Russia’s Enormous Reach: A Geographic Overview
Related Articles: Russia’s Enormous Reach: A Geographic Overview
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Russia’s Enormous Reach: A Geographic Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Russia’s Enormous Reach: A Geographic Overview

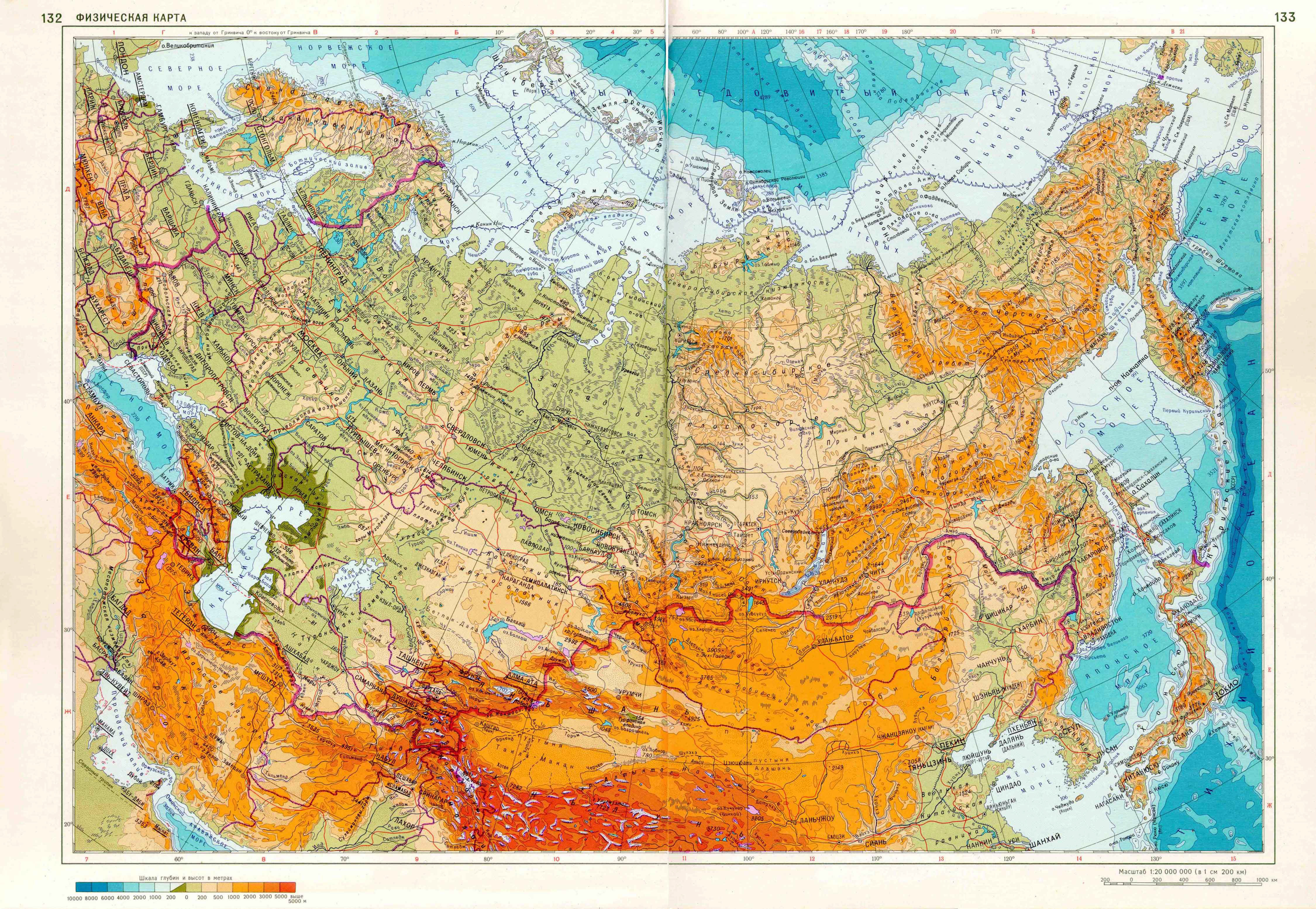
Russia, the largest country in the world by land area, spans a vast expanse of the Northern Hemisphere. Its geographic position, encompassing a diverse range of landscapes and climates, has profoundly shaped its history, culture, and global influence.
A Eurasian Giant:
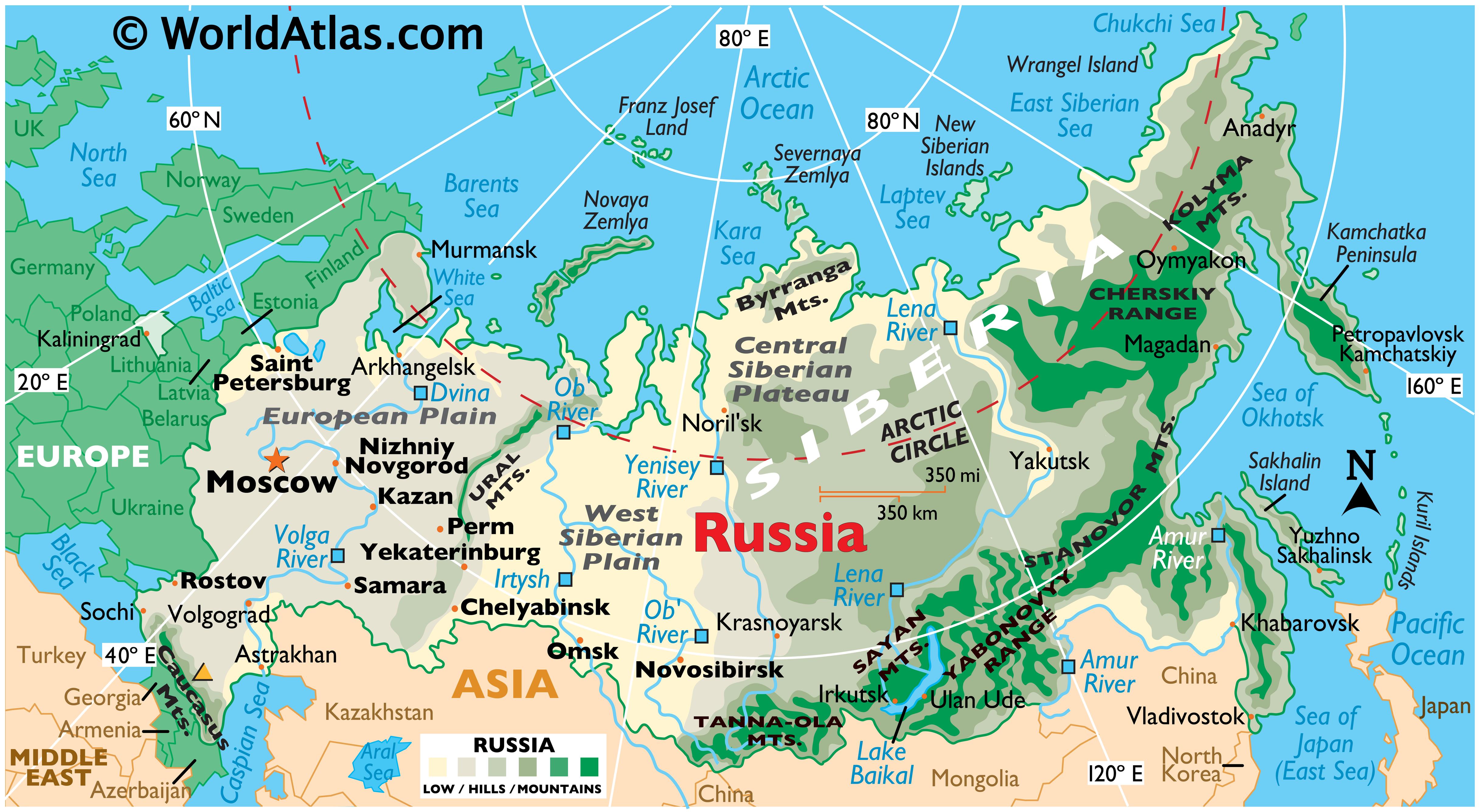
Russia’s territory extends across both Europe and Asia, with the Ural Mountains serving as a traditional dividing line. Its European portion, known as European Russia, encompasses the westernmost regions, including Moscow, the capital, and St. Petersburg, the cultural hub. The vast majority of the country, however, lies in Asia, known as Asian Russia. This region stretches eastward across Siberia, the Russian Far East, and numerous islands in the Arctic Ocean.
A Multi-Continental Presence:
This unique transcontinental location grants Russia access to both the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, as well as the Arctic Ocean. The country’s northern coastline extends along the Arctic Circle, giving it significant strategic and economic interests in the region. To the south, Russia shares borders with numerous countries, including Ukraine, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Mongolia, China, and North Korea.
A Diverse Landscape:
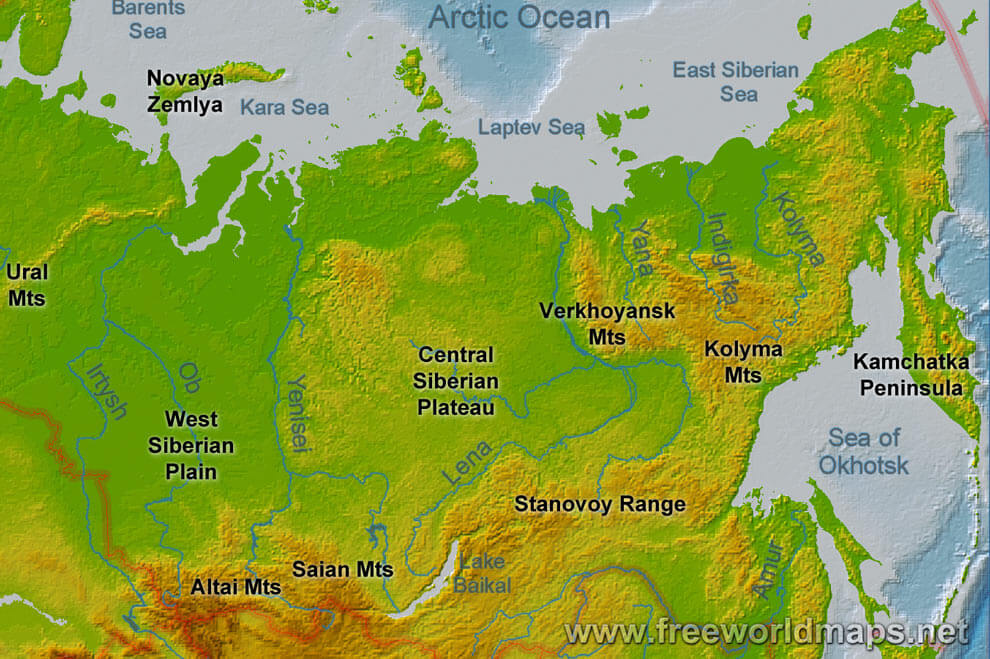
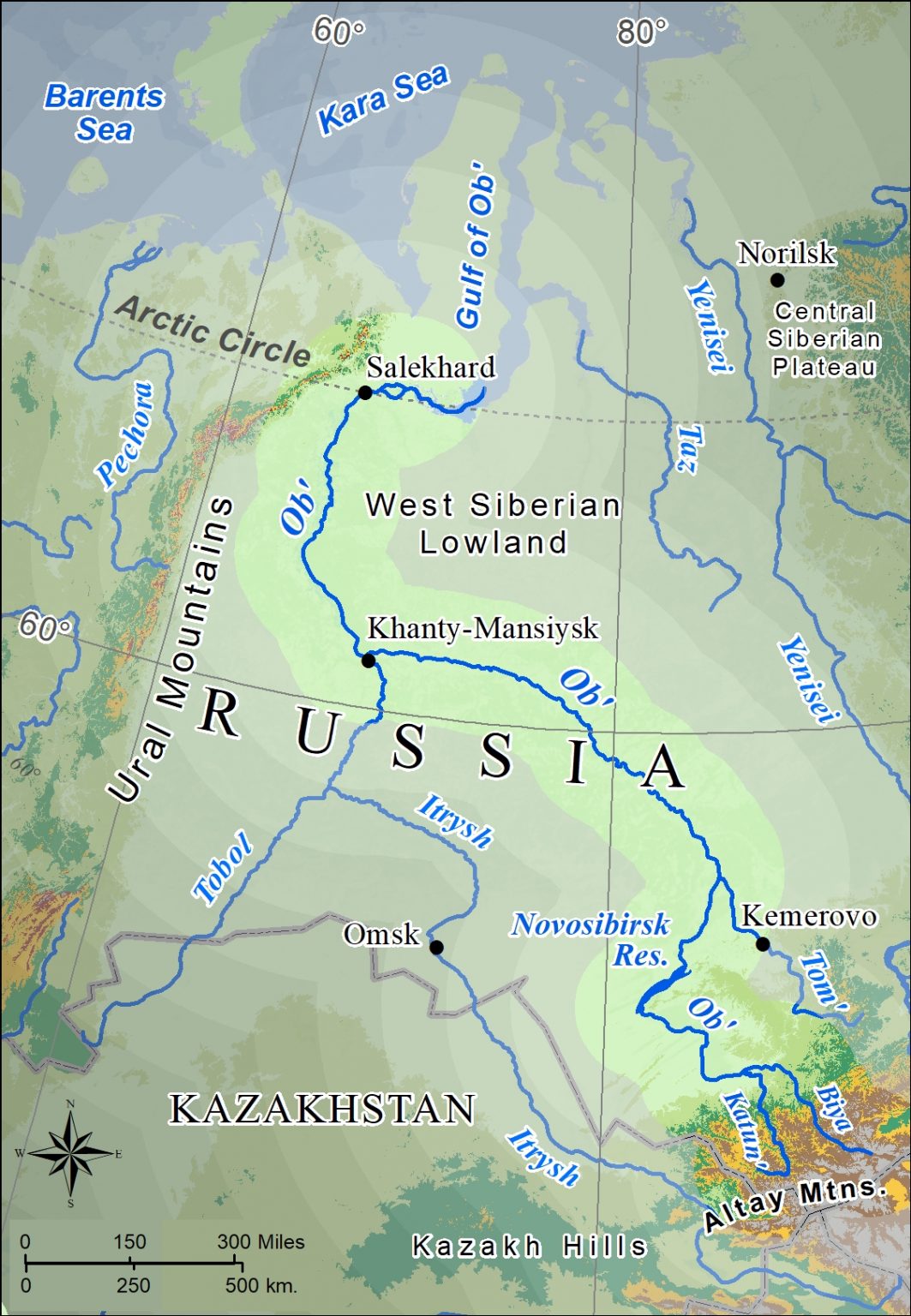
Russia’s vast size allows for a remarkable diversity of landscapes. From the rolling plains of the European part to the towering mountains of the Caucasus and the frozen tundra of the Arctic, the country boasts an array of natural wonders. The Ural Mountains, the Volga River, Lake Baikal (the deepest lake in the world), and the Siberian forests are just a few examples of the country’s geographic richness.
A Continent of Climates:
The expansive nature of Russia’s territory also results in a wide range of climates. The northern regions experience extremely cold winters and short, cool summers, while the southern regions enjoy warmer temperatures and longer growing seasons. This climatic variation has significant implications for agriculture, industry, and the distribution of population.
Strategic Importance:
Russia’s geographic location has historically played a crucial role in its strategic importance. Its vast territory acts as a buffer zone between Europe and Asia, while its access to key waterways has made it a significant maritime power. The country’s natural resources, particularly oil and gas, are also strategically important, contributing to its global influence.
Economic Significance:
Russia’s diverse landscape and rich natural resources have contributed to its economic development. The country is a major producer of oil, gas, metals, and timber, and its vast agricultural land supports a significant agricultural sector. The country’s industrial sector is also significant, with key industries including aerospace, defense, and energy.
Cultural Significance:
Russia’s geographic location has had a profound impact on its culture. The country’s diverse landscape has inspired its literature, music, and art, while its history has shaped its cultural identity. The country’s vast territory has also fostered regional differences in culture, language, and traditions.
FAQs:
Q: What are the geographical features of Russia?
A: Russia is characterized by a diverse landscape, including vast plains, towering mountains, frozen tundras, and extensive forests. Key geographical features include the Ural Mountains, the Volga River, Lake Baikal, and the Siberian forests.
Q: What are the major cities in Russia?
A: Moscow, the capital, and St. Petersburg, the cultural hub, are the two largest and most important cities in Russia. Other major cities include Novosibirsk, Yekaterinburg, Nizhny Novgorod, and Chelyabinsk.
Q: What are the major climate zones in Russia?
A: Russia’s climate varies significantly across its vast territory. The northern regions experience a subarctic climate with extremely cold winters and short, cool summers. The southern regions enjoy a temperate climate with warmer temperatures and longer growing seasons.
Q: What are the main natural resources of Russia?
A: Russia is rich in natural resources, including oil, gas, metals, timber, and minerals. These resources play a significant role in the country’s economy and global influence.
Q: What are the main industries in Russia?
A: Russia’s major industries include oil and gas production, aerospace, defense, energy, and agriculture. The country is also a major producer of metals and timber.
Tips:
- Use a physical map: A physical map will help you visualize the size and shape of Russia, as well as its major geographical features.
- Study a political map: A political map will show you the borders of Russia and its neighboring countries, as well as the location of major cities.
- Research the history of Russia: Understanding the historical context of Russia’s geography will help you appreciate its current importance and influence.
- Consider the impact of climate: Russia’s diverse climate plays a significant role in its economy, culture, and way of life.
- Explore Russia’s natural wonders: From the Ural Mountains to Lake Baikal, Russia offers a wide range of natural wonders to explore.
Conclusion:
Russia’s geographic location has shaped its history, culture, and global influence. Its vast territory, diverse landscape, and rich natural resources have made it a significant player on the world stage. Understanding the country’s geography is crucial for appreciating its complexity and importance in the global context.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Russia’s Enormous Reach: A Geographic Overview. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!