The Indigenous Legacy of Texas: A Journey Through Diverse Tribes and Cultures
Related Articles: The Indigenous Legacy of Texas: A Journey Through Diverse Tribes and Cultures
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Indigenous Legacy of Texas: A Journey Through Diverse Tribes and Cultures. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Indigenous Legacy of Texas: A Journey Through Diverse Tribes and Cultures

Texas, a state renowned for its vast landscapes and vibrant culture, is also home to a rich and multifaceted indigenous history. For millennia, numerous Native American tribes have inhabited this land, leaving an indelible mark on its geography, traditions, and identity. This article explores the diverse tapestry of Texas’s indigenous heritage, offering a glimpse into the unique cultures, languages, and legacies of the tribes who have called this land home.
A Tapestry of Tribes:
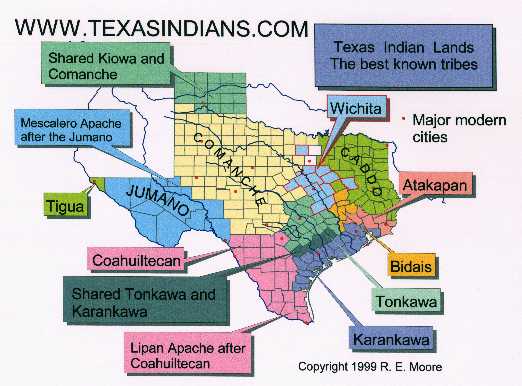
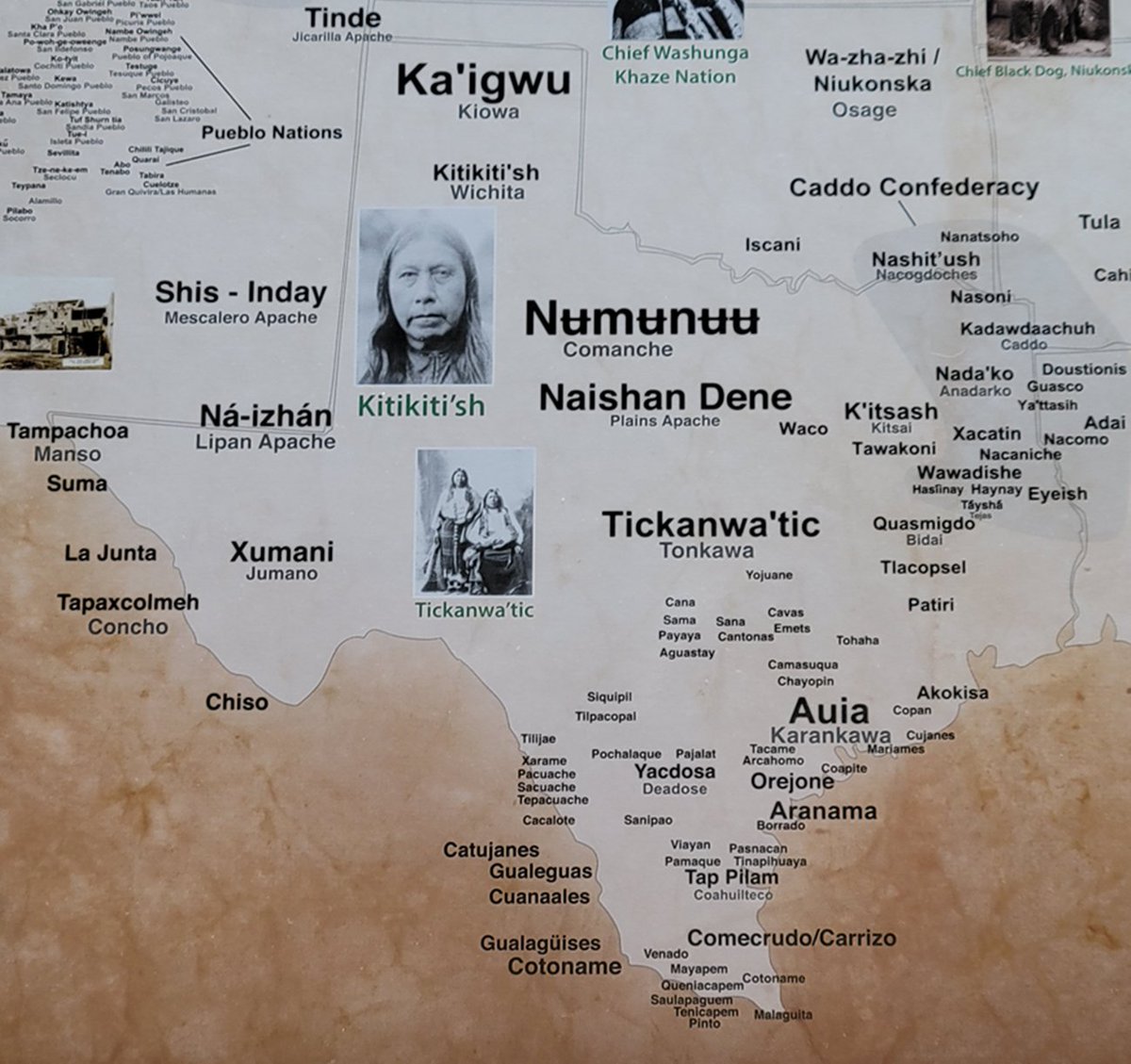
Texas, with its diverse ecosystems ranging from the arid plains to the lush coastal regions, has supported a diverse array of indigenous cultures. Before European arrival, the state was home to over 50 distinct tribes, each with its own language, customs, and way of life. These tribes can be broadly categorized into language families, reflecting their shared ancestral roots and cultural connections:
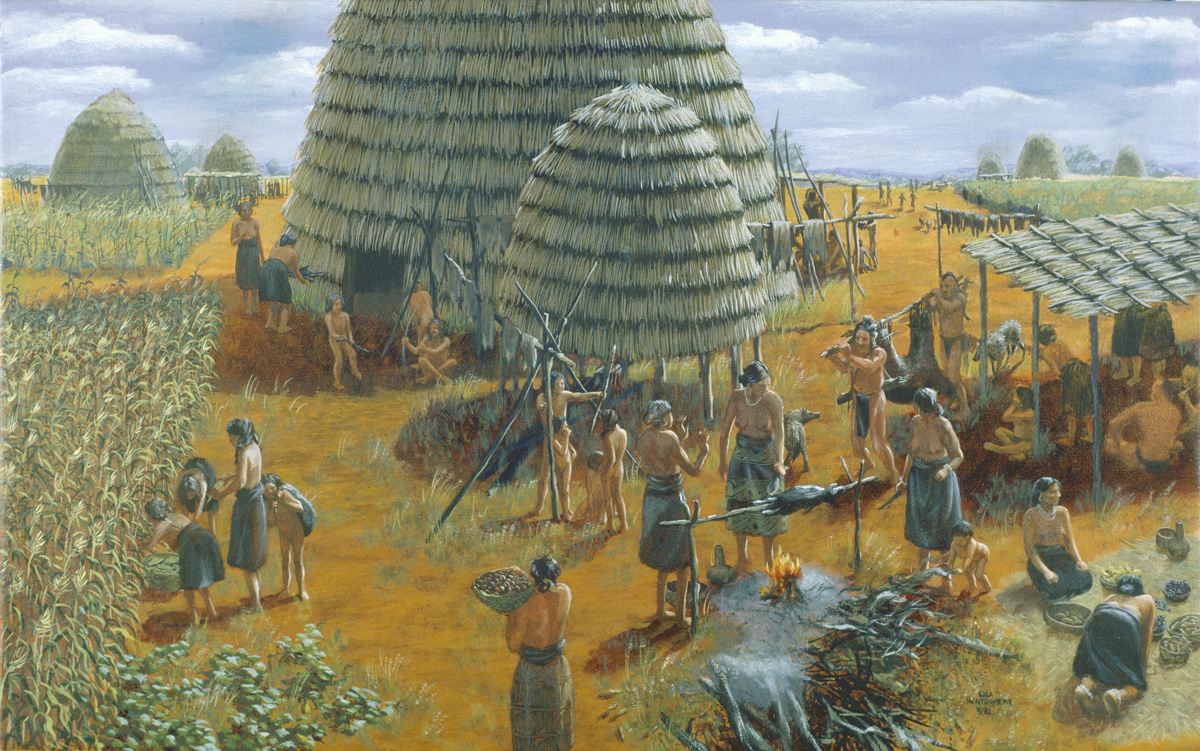
- Caddoan: The Caddoan language family encompasses tribes like the Caddo, Wichita, and Pawnee, who inhabited the eastern and central regions of Texas. Known for their sophisticated agricultural practices and intricate social structures, these tribes were skilled farmers, artisans, and traders.
- Athapaskan: The Athapaskan language family, primarily found in the western regions, includes tribes like the Apache and Navajo. These nomadic hunter-gatherers were known for their adaptability, resilience, and fierce independence.
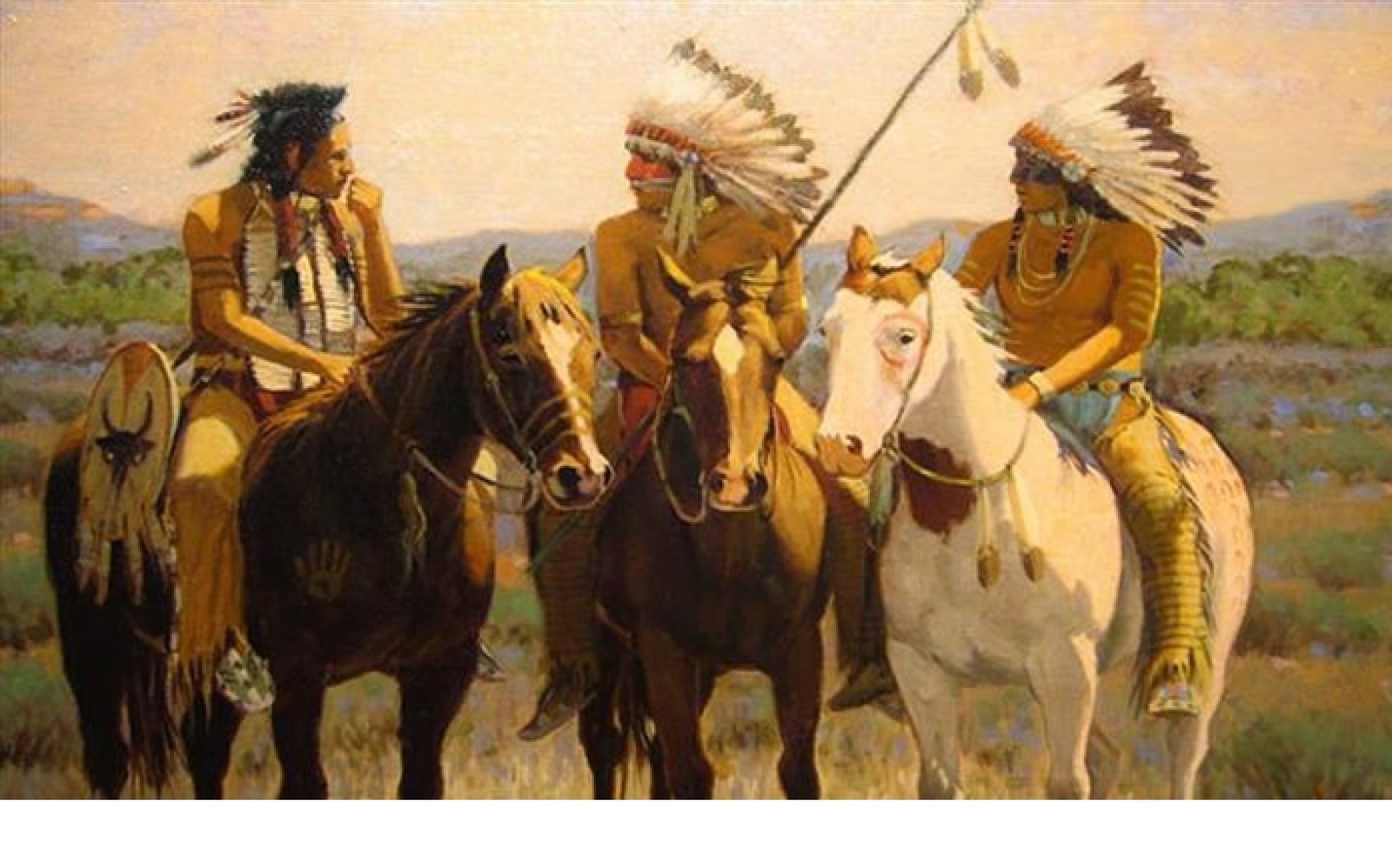
- Uto-Aztecan: This language family, primarily represented by the Comanche, dominated the central and western plains. These skilled horsemen and warriors played a significant role in shaping the history of the region.
- Tonkawa: The Tonkawa, an isolated language group, inhabited the central Texas region. They were known for their nomadic lifestyle and their mastery of hunting and warfare.
- Karankawa: The Karankawa, a coastal tribe, resided along the Gulf Coast. They were known for their maritime skills, their unique cultural practices, and their conflicts with European settlers.
A Legacy of Resilience and Adaptation:
The indigenous tribes of Texas faced numerous challenges throughout their history. The arrival of European settlers in the 16th century marked a turning point, leading to displacement, disease, and conflict. Despite these hardships, the tribes of Texas demonstrated remarkable resilience, adapting to changing circumstances and preserving their cultural heritage.
The Caddo: The Caddo, known for their agricultural prowess, were forced to relocate multiple times due to encroaching settlers. Their rich cultural heritage, including intricate beadwork, pottery, and ceremonial practices, has been preserved through oral traditions and museum collections.
The Apache: The Apache, renowned for their nomadic lifestyle and skilled horsemanship, fought fiercely against encroaching settlers. Their resistance, though ultimately unsuccessful, has become a symbol of their strength and determination.
The Comanche: The Comanche, dominating the central plains, were powerful warriors and skilled horsemen. Their influence extended far beyond Texas, shaping the history of the American West. They faced immense pressure from settlers and the U.S. government, culminating in their forced relocation to reservations in the 19th century.
The Karankawa: The Karankawa, a coastal tribe, were decimated by disease and conflict with European settlers. Their unique language and cultural practices are now largely lost, but their legacy continues to inspire research and understanding of their unique place in Texas history.
The Impact of European Colonization:
The arrival of European settlers had a profound impact on the indigenous tribes of Texas. The introduction of diseases, the disruption of traditional lifestyles, and the forced relocation to reservations resulted in significant population decline and cultural disruption.
The Trail of Tears: The forced relocation of tribes like the Cherokee, who were forcibly removed from their ancestral lands in the Southeast, further underscored the devastating impact of colonization. This tragic event, known as the "Trail of Tears," serves as a powerful reminder of the injustices faced by indigenous peoples.
The Legacy of Resistance:
Despite the hardships they faced, the indigenous tribes of Texas never relinquished their fight for survival and cultural preservation. They resisted colonization through diplomacy, warfare, and cultural adaptation. Their legacy of resistance continues to inspire and inform the ongoing efforts to understand and honor their contributions to Texas history.
Preserving the Legacy:
Recognizing the importance of preserving the legacy of Texas’s indigenous tribes, numerous efforts are underway to ensure their stories and cultures are not forgotten. These efforts include:
- Museums and Cultural Centers: Institutions like the Texas Indian Museum in San Angelo and the American Indian Cultural Center in Oklahoma City provide spaces for showcasing and preserving indigenous art, artifacts, and stories.
- Educational Programs: Schools and universities across Texas are incorporating indigenous history and culture into their curricula, promoting understanding and appreciation of the diverse heritage of the state.
- Tribal Sovereignty: The recognition of tribal sovereignty allows indigenous communities to govern themselves, manage their lands, and preserve their cultural traditions.
- Community Involvement: Indigenous communities are actively involved in preserving their heritage through cultural events, language revitalization programs, and storytelling initiatives.
FAQs:
1. What are some of the most significant tribes that inhabited Texas before European colonization?
Some of the most significant tribes include the Caddo, Wichita, Apache, Comanche, Tonkawa, and Karankawa. Each tribe had its unique language, customs, and way of life, contributing to the rich tapestry of indigenous cultures in Texas.
2. What are some of the key challenges faced by the indigenous tribes of Texas in the wake of European colonization?
The arrival of European settlers brought about numerous challenges, including the introduction of diseases, the disruption of traditional lifestyles, and the forced relocation to reservations. These factors led to significant population decline and cultural disruption.
3. What are some of the efforts underway to preserve the legacy of Texas’s indigenous tribes?
Museums, cultural centers, educational programs, tribal sovereignty, and community involvement are all playing a vital role in preserving the stories and cultures of Texas’s indigenous tribes.
4. What is the significance of recognizing tribal sovereignty?
Recognizing tribal sovereignty allows indigenous communities to govern themselves, manage their lands, and preserve their cultural traditions. This recognition is crucial for empowering indigenous communities and fostering self-determination.
5. How can individuals contribute to the preservation of indigenous cultures in Texas?
Individuals can contribute by supporting museums and cultural centers, learning about indigenous history and culture, engaging with tribal communities, and advocating for policies that support tribal sovereignty and cultural preservation.
Tips:
- Visit museums and cultural centers: Immerse yourself in the rich history and culture of Texas’s indigenous tribes by visiting museums and cultural centers dedicated to their stories and artifacts.
- Engage with tribal communities: Seek opportunities to interact with tribal members, learn about their traditions, and support their efforts to preserve their heritage.
- Support indigenous businesses and artisans: Patronize businesses owned by indigenous people and purchase artwork and crafts created by indigenous artists.
- Educate yourself and others: Learn about the history and culture of Texas’s indigenous tribes and share your knowledge with others.
- Advocate for policies that support indigenous rights: Support policies that protect tribal sovereignty, cultural preservation, and economic development for indigenous communities.
Conclusion:
The indigenous tribes of Texas have left an indelible mark on the state’s history, culture, and identity. From their intricate social structures and skilled craftsmanship to their fierce resilience and unwavering spirit, their contributions continue to inspire and inform our understanding of Texas’s multifaceted heritage. By recognizing and celebrating the legacy of these tribes, we honor their enduring spirit and ensure that their stories continue to resonate for generations to come.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Indigenous Legacy of Texas: A Journey Through Diverse Tribes and Cultures. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!