.
Conclusion
Bolivia’s geography is a defining feature of the country, shaping its history, culture, and economy. From the snow-capped peaks of the Andes to the vast expanse of the Amazon rainforest, its landscape is a tapestry of diverse ecosystems, each with its own unique beauty and challenges. Understanding Bolivia’s geography is crucial for appreciating its rich heritage and for navigating its diverse landscape responsibly.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Diverse Landscape of Bolivia: A Geographic Exploration. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!