Russia: A Geographic Colossus Spanning Two Continents
Related Articles: Russia: A Geographic Colossus Spanning Two Continents
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Russia: A Geographic Colossus Spanning Two Continents. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Russia: A Geographic Colossus Spanning Two Continents

Russia, the largest country in the world by land area, occupies a vast expanse across Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. Its geographical position has profoundly shaped its history, culture, and global influence. Understanding Russia’s location is crucial for grasping its geopolitical significance and the complexities of its interactions with other nations.
A Transcontinental Empire:
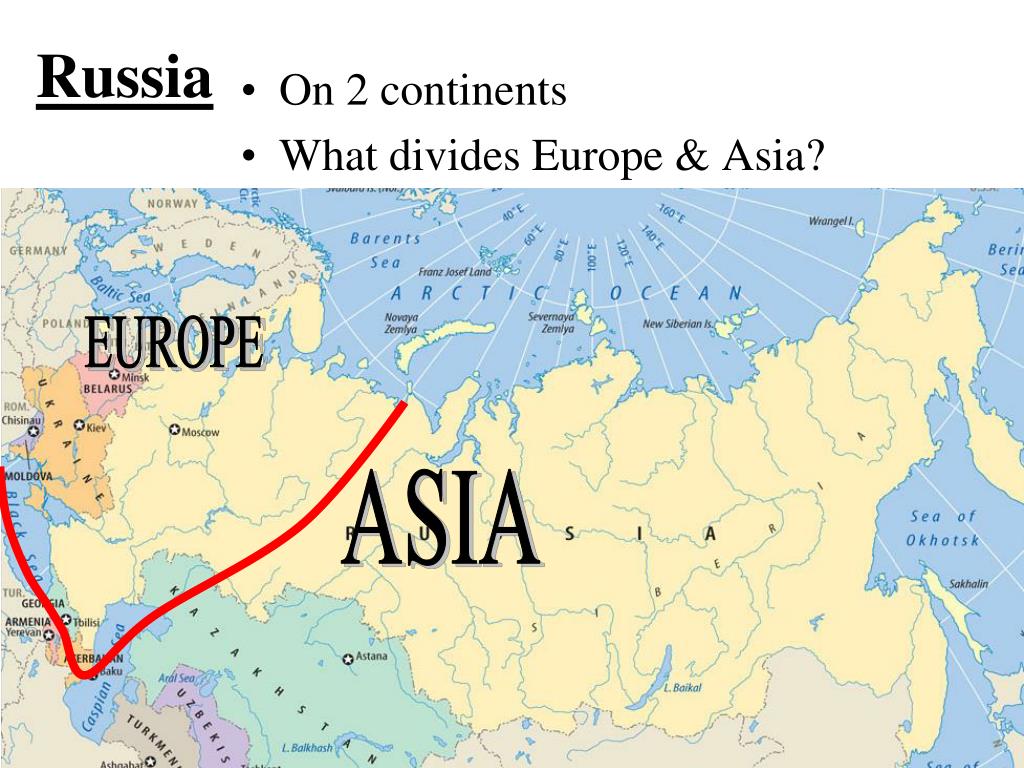
Russia’s unique geographical position is its defining characteristic. It stretches over 11 time zones, from the Baltic Sea in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east, encompassing a diverse range of landscapes and climates. This vast territory encompasses 17.1 million square kilometers, spanning two continents: Europe and Asia.
The European Frontier:
Russia’s European territory, known as European Russia, occupies the westernmost portion of the country. It includes the European Plain, a fertile and densely populated region that has been a historical crossroads for civilizations. Major cities like Moscow, St. Petersburg, and Nizhny Novgorod lie within this European heartland.
The Asian Expanse:
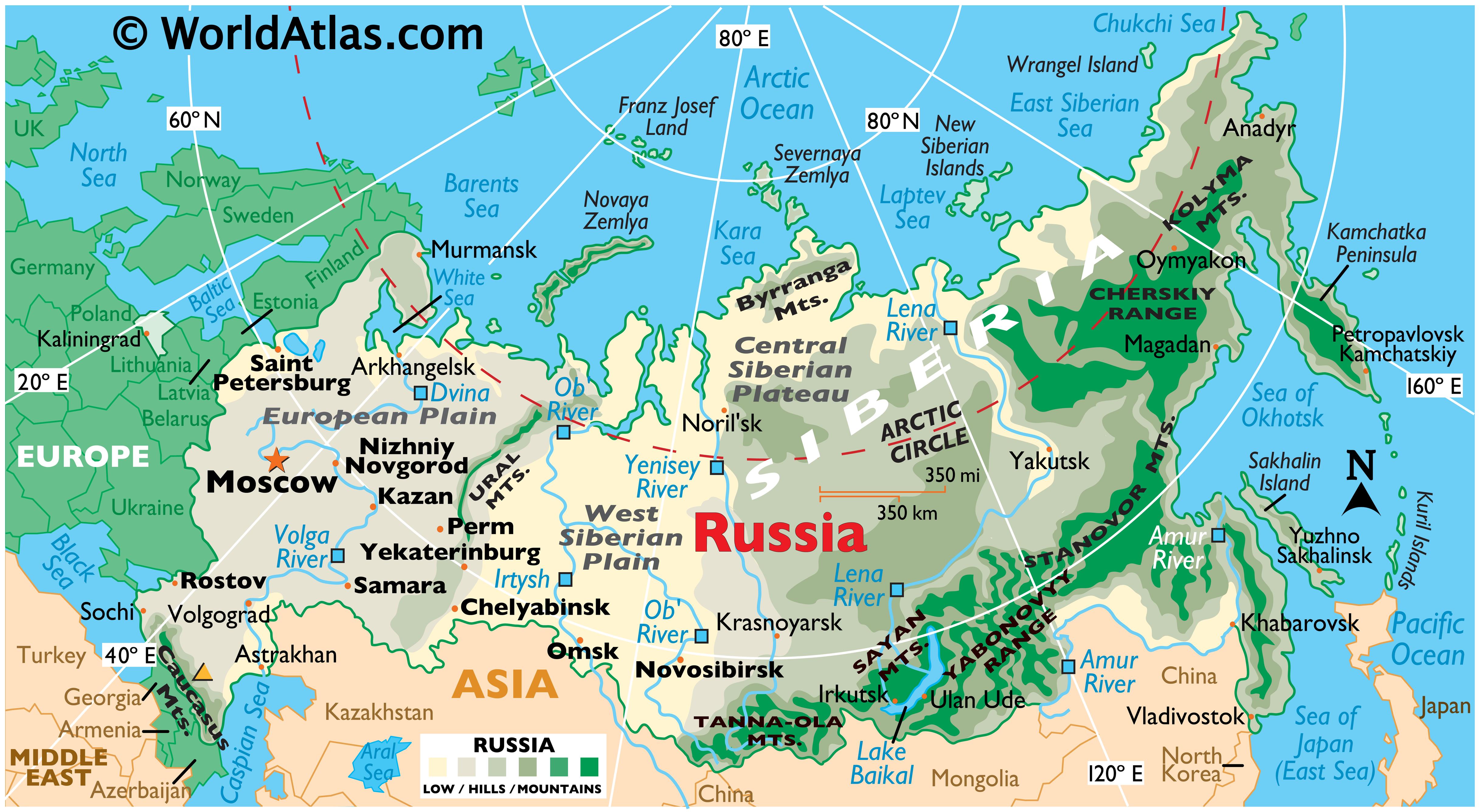
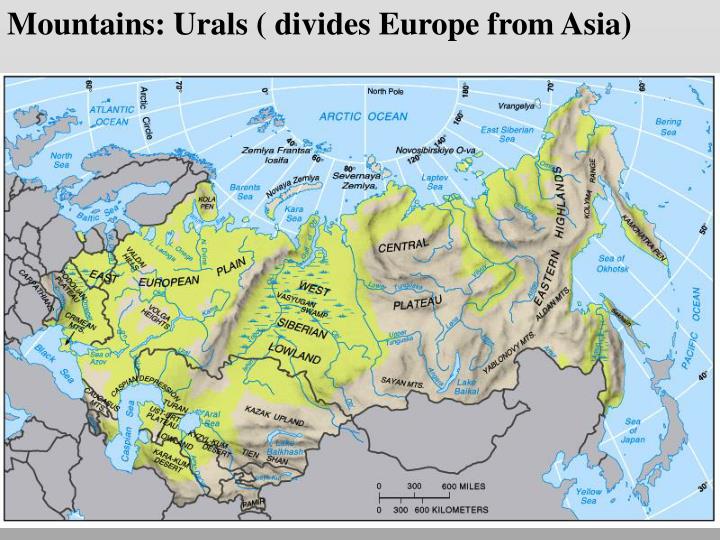
The majority of Russia’s territory lies in Asia, encompassing Siberia, the Ural Mountains, and the Russian Far East. Siberia, a vast and sparsely populated region, is characterized by its harsh climate, abundant natural resources, and sprawling forests. The Ural Mountains, a natural boundary between Europe and Asia, mark the eastern edge of European Russia. The Russian Far East, bordering China, North Korea, and Mongolia, is a strategically important region with access to the Pacific Ocean.
Key Geographic Features:
- The Ural Mountains: These mountains serve as a natural boundary between Europe and Asia and play a significant role in Russia’s geology and climate.
- The Siberian Plain: This vast plain, covering a significant portion of Siberia, is characterized by its harsh winters, permafrost, and abundant natural resources, including oil, gas, and timber.
- The Caucasus Mountains: This mountain range, located in southwestern Russia, is home to diverse ethnic groups and has played a significant role in regional conflicts.
- The Volga River: The longest river in Europe, the Volga flows through Russia’s heartland, serving as a vital transportation route and source of hydroelectric power.
- Lake Baikal: The world’s deepest and oldest freshwater lake, Lake Baikal is a natural wonder located in Siberia and is considered a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Strategic Importance:
Russia’s geographical position has profoundly influenced its history and global role. Its vast territory and diverse resources have made it a major player in global politics and economics. Its location bordering Europe and Asia has positioned it as a bridge between the two continents, enabling it to engage in complex and multifaceted relationships with its neighbors.
Geopolitical Considerations:
- Access to the Arctic: Russia’s northern coastline stretches along the Arctic Ocean, giving it access to significant natural resources and strategic shipping routes.
- Borders with Major Powers: Russia shares borders with 14 countries, including major powers like China, Ukraine, and Kazakhstan. These borders have been the source of historical tensions and conflicts.
- Control of Key Waterways: Russia controls important waterways like the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, which are vital for trade and regional security.
Economic Significance:
Russia’s vast territory contains a wealth of natural resources, including oil, gas, minerals, and timber. These resources have played a significant role in its economy, making it a major exporter of raw materials.
Cultural Diversity:
Russia’s vast territory has resulted in a diverse population and cultural landscape. From the traditional cultures of Siberia to the cosmopolitan atmosphere of Moscow, Russia is a nation of many ethnicities and languages.
FAQs:
- What is the population of Russia? Russia has a population of approximately 144 million people.
- What is the capital of Russia? The capital of Russia is Moscow.
- What is the official language of Russia? The official language of Russia is Russian.
- What are the main religions in Russia? The main religions in Russia are Eastern Orthodox Christianity, Islam, and Buddhism.
- What is the climate like in Russia? Russia has a wide range of climates, from the temperate climate of European Russia to the harsh winters of Siberia.
Tips for Understanding Russia’s Geography:
- Use a map: A map is an essential tool for understanding Russia’s vast territory and its relationship with neighboring countries.
- Explore different regions: Learn about the unique characteristics of each region, from the European heartland to the vast expanse of Siberia.
- Consider historical context: Russia’s history has been shaped by its geography, so understanding its past can shed light on its present.
- Study its natural resources: Russia’s abundant resources have played a significant role in its economic development and global influence.
Conclusion:
Russia’s geographical position is a defining factor in its history, culture, and global role. Its vast territory, diverse landscapes, and strategic location have made it a major player in global politics, economics, and culture. Understanding its geography is crucial for comprehending its complex relationships with other nations and its influence on the world stage.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Russia: A Geographic Colossus Spanning Two Continents. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!