The Great Salt Lake: A Vital Ecosystem Facing Challenges
Related Articles: The Great Salt Lake: A Vital Ecosystem Facing Challenges
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Great Salt Lake: A Vital Ecosystem Facing Challenges. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Great Salt Lake: A Vital Ecosystem Facing Challenges

The Great Salt Lake, a vast inland body of water nestled in the heart of Utah, is a unique and crucial ecosystem within the western United States. Its shimmering surface, often mistaken for a distant sea, reflects the intricate interplay of nature and human activity. This article delves into the geographical significance, ecological importance, and the pressing challenges facing the Great Salt Lake, highlighting its vital role in the regional landscape.
A Geographical Perspective:
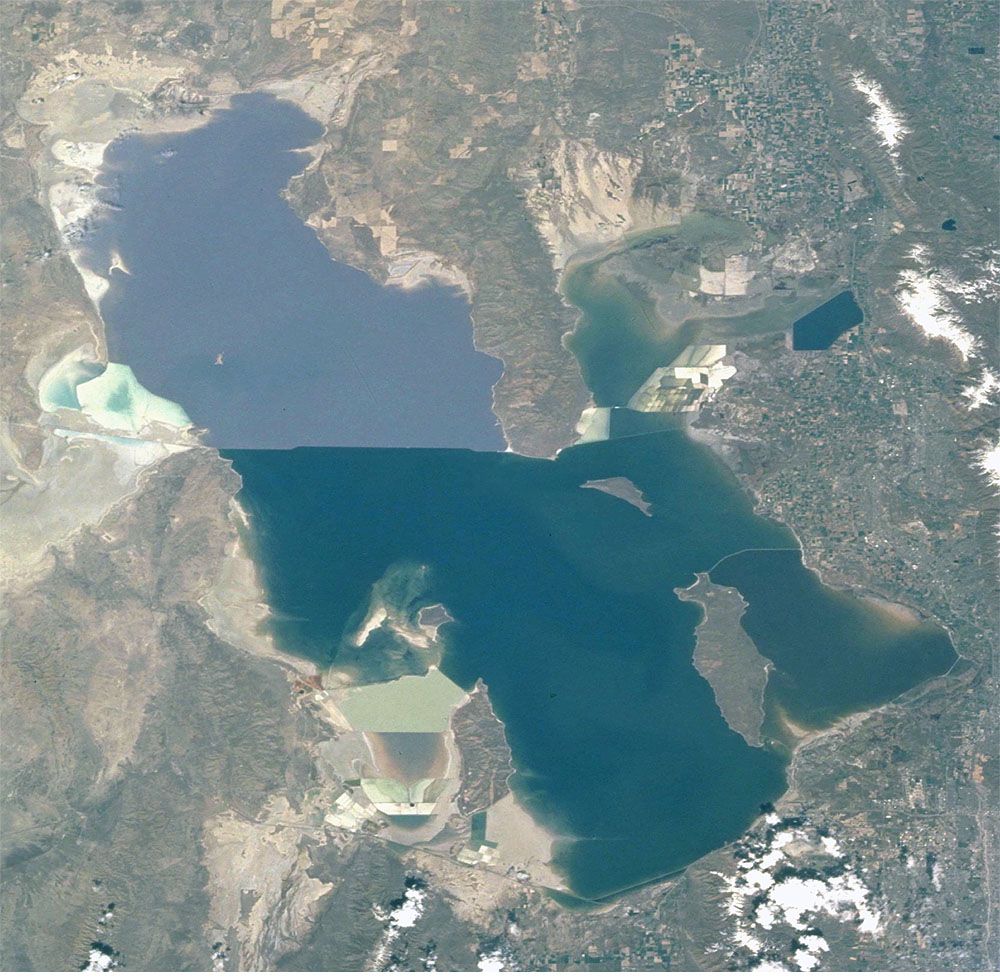
The Great Salt Lake, situated in the western United States, is the largest saltwater lake in the Western Hemisphere and the largest natural lake west of the Mississippi River. It occupies a vast endorheic basin, meaning it has no outlet to the ocean. This unique feature contributes to its high salinity, which is approximately five times greater than that of the ocean.
The lake is divided into two major sections: the northern arm, known as the "North Arm," and the southern arm, known as the "South Arm," connected by a narrow strait. The North Arm, deeper and with a larger surface area, is often dominated by brine shrimp, a crucial food source for migratory birds. The South Arm, shallower and characterized by fluctuating water levels, supports a diverse ecosystem of brine flies, algae, and aquatic invertebrates.
Ecological Significance:
The Great Salt Lake serves as a vital habitat for a diverse array of wildlife, making it a critical part of the regional ecosystem. It is a crucial stopover point for millions of migratory birds, including the American White Pelican, the California Gull, and the Eared Grebe, providing vital sustenance and resting grounds during their long journeys.
The lake’s unique salinity also supports a specialized ecosystem, including the brine shrimp, a key food source for many birds and fish. This tiny crustacean, adapted to thrive in high salinity, plays a crucial role in the lake’s food web. Additionally, the lake’s unique chemical composition supports a variety of algae and bacteria, further enriching its biodiversity.
Human Impact and Challenges:
The Great Salt Lake’s ecological health is increasingly threatened by human activities, primarily water diversion and population growth. The lake’s water levels have been steadily declining for decades due to increased water use for agriculture, urban development, and industrial purposes. This decline has severe consequences for the lake’s ecosystem, impacting its water quality, salinity, and the survival of its inhabitants.
The shrinking lakebed exposes vast areas of dry, alkaline dust, which is easily blown by the wind, posing health risks to nearby communities. The dust contains high levels of arsenic and other toxic substances, contributing to respiratory problems and other health issues.
Economic and Cultural Importance:
The Great Salt Lake holds significant economic and cultural value. It supports a thriving brine shrimp industry, providing a valuable source of food for fish and other animals, as well as a key ingredient in aquaculture and other industries. The lake also attracts millions of visitors annually, generating significant revenue through tourism and recreation.
The Great Salt Lake holds deep cultural significance for the indigenous tribes of the region, particularly the Ute, Shoshone, and Paiute tribes. These tribes have a long history of dependence on the lake for sustenance, spiritual connection, and cultural identity. The shrinking lake poses a significant threat to their traditions and way of life.
FAQs:
Q: What is the primary cause of the Great Salt Lake’s declining water levels?
A: The primary cause is the diversion of water from its tributaries for agricultural, urban, and industrial purposes. This increased water use has significantly reduced the lake’s inflow, leading to its shrinking size.
Q: What are the environmental consequences of the Great Salt Lake’s shrinking size?
A: The shrinking size has several adverse consequences, including increased salinity, reduced water quality, and habitat loss for numerous species. It also leads to the exposure of dry lakebed, which generates toxic dust, posing health risks to surrounding communities.
Q: What are the economic impacts of the shrinking Great Salt Lake?
A: The shrinking lake negatively impacts the brine shrimp industry, a significant economic contributor to the region. It also affects tourism and recreation, reducing visitor numbers and revenue.
Q: What are some potential solutions to address the Great Salt Lake’s challenges?
A: Solutions include water conservation measures, water-use efficiency improvements, and the restoration of natural water flows to the lake. These measures require collaboration between government agencies, industries, and communities.
Tips:
- Conserve water: Reduce water use in homes and gardens, and support water conservation initiatives.
- Support sustainable agriculture: Advocate for water-efficient agricultural practices and support local farmers who prioritize water conservation.
- Engage in community efforts: Participate in local initiatives aimed at restoring the Great Salt Lake and supporting its ecosystem.
- Advocate for policy changes: Support policies that promote water conservation and prioritize the health of the Great Salt Lake.
Conclusion:
The Great Salt Lake, a vital ecosystem facing critical challenges, requires immediate and sustained attention. Its ecological importance, economic benefits, and cultural significance underscore the need for a collaborative approach to address its shrinking size and the threats it faces. Conservation efforts, water management strategies, and community engagement are essential to ensure the lake’s long-term health and the well-being of the diverse species and communities that depend on it. The future of the Great Salt Lake hinges on our collective commitment to its preservation.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Great Salt Lake: A Vital Ecosystem Facing Challenges. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!