The Land Bridge of Beringia: A Gateway to the Americas
Related Articles: The Land Bridge of Beringia: A Gateway to the Americas
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Land Bridge of Beringia: A Gateway to the Americas. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Land Bridge of Beringia: A Gateway to the Americas
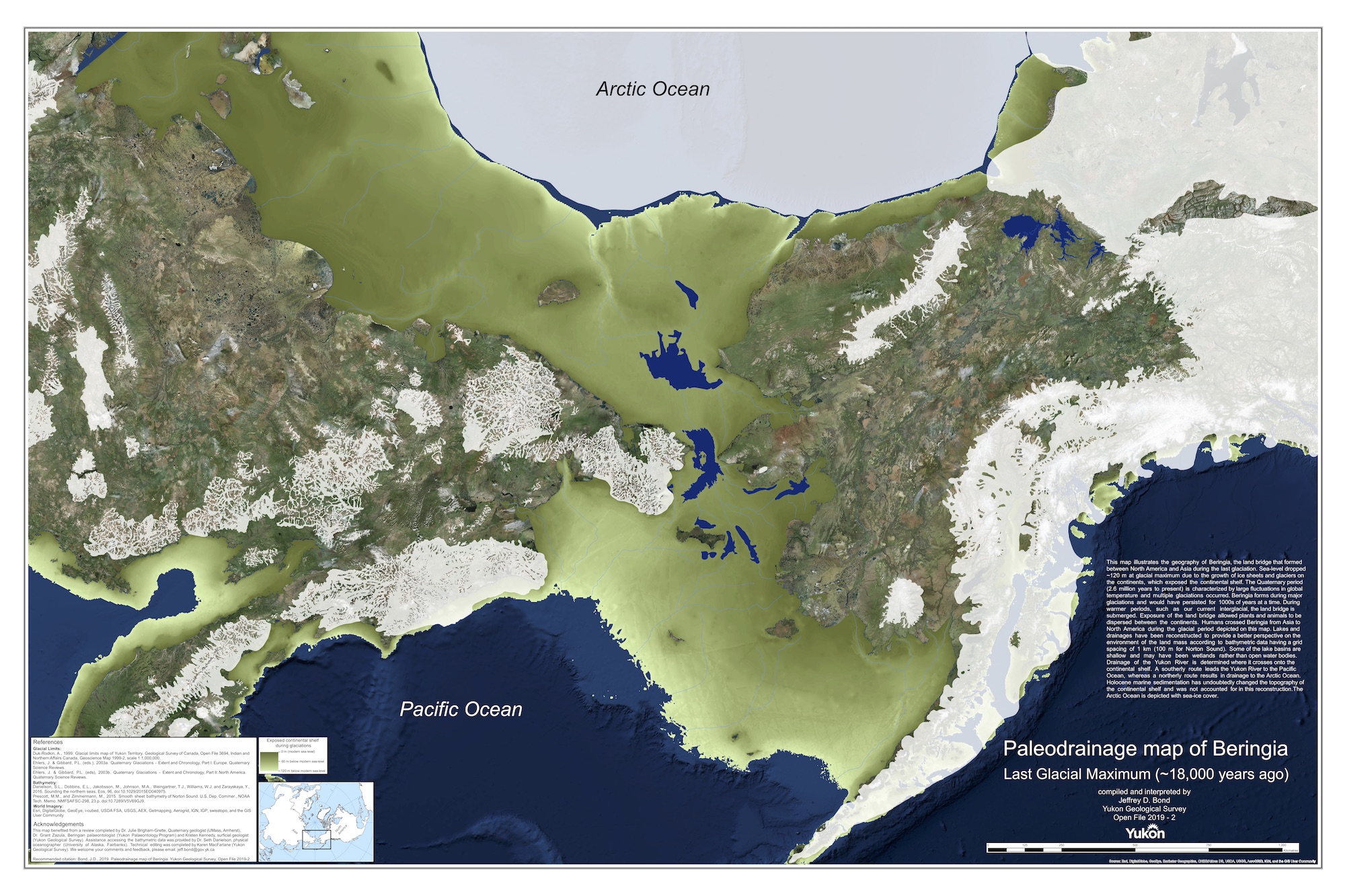
Beringia, a land bridge that once connected Asia and North America, played a pivotal role in shaping the history of human migration, the distribution of flora and fauna, and the geological evolution of the planet. This landmass, submerged beneath the Bering Strait today, was exposed during the Pleistocene epoch, a period of glacial expansion that locked vast amounts of water in ice sheets, lowering sea levels and creating a land connection between continents.
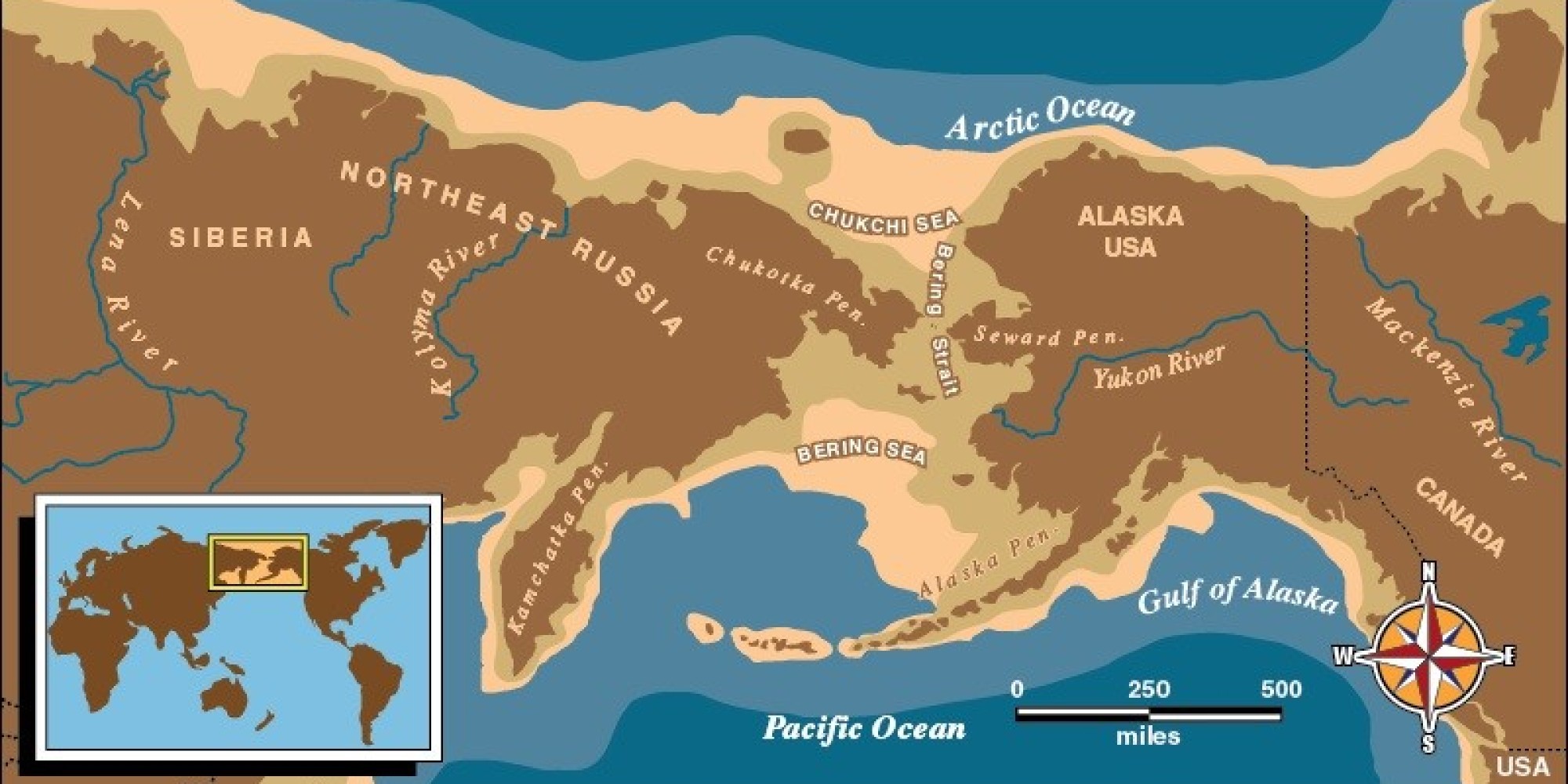
Understanding the Geography of Beringia:
Beringia was not a singular, homogenous landmass. It encompassed a diverse range of environments, from the tundra and ice sheets of the north to the forests and grasslands of the south. This varied landscape provided a mosaic of habitats that supported a rich diversity of life, including large mammals like mammoths, bison, and horses.
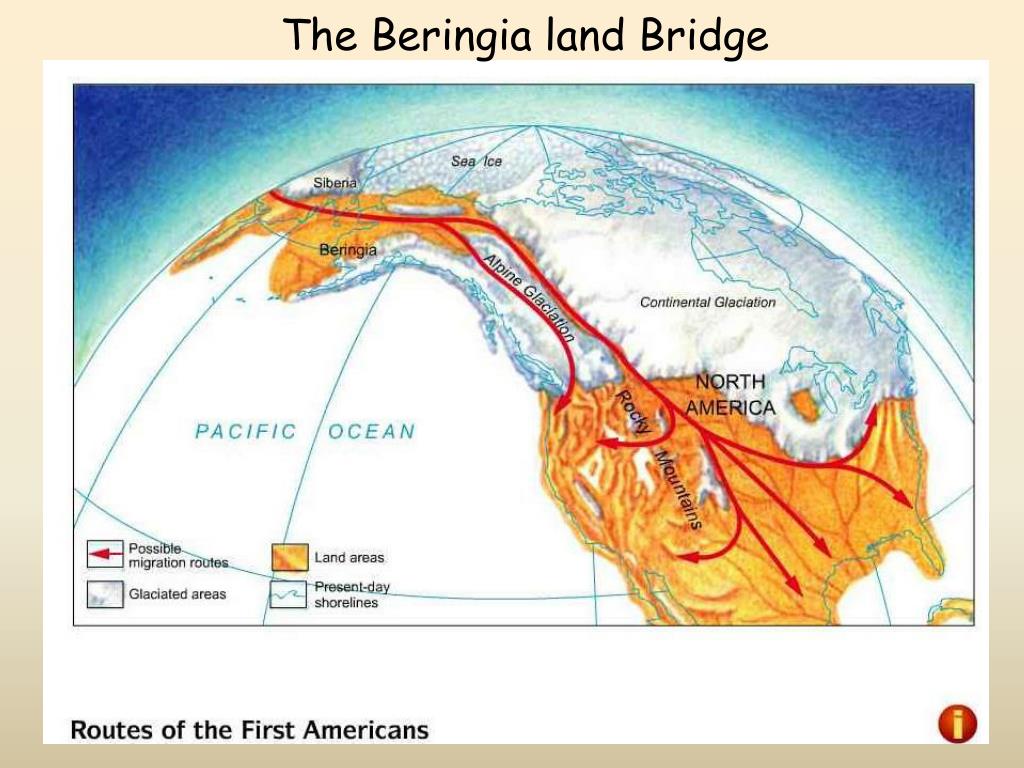
The Bering Land Bridge: A Pathway for Human Migration:
The Bering Land Bridge served as a crucial pathway for the first humans to migrate from Asia to North America. Archaeological evidence suggests that humans began crossing Beringia approximately 15,000 to 20,000 years ago, during the Last Glacial Maximum. These early migrants, known as Paleo-Indians, followed migrating herds of large animals, eventually spreading across North and South America.
The Role of Beringia in the Distribution of Flora and Fauna:
Beringia also facilitated the exchange of flora and fauna between Asia and North America. During periods of glacial expansion, the land bridge allowed for the movement of plants, animals, and insects, leading to the diversification of species on both continents. This exchange contributed to the unique biodiversity found in North America today.
The Geological Significance of Beringia:
The formation and subsequent submergence of Beringia had significant geological implications. The land bridge acted as a barrier between the Pacific and Arctic oceans, influencing ocean currents and climate patterns. The subsequent flooding of the land bridge, caused by rising sea levels at the end of the last glacial period, contributed to the formation of the Bering Strait, a narrow channel that separates Asia and North America.
The Legacy of Beringia:
While Beringia is now submerged beneath the waves, its legacy continues to shape our understanding of human history, the distribution of life on Earth, and the dynamics of our planet. It serves as a reminder of the interconnectedness of our world and the profound impact that past geological events have had on shaping the present.
Frequently Asked Questions about Beringia:
1. How long did the Bering Land Bridge exist?
The Bering Land Bridge existed intermittently throughout the Pleistocene epoch, spanning a period of approximately 2.5 million years. However, the most recent and significant period of exposure occurred during the Last Glacial Maximum, from approximately 26,500 to 19,000 years ago.
2. What evidence supports the existence of the Bering Land Bridge?
Several pieces of evidence support the existence of the Bering Land Bridge:
- Geological evidence: Seafloor sediments and geological formations indicate the presence of a landmass that connected Asia and North America.
- Paleontological evidence: Fossils of similar animal species found on both sides of the Bering Strait suggest that they were able to migrate freely across the land bridge.
- Archaeological evidence: Archaeological sites on both sides of the Bering Strait provide evidence of human migration across the land bridge.
3. What happened to the Bering Land Bridge?
The Bering Land Bridge was submerged beneath the waves as global temperatures rose at the end of the last glacial period. The melting of ice sheets led to a rise in sea levels, eventually flooding the land bridge and separating Asia and North America.
4. What are some of the key species that migrated across Beringia?
Many animal species migrated across Beringia, including:
- Mammals: Mammoths, bison, horses, caribou, and wolves.
- Birds: Various bird species, including ducks, geese, and owls.
- Insects: Various insect species, including beetles, butterflies, and moths.
5. How did the Bering Land Bridge influence the climate of the Earth?
The Bering Land Bridge acted as a barrier between the Pacific and Arctic oceans, influencing ocean currents and climate patterns. The land bridge also played a role in regulating the exchange of heat and moisture between the two oceans, potentially influencing global climate.
Tips for Studying Beringia:
- Explore online resources: Websites like the National Geographic website, the Smithsonian Institution website, and the Bering Land Bridge National Preserve website offer comprehensive information about Beringia.
- Read books and articles: Several books and articles have been written about Beringia, providing detailed insights into its history, geography, and significance.
- Visit museums and exhibits: Museums and exhibits dedicated to human migration and the history of the Americas often feature information about Beringia.
- Engage in discussions: Discuss Beringia with others, sharing your knowledge and learning from their perspectives.
Conclusion:
The Bering Land Bridge, a remarkable geological feature that connected Asia and North America, played a pivotal role in shaping the history of human migration, the distribution of flora and fauna, and the geological evolution of the planet. Its existence provides a powerful testament to the dynamic nature of our planet and the interconnectedness of life on Earth. Understanding Beringia is crucial for appreciating the complex history of our species and the intricate web of life that binds us all.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Land Bridge of Beringia: A Gateway to the Americas. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!