The Mountainous Backbone of India: A Geographic Exploration
Related Articles: The Mountainous Backbone of India: A Geographic Exploration
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Mountainous Backbone of India: A Geographic Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Mountainous Backbone of India: A Geographic Exploration
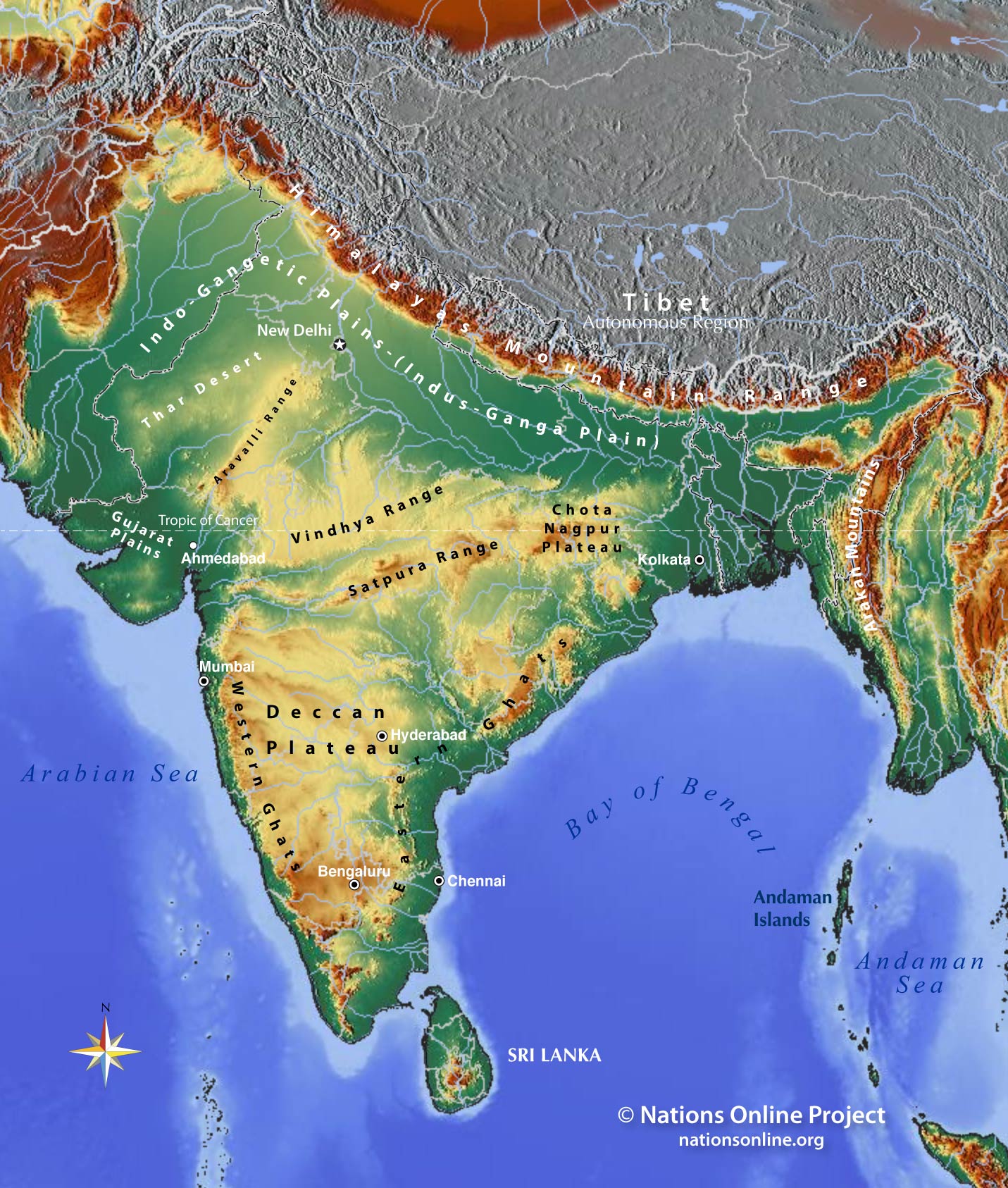
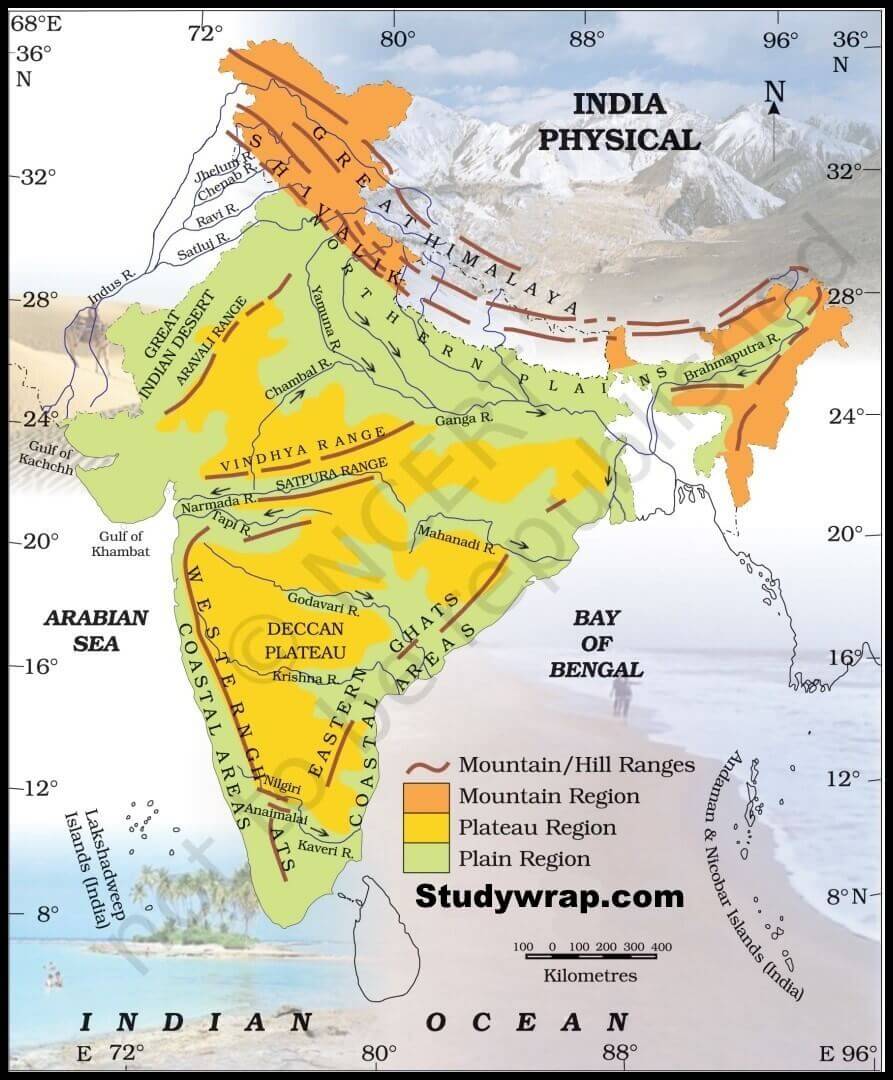
The Indian subcontinent, a land of diverse landscapes and rich cultural tapestry, is defined in part by its majestic mountain ranges. These towering peaks, stretching across the northern and eastern borders, form a natural barrier, influencing the country’s climate, ecology, and cultural identity. Understanding the geography of these mountains is crucial to grasping the intricate interplay of nature and human life in India.
The Himalayan Giants:
Dominating the northern frontier, the Himalayas are arguably the most iconic mountain range in India. These colossal peaks, including the world’s highest, Mount Everest, are a testament to the immense tectonic forces that shaped the Earth. The Himalayas are not just a single range, but a complex system of interconnected mountain chains, each with its own unique characteristics:
- The Great Himalayas: The highest and most prominent range, encompassing the world’s tallest peaks, including Mount Everest, Kanchenjunga, and Lhotse. This range is home to glaciers, snow-capped peaks, and alpine meadows, making it a popular destination for mountaineering and adventure tourism.
- The Lesser Himalayas: Located south of the Great Himalayas, this range is characterized by lower elevations and a more temperate climate. It features rolling hills, fertile valleys, and dense forests, supporting diverse flora and fauna.
- The Siwalik Hills: The outermost range, known for its foothills, river valleys, and fertile plains. This region is crucial for agriculture and supports a large population.
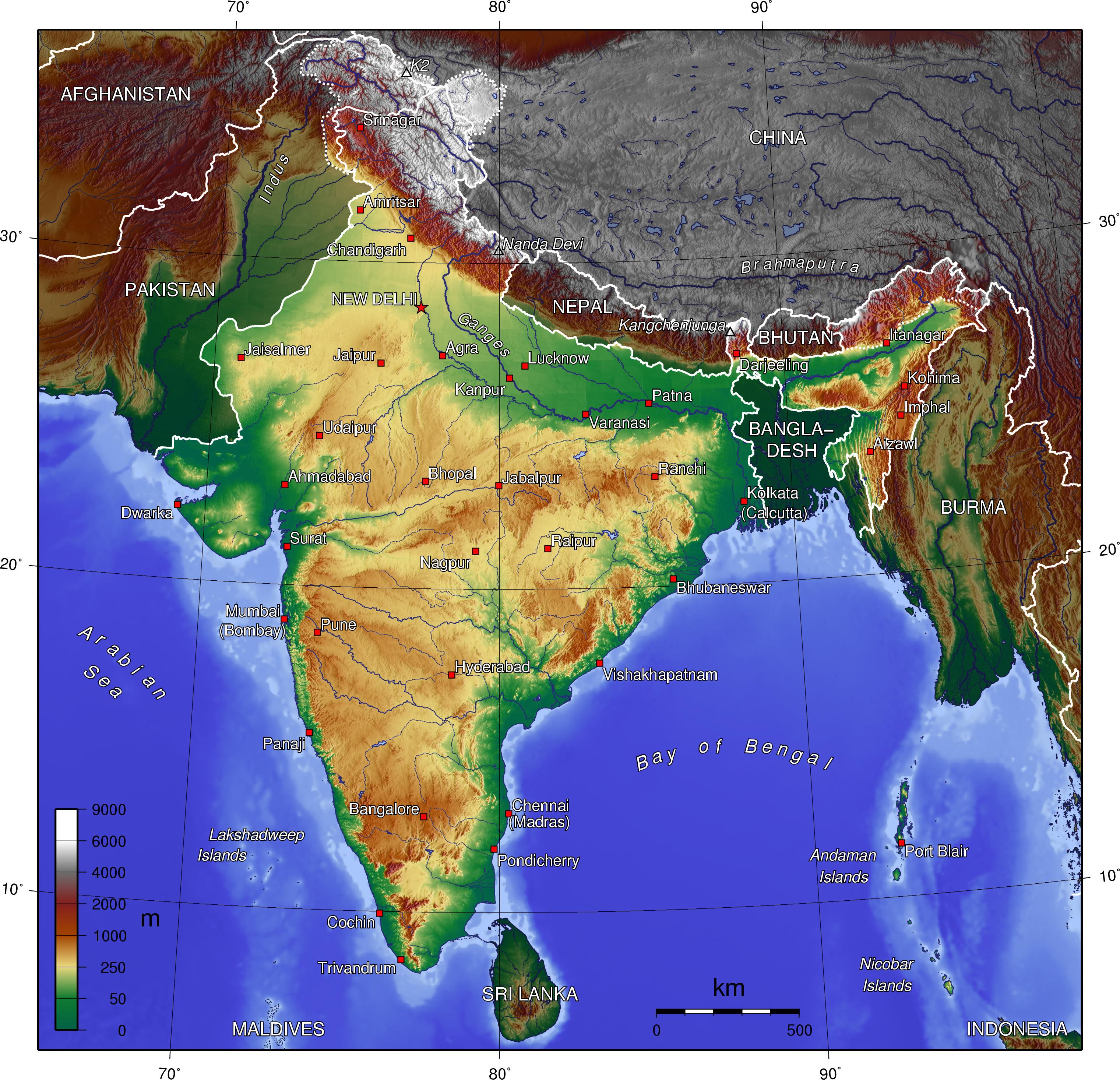
The Karakoram Range:
Sharing a border with Pakistan and China, the Karakoram Range is known for its formidable peaks and vast glaciers. It is home to the second-highest peak in the world, K2, and other challenging climbs. The Karakoram’s rugged terrain and extreme weather conditions make it a daunting but rewarding destination for experienced mountaineers.
The Eastern Himalayas:
Extending eastwards from the Great Himalayas, the Eastern Himalayas encompass the states of Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh, and parts of West Bengal. This region is known for its diverse flora and fauna, including rare and endangered species. The Eastern Himalayas are also home to several important rivers, including the Brahmaputra and the Teesta, which provide water resources for millions of people.
The Importance of India’s Mountains:
Beyond their awe-inspiring beauty, India’s mountains play a vital role in the country’s ecosystem and human life:
- Water Resources: The Himalayas are the source of numerous rivers that flow across India, providing essential water for irrigation, drinking, and hydropower generation.
- Biodiversity Hotspot: The mountains are home to a rich biodiversity, with unique plant and animal species adapted to the challenging environment. Many of these species are endemic to the region, highlighting the importance of conservation efforts.
- Climate Regulation: The mountains act as a natural barrier, influencing rainfall patterns and creating distinct microclimates. They also play a significant role in regulating the monsoon winds, which are crucial for agriculture in India.
- Cultural Heritage: The mountains have been a source of inspiration and cultural influence for centuries. They are home to numerous indigenous communities with unique traditions, languages, and beliefs.
- Tourism and Recreation: The mountains attract tourists from all over the world, providing economic opportunities and supporting local communities. They are also popular destinations for trekking, mountaineering, and adventure sports.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Despite their immense value, India’s mountains face numerous challenges:
- Climate Change: The Himalayas are particularly vulnerable to climate change, with glaciers retreating and temperatures rising. This poses a threat to water security and biodiversity.
- Deforestation: Unsustainable logging and agricultural practices have led to deforestation in some areas, impacting soil erosion and biodiversity.
- Pollution: Industrial pollution and waste disposal have contaminated rivers and affected the health of mountain ecosystems.
- Overtourism: The increasing popularity of mountain tourism can lead to overcrowding, environmental degradation, and cultural homogenization.
Addressing these challenges requires collaborative efforts from the government, local communities, and stakeholders. Sustainable development practices, conservation efforts, and responsible tourism are essential for protecting these precious natural resources and ensuring their continued benefits for future generations.
FAQs about the Mountains of India:
Q: What is the highest mountain in India?
A: The highest mountain in India is Kangchenjunga, with an elevation of 8,586 meters (28,169 feet). It is located in the Great Himalayas and is the third-highest mountain in the world.
Q: What are some of the major rivers that originate in the Himalayas?
A: The Himalayas are the source of several major rivers, including the Ganga, Yamuna, Brahmaputra, Indus, and Sutlej. These rivers are vital for irrigation, drinking water, and hydropower generation in India.
Q: What are the main challenges facing the mountains of India?
A: The mountains of India face several challenges, including climate change, deforestation, pollution, and overtourism. These issues threaten the environment, biodiversity, and livelihoods of people living in the mountains.
Q: What can be done to protect the mountains of India?
A: Protecting the mountains of India requires a multi-pronged approach, including sustainable development practices, conservation efforts, responsible tourism, and community involvement.
Tips for Visiting the Mountains of India:
- Plan your trip carefully: Research the area you plan to visit, including weather conditions, altitude, and trekking routes.
- Respect the local culture: Dress appropriately, avoid loud behavior, and be mindful of local customs.
- Leave no trace: Pack out all your trash and avoid littering.
- Support local communities: Stay in eco-friendly accommodations and purchase goods from local artisans.
- Be aware of altitude sickness: Acclimatize gradually and consult a doctor if you experience any symptoms.
Conclusion:
The mountains of India are a vital part of the country’s natural heritage, providing essential resources, shaping the climate, and supporting diverse communities. Understanding the geography, importance, and challenges facing these majestic peaks is crucial for ensuring their protection and sustainable development. By promoting responsible tourism, conservation efforts, and community engagement, we can help preserve these natural wonders for generations to come.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Mountainous Backbone of India: A Geographic Exploration. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!