Navigating the Tapestry of Germanic Languages: A Geographic Exploration
Related Articles: Navigating the Tapestry of Germanic Languages: A Geographic Exploration
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Tapestry of Germanic Languages: A Geographic Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Tapestry of Germanic Languages: A Geographic Exploration
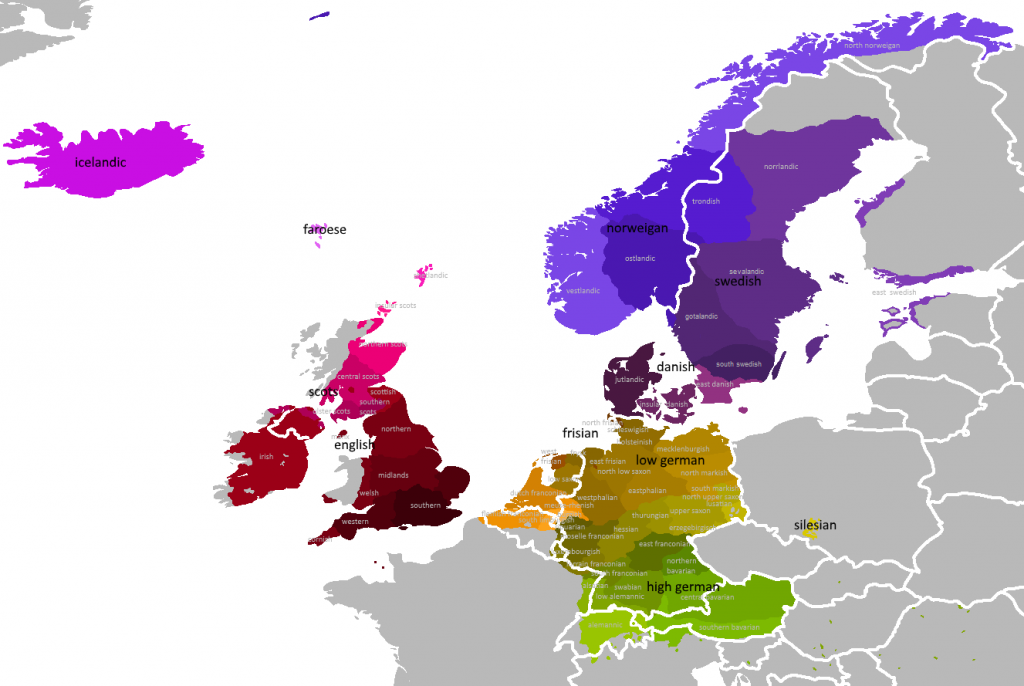
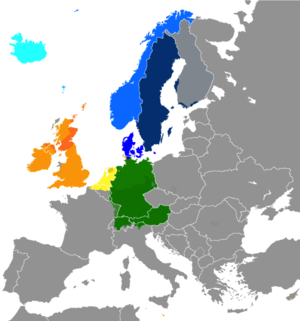
The Germanic languages, a branch of the Indo-European language family, paint a vibrant tapestry across Europe and beyond. Their geographical distribution, as depicted in a Germanic languages map, reveals not only the historical movement of peoples but also the intricate interplay of linguistic evolution, cultural exchange, and political influence. This map serves as a powerful tool for understanding the complex history and diversity of these languages, offering insights into their origins, relationships, and ongoing development.
A Journey Through Time and Space:
The Germanic languages map showcases the geographical spread of this language family, highlighting the areas where Germanic languages are spoken today. It traces the migration of Germanic tribes from their ancestral homeland in southern Scandinavia across Europe, resulting in the establishment of distinct language branches. The map reveals the following key areas:
- North Germanic: This branch encompasses the Scandinavian languages – Swedish, Norwegian, Danish, Icelandic, and Faroese – spoken in Scandinavia and the North Atlantic. These languages share a relatively close relationship, demonstrating a strong common heritage.
- West Germanic: This branch encompasses the languages spoken in Western Europe, including English, German, Dutch, Frisian, Afrikaans, and Yiddish. The map highlights the influence of Anglo-Saxon and Norman conquests on English, the spread of High German in Central Europe, and the unique development of Dutch and Frisian along the North Sea coast.
- East Germanic: This branch, once spoken in Eastern Europe, is now extinct. The map illustrates the former territory of Gothic, the only East Germanic language with a significant literary legacy, and highlights the impact of migration and cultural exchange on its decline.
Unveiling Linguistic Relationships:
Beyond geographical distribution, the Germanic languages map illustrates the intricate relationships between languages within the family. It depicts the degree of mutual intelligibility, showcasing how closely related languages are, allowing speakers to understand each other to varying degrees. For example, the map reveals the close connection between Dutch and German, while English, despite its Germanic roots, has diverged significantly due to its extensive borrowing from French and other languages.
The Importance of Historical Context:
The Germanic languages map provides a vital historical context, revealing the impact of historical events on language development. The map illustrates how the Roman Empire’s influence shaped the evolution of Western Germanic languages, while the Viking Age brought Norse influence to England and Ireland. It also highlights the impact of the Reformation and the rise of national identities on the standardization and codification of various Germanic languages.
Understanding Linguistic Diversity:
The Germanic languages map serves as a powerful tool for appreciating the rich linguistic diversity within the family. It showcases the unique features of each language, from the complex grammar of German to the subtle nuances of Swedish pronunciation. The map highlights the distinct dialects and regional variations within each language, emphasizing the vibrant linguistic landscape of Germanic-speaking regions.
FAQs by Germanic Languages Map:
1. What is the significance of the Germanic languages map?
The Germanic languages map provides a visual representation of the geographical distribution and historical development of this language family. It offers insights into the relationships between languages, the influence of historical events, and the linguistic diversity within the family.
2. What are the main branches of the Germanic languages?
The main branches are North Germanic, West Germanic, and East Germanic. North Germanic includes Scandinavian languages, West Germanic encompasses languages like English, German, and Dutch, and East Germanic, now extinct, was once spoken in Eastern Europe.
3. How does the map illustrate the impact of historical events on language development?
The map shows how migrations, conquests, and cultural exchange shaped the distribution and evolution of Germanic languages. It highlights the influence of the Roman Empire, the Viking Age, and the Reformation on language development.
4. What are some of the key features of the Germanic languages?
Key features include a common ancestor, shared vocabulary, and grammatical similarities. However, each language has developed unique characteristics, resulting in a diverse range of sounds, grammar, and vocabulary.
5. What are the benefits of studying the Germanic languages map?
Studying the map enhances our understanding of language evolution, historical relationships between cultures, and the impact of political and social factors on language development. It provides a valuable tool for linguistic research and cultural studies.
Tips by Germanic Languages Map:
- Explore the map in detail: Pay attention to the geographical distribution of each language branch and the areas where languages overlap.
- Consider historical context: Research the historical events that shaped the development and spread of each language.
- Compare and contrast languages: Identify similarities and differences between languages within the family, exploring their unique features.
- Explore dialects and regional variations: Delve into the diverse linguistic landscapes of Germanic-speaking regions, discovering the rich tapestry of dialects.
- Use the map as a starting point for further research: Explore the literature and resources available on specific languages and their histories.
Conclusion by Germanic Languages Map:
The Germanic languages map serves as a valuable tool for understanding the history, distribution, and relationships of this diverse language family. It offers a window into the fascinating journey of linguistic evolution, highlighting the interplay of historical events, cultural exchange, and linguistic adaptation. By exploring the map and delving deeper into the individual languages, we gain a richer appreciation for the vibrant tapestry of the Germanic language family and its enduring impact on the world.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Tapestry of Germanic Languages: A Geographic Exploration. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!