Navigating the Northern European Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to its Countries and Significance
Related Articles: Navigating the Northern European Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to its Countries and Significance
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Northern European Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to its Countries and Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Northern European Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to its Countries and Significance
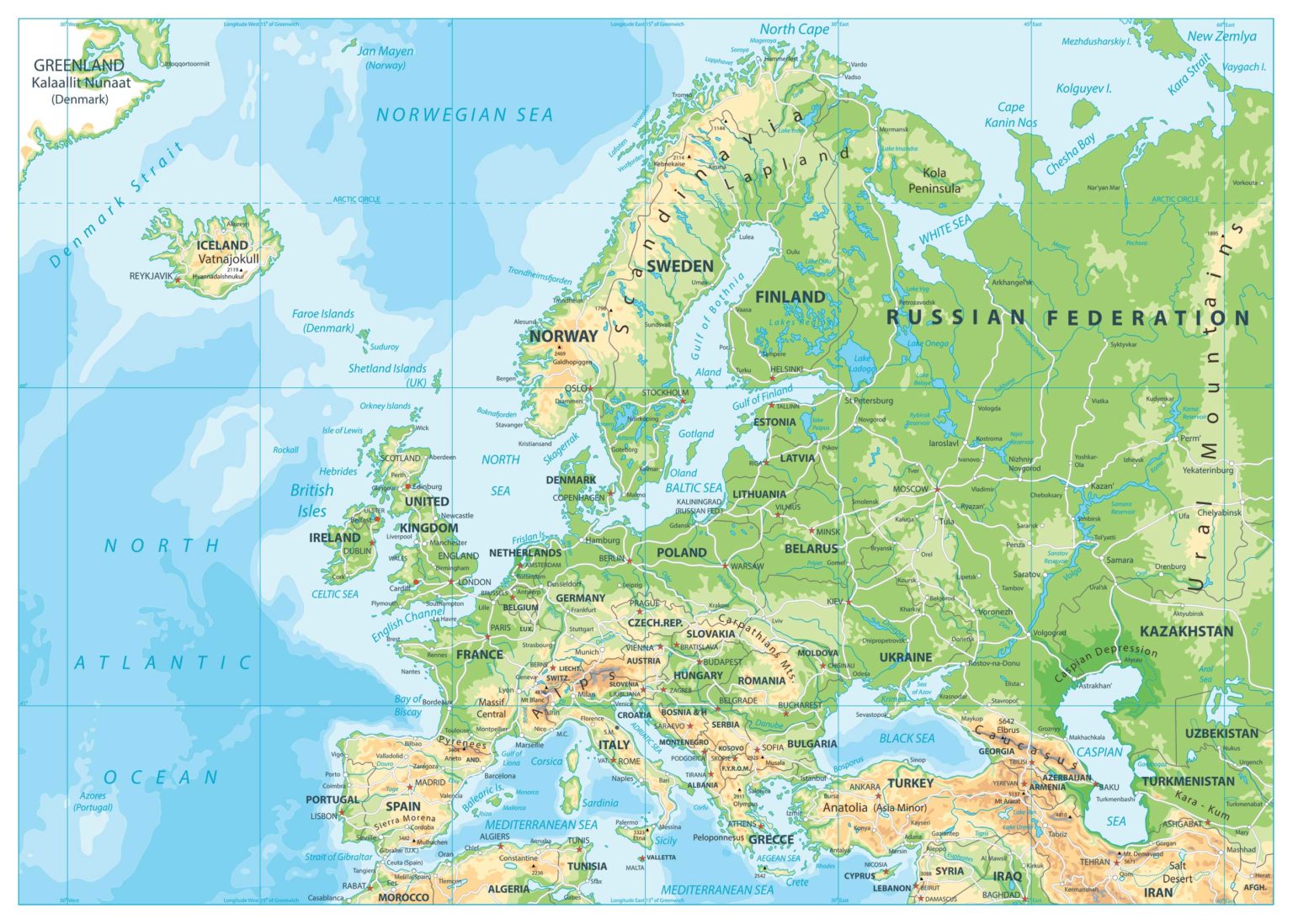
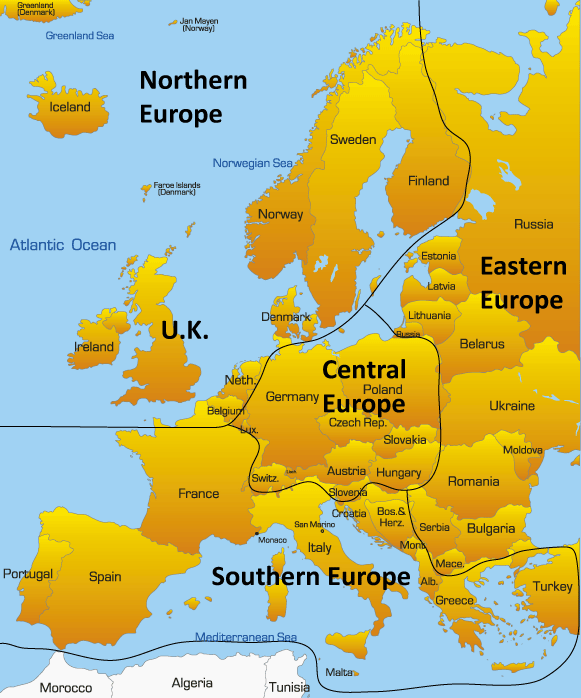
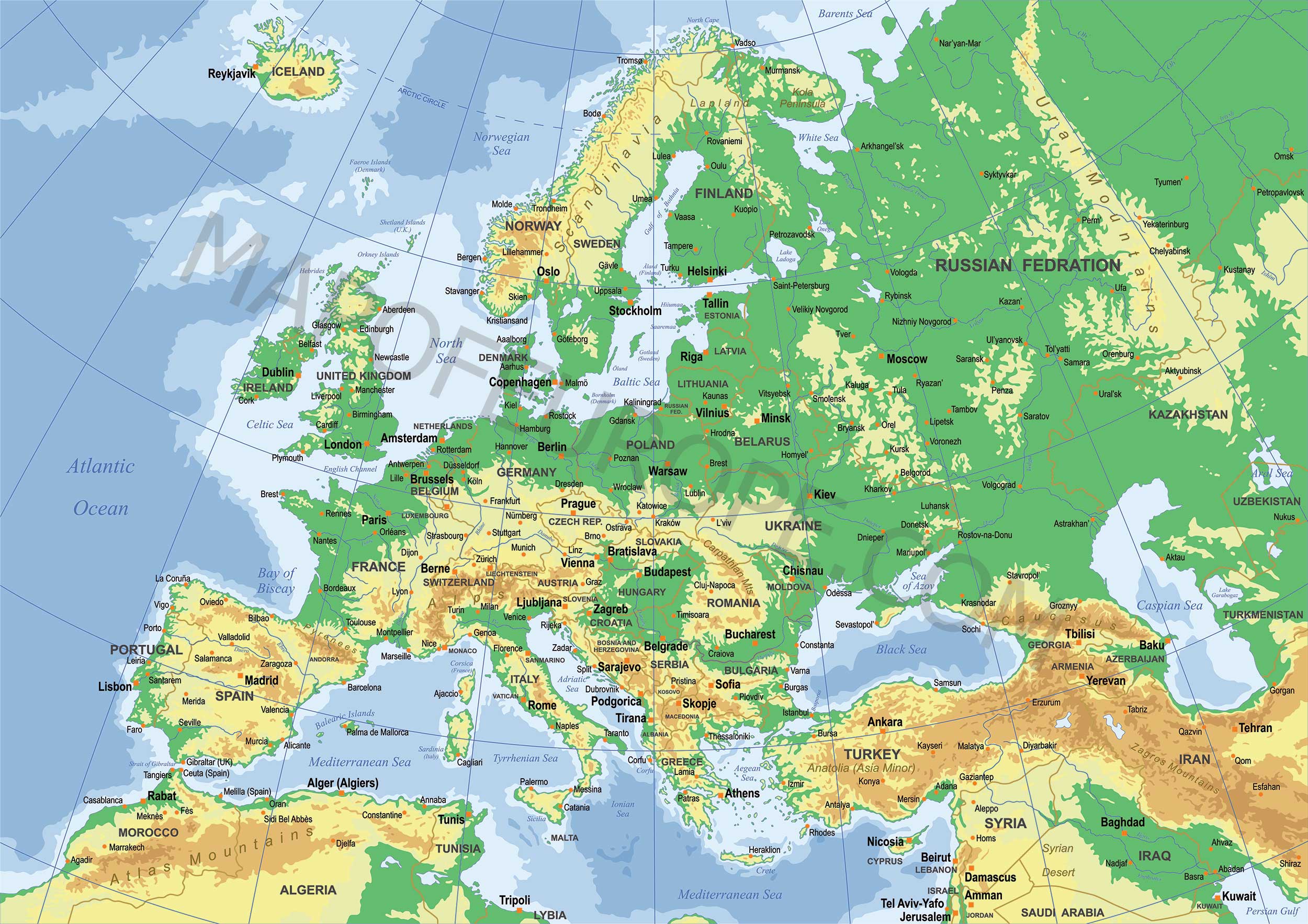
Northern Europe, a region often associated with striking landscapes, vibrant cultures, and a strong sense of social welfare, comprises a unique collection of countries that share a common geographical location but boast diverse histories, languages, and traditions. Understanding the individual characteristics of these nations provides valuable insight into the region’s rich tapestry and its global impact.
A Geographic Overview
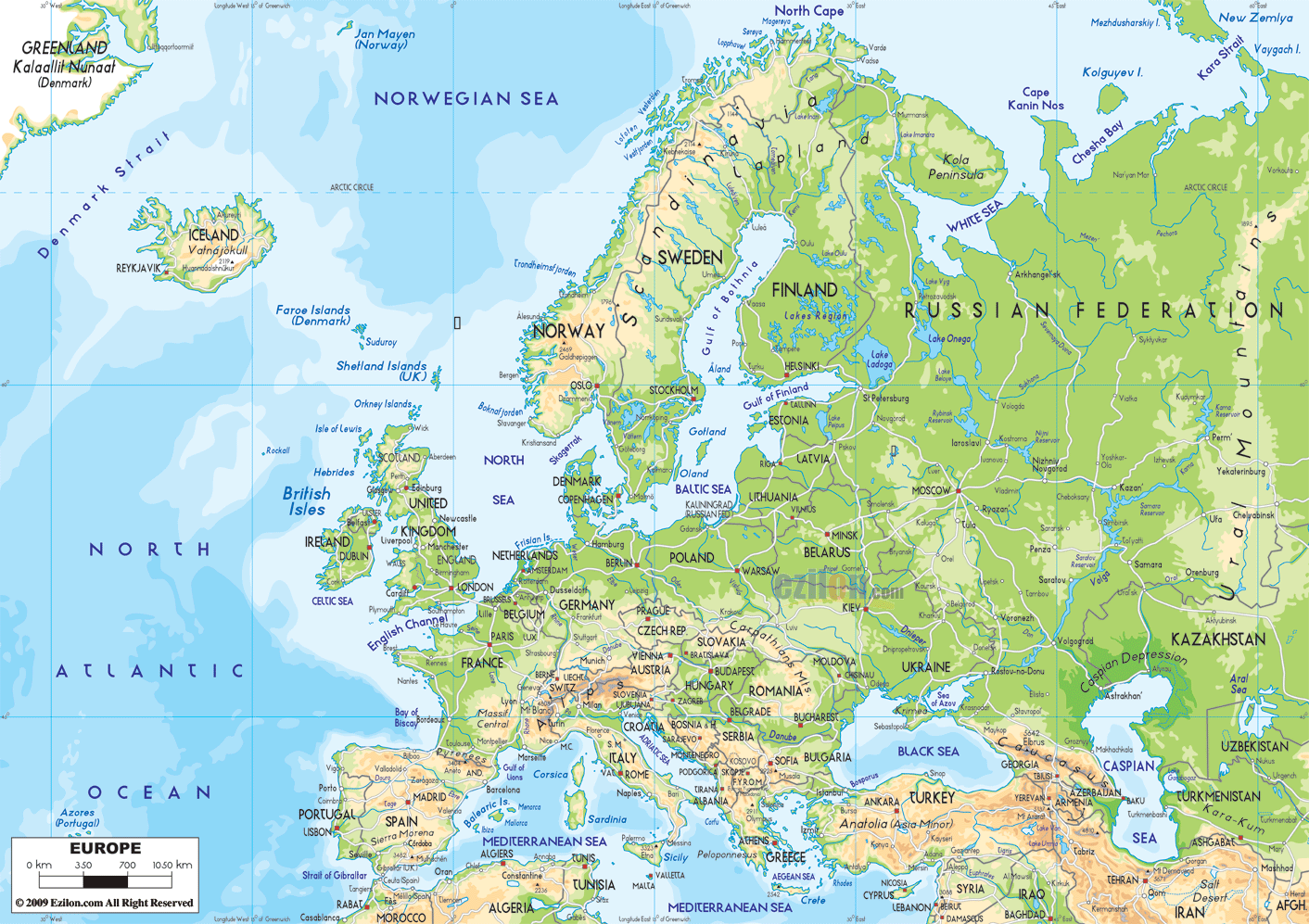
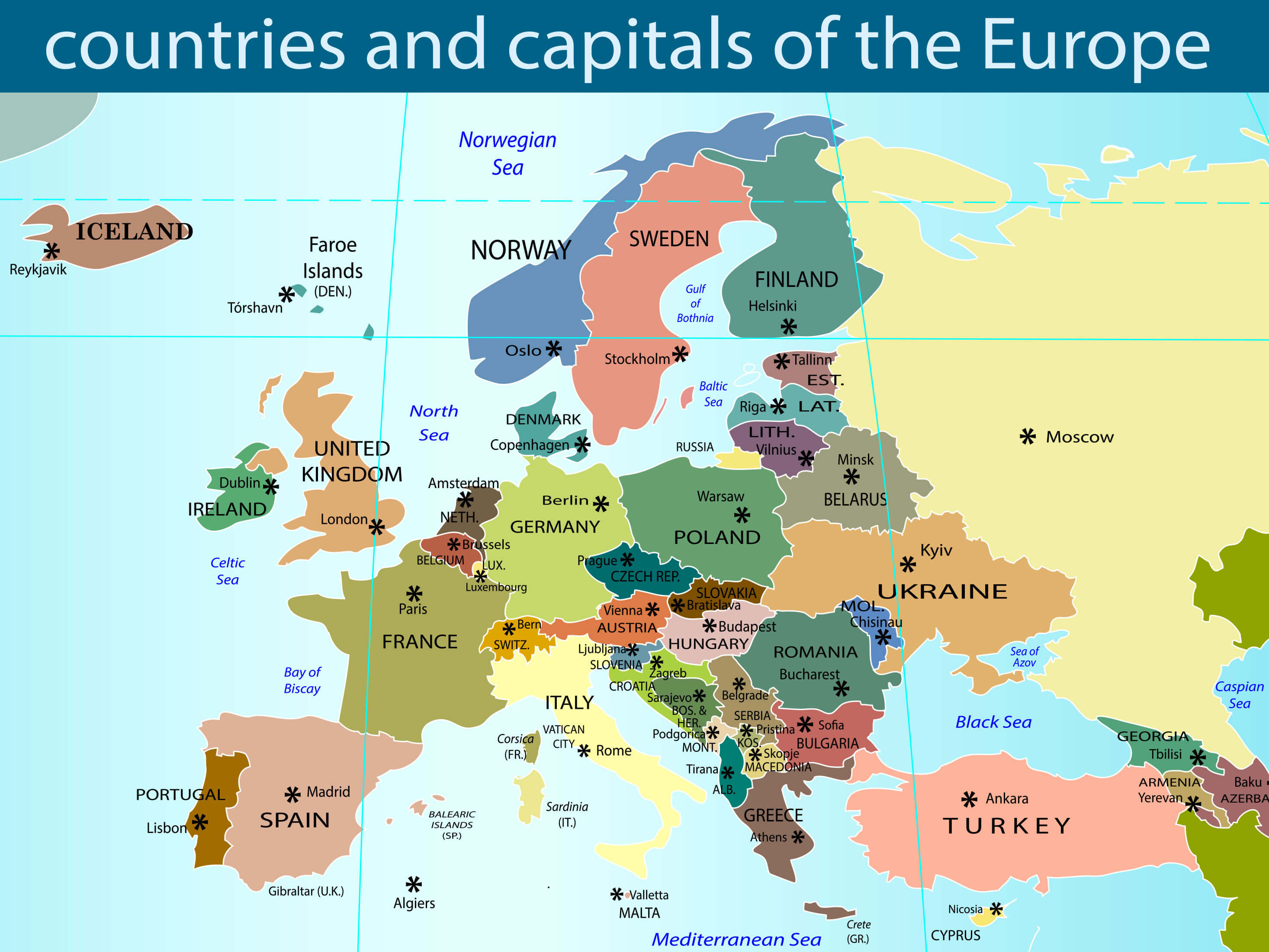
Northern Europe, also known as Scandinavia, encompasses the northernmost portion of the European continent, encompassing countries situated north of the Baltic Sea and west of the Ural Mountains. These countries include:
- Denmark: Located on the Jutland Peninsula and surrounding islands, Denmark serves as a bridge between mainland Europe and Scandinavia, with its unique cultural heritage and historical significance.
- Estonia: Situated on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, Estonia is known for its stunning coastline, technological advancement, and rich cultural heritage.
- Finland: Sharing a long border with Russia, Finland is renowned for its extensive forests, pristine lakes, and strong sense of national identity.
- Iceland: A volcanic island nation in the North Atlantic Ocean, Iceland boasts breathtaking natural wonders, geothermal activity, and a distinct language and culture.
- Latvia: Located on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, Latvia shares a strong cultural connection with its neighboring Baltic states and is known for its diverse landscapes and vibrant cities.
- Lithuania: Bordering Latvia and Poland, Lithuania is a nation rich in history and culture, with a vibrant capital city and a strong sense of national identity.
- Norway: Known for its towering fjords, majestic mountains, and breathtaking coastline, Norway boasts a unique cultural heritage, strong social welfare system, and a significant oil and gas industry.
- Sweden: The largest country in Scandinavia, Sweden is recognized for its innovative technology, high quality of life, and rich cultural heritage, including its distinctive design aesthetic.
A Historical Perspective
The history of Northern Europe is a captivating blend of Viking voyages, medieval kingdoms, and modern societal transformations. The region’s strategic location and access to the sea have shaped its historical development, influencing trade routes, cultural exchanges, and political alliances.
- Viking Legacy: The Vikings, originating from Scandinavia, played a pivotal role in shaping the history of Northern Europe. Their maritime prowess and exploration led to extensive trade networks, cultural exchanges, and the establishment of settlements across Europe and beyond.
- Medieval Kingdoms: The emergence of powerful kingdoms, such as Denmark, Sweden, and Norway, marked the transition from Viking Age to the Middle Ages. These kingdoms established strong political structures, fostered cultural development, and played significant roles in European affairs.
- Modern Transformation: The 20th century witnessed significant political and social transformations in Northern Europe. The rise of social democracy, the implementation of welfare states, and the pursuit of neutrality during the Cold War era shaped the region’s modern identity.
Cultural Tapestry
Northern Europe is a region of diverse cultural expressions, shaped by historical influences, geographical characteristics, and societal values.
- Language and Literature: The region boasts a rich linguistic landscape, with distinct languages spoken in each country. Scandinavian languages, including Swedish, Danish, Norwegian, and Icelandic, share common origins and influences. Finnish and Estonian, belonging to the Finno-Ugric language family, offer unique linguistic perspectives.
- Art and Design: Northern European art and design are renowned for their minimalist aesthetic, functionalism, and focus on natural elements. The region has produced iconic artists, designers, and architects who have influenced global trends in design and architecture.
- Music and Folklore: Northern European music is characterized by its folk traditions, contemporary pop music, and classical compositions. Folklore plays a significant role in preserving cultural heritage, with traditional songs, dances, and stories passed down through generations.
- Food and Cuisine: Northern European cuisine emphasizes fresh, seasonal ingredients, with a focus on seafood, meat, and dairy products. The region boasts culinary traditions that reflect its geographical location and historical influences, offering a diverse range of flavors and dishes.
Economic Significance
Northern Europe is a region of economic strength and innovation, with a strong emphasis on social welfare and sustainable development.
- High Standard of Living: Northern European countries consistently rank among the highest in the world in terms of quality of life, with strong social safety nets, high levels of education, and access to healthcare.
- Technological Advancements: The region is a hub of technological innovation, with companies and research institutions at the forefront of development in areas such as telecommunications, renewable energy, and biotechnology.
- Sustainable Development: Northern European countries are committed to sustainable development, promoting environmental conservation, renewable energy sources, and responsible resource management.
Challenges and Opportunities
While Northern Europe enjoys a strong reputation for its social welfare, economic prosperity, and cultural achievements, it faces challenges and opportunities that will shape its future.
- Demographic Shifts: The region faces an aging population and declining birth rates, posing challenges to maintaining social welfare systems and supporting economic growth.
- Climate Change: Climate change poses significant challenges to Northern Europe, with rising sea levels, melting glaciers, and extreme weather events impacting ecosystems, infrastructure, and economies.
- Globalization and Integration: The increasing interconnectedness of the global economy presents both opportunities and challenges for Northern Europe, requiring adaptation and collaboration to maintain competitiveness and address shared concerns.
FAQs
Q: What is the most populous country in Northern Europe?
A: Sweden is the most populous country in Northern Europe, with a population of over 10 million.
Q: What is the official language of Denmark?
A: The official language of Denmark is Danish.
Q: Which country in Northern Europe has the highest GDP per capita?
A: Norway boasts the highest GDP per capita in Northern Europe, driven by its oil and gas industry and strong social welfare system.
Q: What are some popular tourist destinations in Northern Europe?
A: Popular tourist destinations in Northern Europe include the fjords of Norway, the Icelandic glaciers, the Finnish lakes, and the historic cities of Copenhagen, Stockholm, and Helsinki.
Tips for Visiting Northern Europe
- Plan Ahead: Northern Europe experiences seasonal variations in weather and daylight hours, so it’s crucial to plan ahead and book accommodations and transportation in advance.
- Embrace the Outdoors: Northern Europe offers breathtaking natural landscapes, so take advantage of opportunities to explore the outdoors, whether hiking, kayaking, or simply enjoying the scenery.
- Respect Local Culture: Show respect for local customs and traditions, dress appropriately, and be mindful of noise levels, especially in residential areas.
- Learn Basic Phrases: While English is widely spoken in Northern Europe, learning a few basic phrases in the local language can enhance your travel experience and show respect for the local culture.
- Enjoy the Food and Drink: Northern European cuisine offers a unique culinary experience, so be sure to sample local specialties and enjoy the region’s renowned beers and spirits.
Conclusion
Northern Europe is a region of captivating landscapes, rich cultural heritage, and strong social welfare systems. Its unique blend of history, language, and tradition has shaped its distinctive identity and contributed significantly to global trends in art, design, and innovation. Understanding the individual characteristics of these countries provides valuable insight into the region’s complex tapestry and its global impact. As Northern Europe navigates the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century, its commitment to social progress, sustainable development, and cultural diversity will continue to shape its future and inspire the world.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Northern European Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to its Countries and Significance. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!