Russia: A Vast Landmass Spanning Two Continents
Related Articles: Russia: A Vast Landmass Spanning Two Continents
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Russia: A Vast Landmass Spanning Two Continents. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Russia: A Vast Landmass Spanning Two Continents

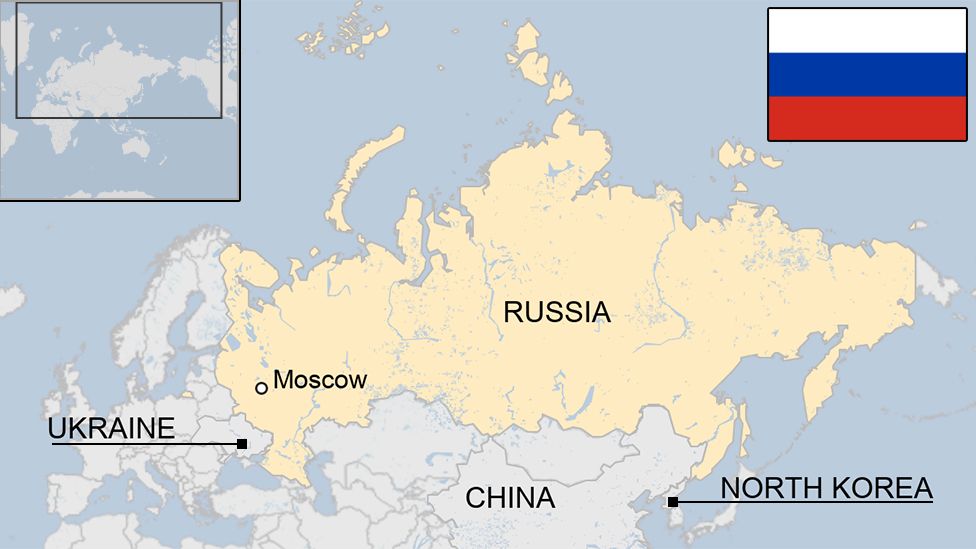
Russia, the largest country in the world by land area, occupies a geographically significant position, spanning vast swathes of Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. Its immense size and strategic location have historically shaped its political, economic, and cultural influence, making it a pivotal player on the global stage. Understanding Russia’s geographical position is crucial for comprehending its history, current affairs, and future prospects.
A Nation of Extremes: Geographical Characteristics
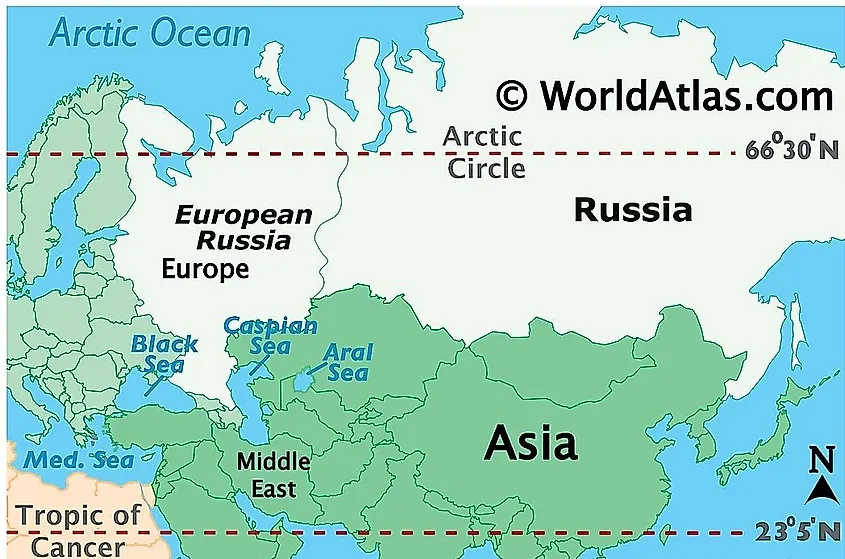
Russia’s vast territory encompasses diverse landscapes and climates, offering a unique tapestry of geographical features. Its western border stretches across Eastern Europe, while its eastern frontier extends across Northern Asia, bordering the Pacific Ocean. This transcontinental expanse encompasses a wide range of geographical features, including:
-
The European Plain: This vast, fertile plain stretches from the Baltic Sea to the Ural Mountains, forming the heartland of Russia’s European territory. It is home to major cities like Moscow and St. Petersburg and supports extensive agricultural production.
-
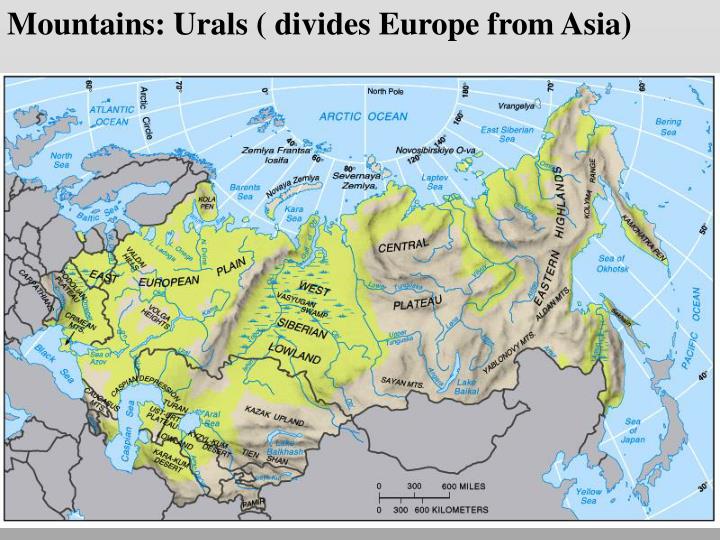
The Ural Mountains: This ancient mountain range serves as a natural boundary between Europe and Asia, marking the eastern edge of the European Plain. It is rich in mineral resources and plays a crucial role in Russia’s industrial development.
-
Siberia: This vast region, covering a significant portion of Northern Asia, is characterized by its harsh climate, vast forests, and abundant natural resources. It is home to diverse indigenous communities and plays a vital role in Russia’s energy sector.
-
The Caucasus Mountains: This mountain range, located in the southwestern corner of Russia, is a region of cultural diversity and strategic importance. It borders the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, connecting Russia to the Middle East and Central Asia.
-
The Far East: This region, situated in the easternmost part of Russia, borders the Pacific Ocean and encompasses the Kamchatka Peninsula and the Kuril Islands. It is known for its volcanic landscapes, rich marine resources, and strategic importance in the Asia-Pacific region.
Strategic Significance: A Land of Power and Influence
Russia’s geographical location has profoundly influenced its history and international relations. Its vast territory, encompassing a diverse range of natural resources, has made it a major geopolitical power. The following factors highlight the strategic significance of Russia’s location:
-
Bordering Key Regions: Russia shares borders with 14 countries, including major powers like China, Ukraine, and Turkey. This strategic proximity has shaped Russia’s foreign policy and its involvement in regional conflicts.
-
Control of Vital Waterways: Russia has access to major waterways like the Black Sea, the Baltic Sea, and the Arctic Ocean, granting it control over key shipping routes and strategic access to global markets.
-
Abundant Natural Resources: Russia possesses vast reserves of oil, natural gas, minerals, and timber, making it a global energy powerhouse and a key player in the global economy.
-
Military Strength: Russia’s vast territory and strategic location allow for the deployment of a formidable military force, making it a significant military power with the ability to project its influence across the globe.
Challenges and Opportunities: A Nation in Transition
Despite its strategic advantages, Russia faces several challenges related to its geographical position. These include:
-
Climate Change: Russia’s vast territory is particularly vulnerable to the effects of climate change, with rising temperatures, melting permafrost, and extreme weather events posing significant risks to its infrastructure, economy, and environment.
-
Infrastructure Development: Russia’s vast size and diverse geography pose significant challenges to infrastructure development, requiring substantial investments to connect its regions and facilitate economic growth.
-
Population Decline: Russia’s population has been declining for several years, driven by low birth rates and emigration. This demographic trend poses a significant challenge to its economic growth and long-term sustainability.
However, Russia’s vast territory also presents opportunities for economic development and global cooperation. These include:
-
Energy Exports: Russia’s vast reserves of oil and natural gas offer significant potential for energy exports, playing a vital role in global energy security.
-
Tourism Potential: Russia’s diverse landscapes, rich culture, and historical sites offer significant potential for tourism, attracting visitors from around the world.
-
Scientific Research: Russia’s vast territory and diverse ecosystems offer unique opportunities for scientific research, particularly in the fields of climate change, biodiversity, and resource management.
FAQs about Russia’s Location
Q: What are the major cities in Russia?
A: The most populous and important cities in Russia include:
- Moscow: The capital city, a major economic and cultural hub.
- St. Petersburg: Russia’s second-largest city, a historic port city with significant cultural significance.
- Novosibirsk: The third-largest city, a major industrial and scientific center in Siberia.
- Yekaterinburg: A significant industrial and cultural center in the Ural Mountains.
- Chelyabinsk: A major industrial city in the Ural Mountains.
- Krasnoyarsk: A major industrial and cultural center in Siberia.
- Vladivostok: A major port city in the Russian Far East.
Q: What are the major rivers in Russia?
A: Some of the most important rivers in Russia include:
- Volga: The longest river in Europe, flowing through the European Plain and playing a vital role in transportation and agriculture.
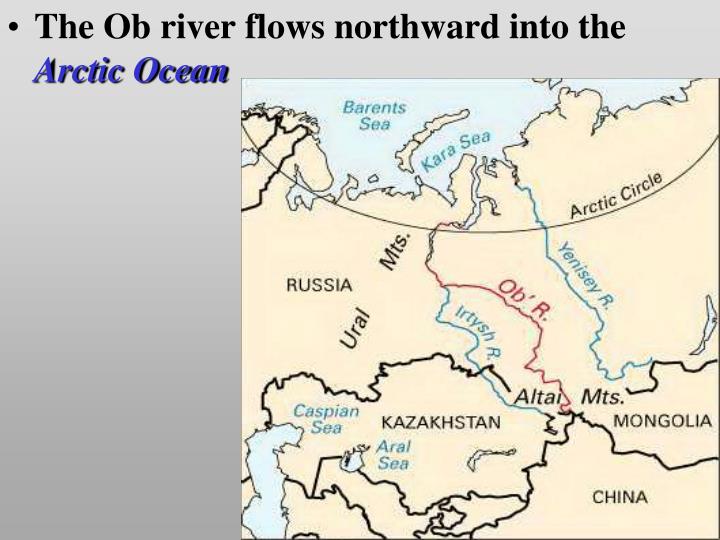
- Ob: A major river in Siberia, flowing through the West Siberian Plain and playing a vital role in transportation and energy production.
- Yenisei: A major river in Siberia, flowing through the Central Siberian Plateau and playing a vital role in transportation and energy production.
- Lena: A major river in Siberia, flowing through the Yakutia region and playing a vital role in transportation and resource extraction.
- Amur: A major river in the Russian Far East, flowing through the Amur River Basin and playing a vital role in transportation and resource extraction.
Q: What are the major mountains in Russia?
A: Russia’s major mountain ranges include:
- Ural Mountains: A natural boundary between Europe and Asia, rich in mineral resources.
- Caucasus Mountains: A strategically important mountain range in southwestern Russia, bordering the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea.
- Altai Mountains: A mountain range in southern Siberia, rich in mineral resources and home to diverse ecosystems.
- Sayan Mountains: A mountain range in southern Siberia, home to diverse ecosystems and mineral resources.
- Stanovoy Mountains: A mountain range in eastern Siberia, home to diverse ecosystems and mineral resources.
Tips for Understanding Russia’s Location
- Use maps and atlases: Visualizing Russia’s location on a map is essential for understanding its geographical extent and strategic importance.
- Study its neighbors: Understanding the countries bordering Russia provides insight into its geopolitical relationships and regional conflicts.
- Learn about its climate and landscapes: Understanding Russia’s diverse climate and landscapes helps to appreciate the challenges and opportunities associated with its vast territory.
- Explore its history and culture: Studying Russia’s history and culture provides a deeper understanding of its national identity and its role in the world.
Conclusion
Russia’s vast territory and strategic location have shaped its history, its current affairs, and its future prospects. Its geographical position has made it a pivotal player on the global stage, with significant influence over international relations, energy markets, and global security. Understanding Russia’s location is essential for comprehending its role in the world and for navigating the complex geopolitical landscape of the 21st century.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Russia: A Vast Landmass Spanning Two Continents. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!