The Iberian Peninsula: A Crossroads of History and Culture
Related Articles: The Iberian Peninsula: A Crossroads of History and Culture
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Iberian Peninsula: A Crossroads of History and Culture. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Iberian Peninsula: A Crossroads of History and Culture

The Iberian Peninsula, a geographically distinct landmass jutting out into the Atlantic Ocean, holds a significant place in the world’s history and cultural tapestry. It is a region of diverse landscapes, rich history, and vibrant cultures, making it a captivating destination for travelers and a subject of enduring fascination for scholars.
A Geographical Overview:
The Iberian Peninsula, located in southwestern Europe, is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the west and north, the Mediterranean Sea to the east, and the Strait of Gibraltar to the south. It encompasses the countries of Spain, Portugal, Andorra, and a small portion of southern France. The peninsula’s distinctive shape, resembling a boot, is a result of its geological history, marked by the collision of the Eurasian and African tectonic plates.
The peninsula’s diverse topography is a defining characteristic. From the snow-capped peaks of the Pyrenees Mountains in the north to the sun-drenched plains of Andalusia in the south, the Iberian Peninsula offers a variety of landscapes. The rugged mountains of the Sierra Nevada in the south, the rolling hills of Extremadura in the west, and the fertile plains of the Ebro River Valley in the northeast contribute to the peninsula’s remarkable biodiversity.
A Tapestry of Cultures:
The Iberian Peninsula has been a crossroads of cultures for millennia, attracting various civilizations and leaving its mark on the region’s history and identity. The legacy of the ancient Romans, who established their presence in the 3rd century BC, is evident in the peninsula’s architectural marvels, including the impressive Roman aqueducts and amphitheaters. The Visigoths, a Germanic tribe, established their kingdom in the 5th century AD, influencing the peninsula’s legal and cultural framework.
The arrival of the Moors in the 8th century AD marked a significant turning point. Islamic rule, spanning over seven centuries, left an enduring legacy on the peninsula’s architecture, art, and language. The Moorish influence is visible in the majestic Alhambra palace in Granada, the intricate tilework of mosques, and the introduction of Arabic words into the Spanish and Portuguese languages.
Following the Reconquista, a long process of Christian reconquest, the Iberian Peninsula witnessed the rise of powerful kingdoms, including Castile, Leon, and Aragon. These kingdoms played a pivotal role in the exploration of the New World, leading to the establishment of vast colonial empires in the Americas.
Economic Significance:
The Iberian Peninsula holds significant economic importance, fueled by its diverse industries and strategic location. Spain and Portugal, the two largest countries on the peninsula, are members of the European Union and have developed robust economies. Tourism plays a crucial role in the region’s economic prosperity, with Spain being a major tourist destination known for its beaches, historical sites, and vibrant culture.
The peninsula is also rich in natural resources, including minerals, agricultural products, and renewable energy sources. Spain is a leading producer of olive oil, wine, and citrus fruits, while Portugal is known for its cork production and fishing industry. The peninsula’s strategic location at the crossroads of Europe, Africa, and the Americas makes it a crucial hub for international trade and transportation.
Cultural and Artistic Heritage:
The Iberian Peninsula is a treasure trove of cultural and artistic heritage. From the ancient Roman ruins of Mérida to the architectural marvels of the Alhambra, the peninsula boasts a wealth of historical sites that attract visitors from around the world. The region is also renowned for its vibrant arts scene, encompassing painting, sculpture, literature, and music.
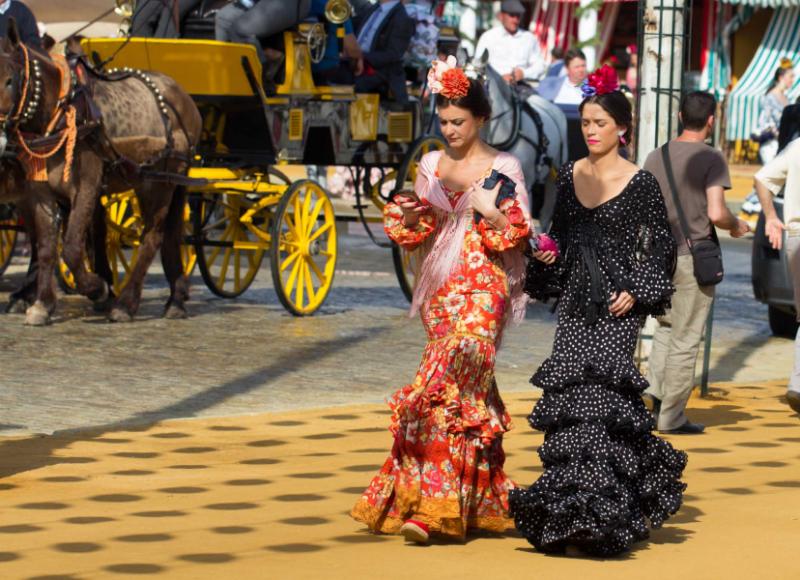
Spain is home to renowned artists like Pablo Picasso, Salvador Dalí, and Joan Miró, while Portugal has produced celebrated writers like Fernando Pessoa and José Saramago. The peninsula’s diverse musical traditions include flamenco, a passionate dance form originating in Andalusia, and fado, a melancholic musical style originating in Portugal.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Despite its rich history and economic potential, the Iberian Peninsula faces a number of challenges. Economic disparities between regions, unemployment, and a growing dependence on tourism are some of the key issues that require attention. The peninsula also faces challenges related to climate change, including drought, desertification, and the impact on agricultural production.
However, the Iberian Peninsula also presents numerous opportunities for growth and development. The region’s strategic location, its diverse industries, and its skilled workforce offer potential for economic diversification and innovation. The peninsula is also well-positioned to become a leader in renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, and green technologies.
FAQs about the Iberian Peninsula:
1. What are the main languages spoken in the Iberian Peninsula?
The main languages spoken in the Iberian Peninsula are Spanish, Portuguese, Catalan, Galician, and Basque. Spanish is the official language of Spain and is widely spoken throughout the peninsula. Portuguese is the official language of Portugal and is also spoken in parts of Spain. Catalan is spoken in Catalonia, a region in northeastern Spain. Galician is spoken in Galicia, a region in northwestern Spain. Basque is a language isolate, meaning it is not related to any other known language, and is spoken in the Basque Country, a region that spans parts of Spain and France.
2. What are some of the most popular tourist destinations in the Iberian Peninsula?
The Iberian Peninsula is home to a variety of popular tourist destinations, including:
- Barcelona, Spain: Renowned for its modernist architecture, vibrant nightlife, and beautiful beaches.
- Madrid, Spain: The capital of Spain, known for its museums, art galleries, and bustling atmosphere.
- Lisbon, Portugal: A charming city with historic neighborhoods, colorful architecture, and stunning views of the Tagus River.
- Seville, Spain: A vibrant city with a rich Moorish heritage, known for its flamenco dancing, bullfighting, and beautiful plazas.
- Granada, Spain: Home to the Alhambra, a stunning palace complex with breathtaking views of the city.
3. What are some of the main industries in the Iberian Peninsula?
The Iberian Peninsula has a diverse economy with industries ranging from tourism to manufacturing to agriculture. Some of the main industries include:
- Tourism: A major contributor to the region’s economy, especially in Spain and Portugal.
- Agriculture: The peninsula is a major producer of olive oil, wine, citrus fruits, and other agricultural products.
- Manufacturing: Spain and Portugal have a strong manufacturing sector, producing a wide range of goods, including automobiles, electronics, and textiles.
- Renewable energy: The peninsula is well-positioned to become a leader in renewable energy, with abundant solar and wind resources.
Tips for Visiting the Iberian Peninsula:
- Plan your trip in advance: The Iberian Peninsula offers a wealth of destinations, so it’s important to plan your itinerary in advance.
- Learn a few basic phrases in Spanish or Portuguese: This will make it easier to communicate with locals and enhance your travel experience.
- Sample the local cuisine: The Iberian Peninsula is known for its delicious cuisine, so be sure to try some of the local specialties.
- Explore the region’s history and culture: The peninsula is rich in history and culture, so take the time to visit some of the region’s many historical sites and museums.
- Enjoy the outdoors: The peninsula offers a variety of outdoor activities, from hiking and biking to skiing and surfing.
Conclusion:
The Iberian Peninsula, a land of contrasts and captivating beauty, offers a unique blend of history, culture, and natural wonders. From the majestic mountains of the Pyrenees to the sun-kissed beaches of Andalusia, the peninsula is a destination that promises to enchant and inspire. Its rich history, diverse cultures, and strategic location make it a region of enduring significance, shaping the world’s cultural landscape and contributing to its economic prosperity. As the peninsula continues to navigate its challenges and embrace its opportunities, it is poised to play an even more prominent role in the global stage.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Iberian Peninsula: A Crossroads of History and Culture. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!