Navigating the Unseen: A Comprehensive Exploration of Air Quality Mapping
Related Articles: Navigating the Unseen: A Comprehensive Exploration of Air Quality Mapping
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Unseen: A Comprehensive Exploration of Air Quality Mapping. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Unseen: A Comprehensive Exploration of Air Quality Mapping
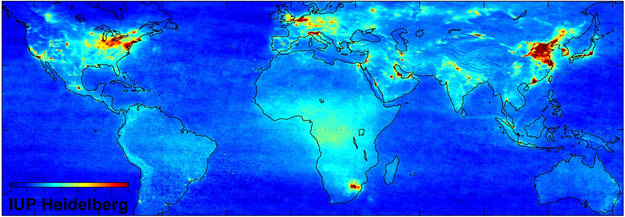
Air quality, an invisible yet potent force, profoundly impacts our health, environment, and overall well-being. Understanding its nuances and complexities is crucial for informed decision-making and proactive measures. This is where air quality mapping, a powerful tool leveraging data and technology, comes into play.
Air quality mapping, as the name suggests, involves creating visual representations of air quality data across geographical areas. These maps, often interactive and dynamic, provide a comprehensive overview of air pollution levels, identifying areas with high concentrations of pollutants and pinpointing potential sources of contamination.
The Foundation of Air Quality Mapping: Data and Technology
The foundation of effective air quality mapping lies in the robust collection and analysis of data. Several sources contribute to this data pool:
- Ground-based monitoring stations: These stations, strategically placed throughout a region, measure real-time air quality parameters like particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10), ozone (O3), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and sulfur dioxide (SO2).
- Satellite imagery: Satellites equipped with specialized sensors can capture data on atmospheric composition, providing a broader perspective on air quality across vast regions.
- Mobile sensors: Increasingly, mobile sensors mounted on vehicles or carried by individuals contribute to real-time air quality data collection, offering a more granular understanding of local pollution levels.
- Weather data: Meteorological information, including wind speed and direction, temperature, and humidity, plays a crucial role in understanding the dispersion and transport of pollutants.
This diverse array of data is then processed and analyzed using sophisticated algorithms and software, enabling the creation of informative and insightful air quality maps.
Types of Air Quality Maps: Unveiling the Diverse Applications
Air quality maps serve a multitude of purposes, each tailored to specific needs and applications. Here are some prominent types:
- Real-time air quality maps: These maps display current air quality conditions, providing immediate insights into pollution levels and hotspots. They are invaluable for public awareness, emergency response, and personal health decisions.
- Historical air quality maps: By analyzing historical data, these maps depict long-term trends in air quality, allowing for the identification of patterns, seasonal variations, and the impact of specific events on air quality.
- Predictive air quality maps: Leveraging advanced forecasting models and machine learning algorithms, these maps predict future air quality conditions, enabling proactive measures to mitigate potential health risks and environmental impacts.
- Source apportionment maps: These maps identify the sources of air pollution, attributing contributions from industrial emissions, traffic, residential heating, and other factors. This information is crucial for developing targeted pollution control strategies.
The Benefits of Air Quality Mapping: Empowering Action and Progress
Air quality mapping offers numerous benefits, contributing to a healthier environment and informed decision-making:
- Public health: By providing real-time and historical data on air quality, these maps empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health, such as reducing outdoor activities during periods of high pollution or wearing masks in polluted areas.
- Environmental protection: Air quality maps help identify areas with elevated pollution levels, allowing authorities to implement targeted interventions to reduce emissions and improve air quality.
- Policy and regulation: The data provided by air quality maps informs policy decisions, enabling the development of effective regulations to control air pollution sources and promote cleaner air.
- Urban planning: These maps assist urban planners in designing cities that prioritize air quality, promoting sustainable transportation, green spaces, and efficient energy consumption.
- Research and development: Air quality maps serve as valuable tools for researchers studying the impact of air pollution on human health, the environment, and climate change.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Air Quality Mapping
1. How accurate are air quality maps?
The accuracy of air quality maps depends on the quality and density of the data used to create them. While ground-based monitoring stations provide accurate localized data, satellite imagery offers a broader but less precise picture. Combining different data sources and advanced algorithms enhances map accuracy.
2. What are the limitations of air quality maps?
Air quality maps are subject to limitations, such as:
- Data availability: Data gaps and inconsistencies can affect the accuracy and completeness of the maps.
- Spatial resolution: The granularity of the data, influenced by the density of monitoring stations and satellite resolution, limits the ability to pinpoint localized pollution sources.
- Model limitations: Forecasting models used for predictive maps are subject to inherent uncertainties and may not always accurately reflect real-world conditions.
3. How can I access air quality maps?
Numerous websites and mobile applications offer access to real-time and historical air quality maps. Government agencies, environmental organizations, and private companies often provide these services.
4. What can I do with air quality map information?
You can use air quality map information to:
- Plan outdoor activities: Avoid areas with high pollution levels, especially during periods of high air quality risk.
- Reduce personal exposure: Minimize time spent outdoors during periods of high pollution and consider wearing masks in polluted areas.
- Support clean air initiatives: Advocate for policies and regulations aimed at reducing air pollution and promoting clean air technologies.
Tips for Utilizing Air Quality Maps Effectively
- Understand the limitations: Be aware of the data sources, spatial resolution, and model limitations of the maps you are using.
- Compare different maps: Explore multiple sources to gain a comprehensive understanding of air quality conditions.
- Consider local factors: Take into account local factors such as traffic patterns, industrial activity, and weather conditions that can influence air quality.
- Use maps for informed decision-making: Integrate air quality information into your daily routines and support initiatives that promote cleaner air.
Conclusion: Embracing Air Quality Mapping for a Healthier Future
Air quality mapping is a powerful tool for understanding and managing air pollution, fostering a healthier environment and improving public health. By leveraging data, technology, and informed decision-making, we can harness the insights provided by these maps to create a cleaner, safer, and more sustainable future for all.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Unseen: A Comprehensive Exploration of Air Quality Mapping. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!