Navigating the Western World: A Comprehensive Look at a Vital Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Western World: A Comprehensive Look at a Vital Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Western World: A Comprehensive Look at a Vital Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Western World: A Comprehensive Look at a Vital Map
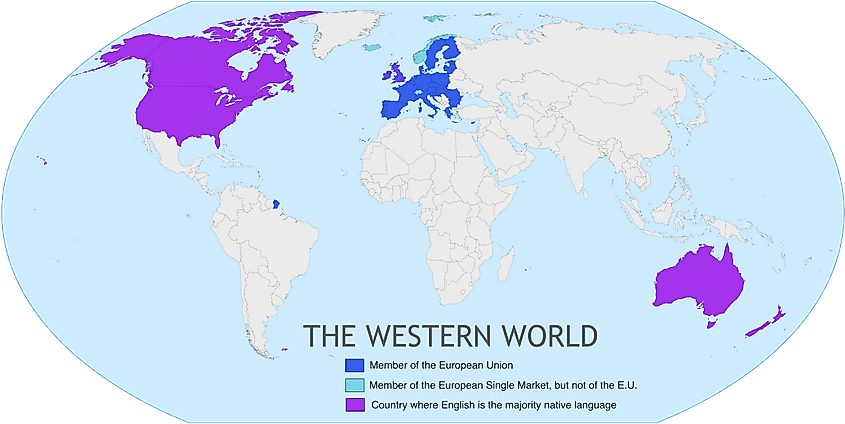
The Western World, a term encompassing the countries and cultures of Europe, North America, and sometimes Australia and New Zealand, is a vast and interconnected region. Understanding its geography, history, and cultural influences is crucial for navigating the complexities of the modern world. This article delves into the significance of the Western World Map, exploring its historical evolution, its key components, and its enduring influence on global affairs.
A Historical Journey: From Antiquity to Modernity
The concept of a Western World map has evolved over centuries, reflecting changing political, economic, and technological realities. Early maps, crafted by ancient Greek and Roman cartographers, primarily focused on the Mediterranean region, with Europe, North Africa, and the Middle East forming the core. These maps were rudimentary, often incorporating mythical creatures and fantastical lands, but they laid the foundation for future cartographic advancements.
The Renaissance ushered in a period of renewed exploration and scientific inquiry, leading to more accurate and detailed maps. Explorers like Christopher Columbus and Ferdinand Magellan embarked on daring voyages, expanding the known world and challenging existing geographical conceptions. This period saw the development of projection techniques, allowing for more precise representation of the Earth’s spherical surface on a flat map.
The Age of Enlightenment witnessed the rise of empirical observation and scientific rigor. The 18th and 19th centuries saw the creation of increasingly sophisticated maps, incorporating new discoveries and incorporating geographical features with greater accuracy. The invention of the printing press facilitated the widespread distribution of maps, making them accessible to a broader audience.
The Components of a Western World Map: A Visual Narrative
A Western World map provides a visual representation of the region’s diverse landscape, encompassing a range of geographical features:
- Continents: Europe, North America, and sometimes Australia and New Zealand are the core components of the Western World. These continents boast a vast array of terrains, from the snow-capped Alps to the rugged Rocky Mountains, from the fertile plains of the Midwest to the windswept coastlines of Scandinavia.
- Oceans: The Atlantic Ocean, separating Europe and North America, and the Pacific Ocean, bordering North America and Australia, play a crucial role in shaping the region’s history and culture. They have facilitated trade and migration, while also serving as natural barriers.
- Seas and Waterways: The Mediterranean Sea, the North Sea, the Baltic Sea, and the Great Lakes are significant bodies of water within the Western World, influencing its climate, economy, and cultural development.
- Major Cities: From London and Paris to New York and Los Angeles, the Western World is home to some of the world’s most influential cities, serving as centers of commerce, culture, and innovation.
- Political Boundaries: The Western World is comprised of numerous independent nations, each with its own unique history, culture, and political system. The map highlights these boundaries, offering a glimpse into the complex geopolitical landscape of the region.
Beyond the Map: Understanding the Western World’s Impact
The Western World Map is more than a mere geographical representation; it serves as a visual narrative, reflecting the region’s historical and cultural significance.
- Cultural Exchange and Diffusion: The map highlights the interconnectedness of the Western World, showcasing the flow of ideas, innovations, and cultural practices across borders. From the spread of Roman law to the influence of Renaissance art, the Western World has witnessed a dynamic exchange of cultural elements.
- Global Influence and Power: The Western World has historically exerted significant influence on global affairs, shaping political structures, economic systems, and cultural norms. The map underscores the region’s historical dominance, while also highlighting the rise of new powers and the changing dynamics of the global order.
- Challenges and Opportunities: The Western World faces a range of challenges, including economic inequality, environmental degradation, and political instability. The map provides a visual framework for understanding these issues and exploring potential solutions. It also highlights the region’s potential for innovation, collaboration, and positive change.
FAQs about the Western World Map
Q: Why is the Western World Map important?
A: The Western World Map is crucial for understanding the region’s geography, history, culture, and global influence. It provides a visual framework for navigating the complexities of the Western World and its interconnectedness with other parts of the globe.
Q: What are some of the limitations of the Western World Map?
A: Maps, by their nature, are simplifications of reality. The Western World Map can be criticized for its focus on European and North American perspectives, potentially overlooking the contributions of other regions and cultures. Additionally, it can be challenging to accurately represent the complexities of the region’s diverse populations and cultural identities on a single map.
Q: How does the Western World Map contribute to global understanding?
A: By providing a visual representation of the region’s geography, history, and culture, the Western World Map fosters a greater understanding of its role in global affairs. It helps to bridge cultural divides, promote dialogue, and encourage cooperation.
Tips for Using the Western World Map
- Consider the context: When interpreting the Western World Map, it’s crucial to consider the historical and cultural context surrounding the region.
- Engage with multiple perspectives: The Western World Map should be viewed alongside other maps and sources to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the region’s diversity and complexity.
- Embrace critical thinking: Don’t simply accept the map’s representation at face value. Engage in critical thinking, questioning assumptions and exploring alternative interpretations.
Conclusion: A Vital Tool for Navigating the Modern World
The Western World Map is a valuable tool for navigating the complexities of the modern world. It offers a visual representation of a region that has played a pivotal role in shaping global history, culture, and politics. While recognizing its limitations, the Western World Map remains an essential resource for understanding the region’s interconnectedness, its influence on global affairs, and the challenges and opportunities it faces in the 21st century. By engaging with the map thoughtfully and critically, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the Western World’s contributions to human civilization and its enduring role in shaping the future.
![]()


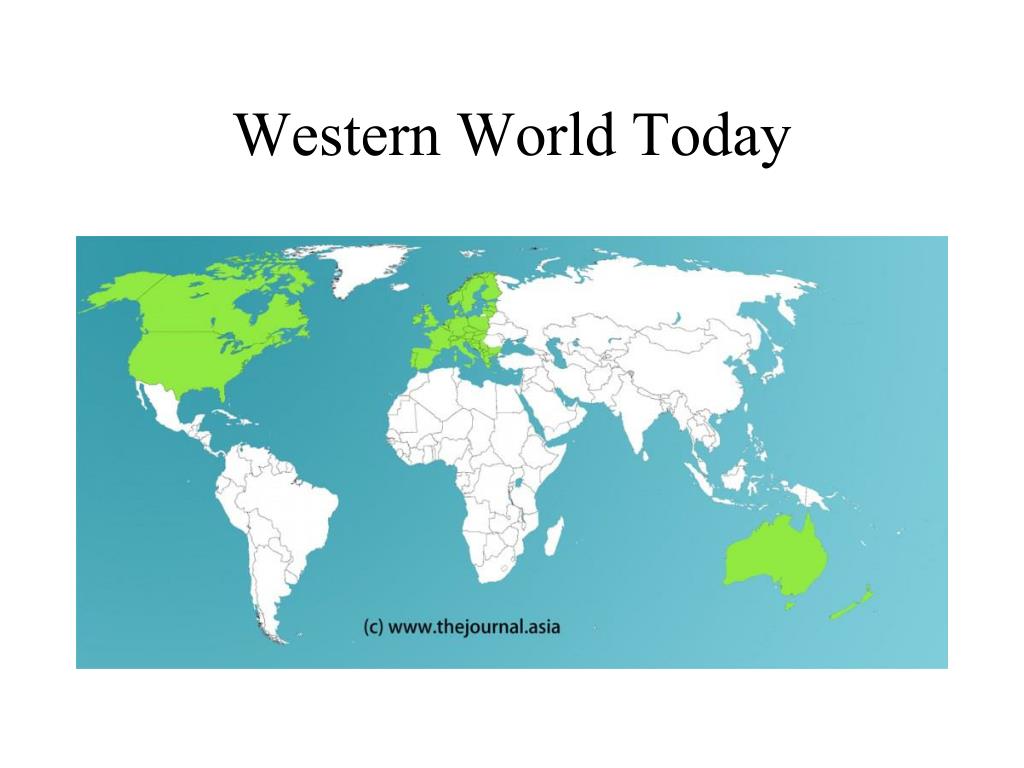



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Western World: A Comprehensive Look at a Vital Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!