Understanding the Earth’s Dynamic Skin: A Guide to World Plate Tectonics
Related Articles: Understanding the Earth’s Dynamic Skin: A Guide to World Plate Tectonics
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Earth’s Dynamic Skin: A Guide to World Plate Tectonics. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Earth’s Dynamic Skin: A Guide to World Plate Tectonics

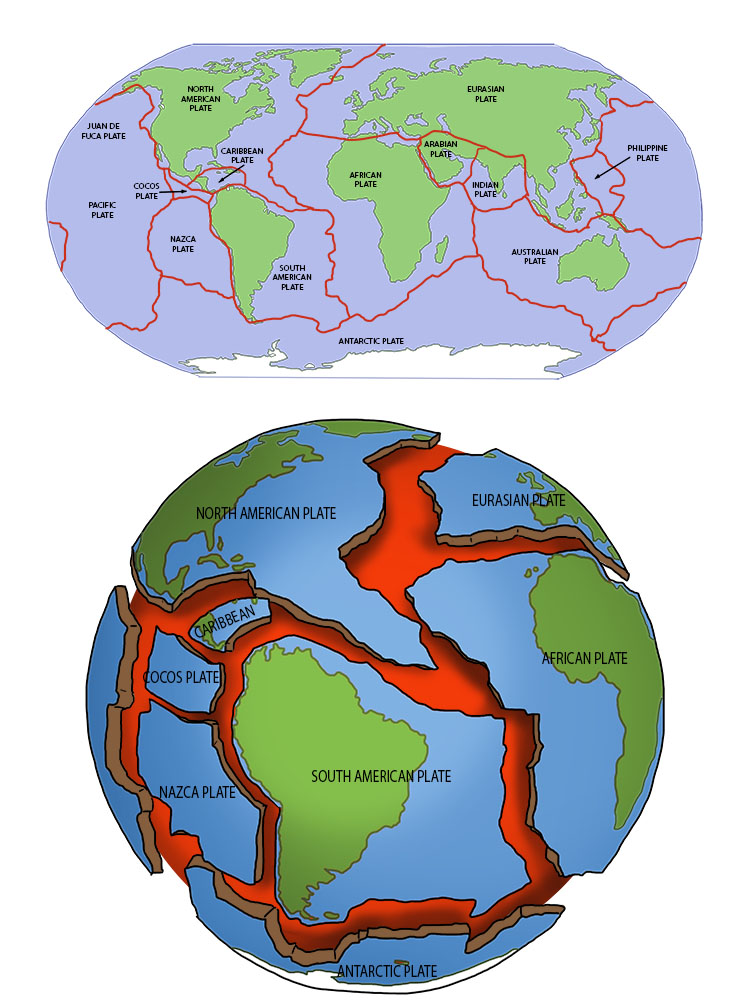
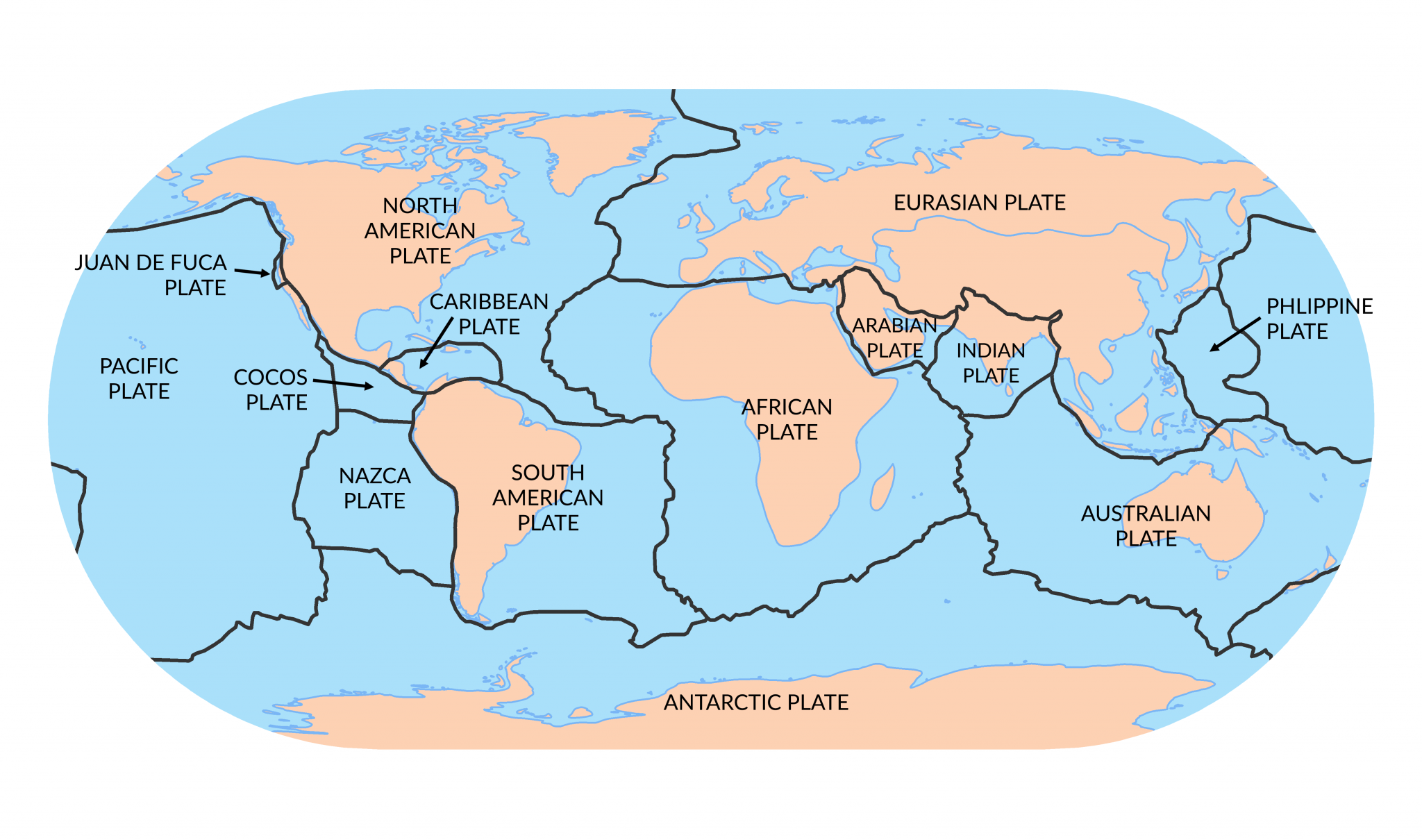
The Earth’s surface, seemingly solid and unchanging, is in fact a dynamic, ever-shifting landscape. This dynamism is driven by the movement of colossal plates of rock, known as tectonic plates, which constantly interact, collide, and slide past each other. The map of these plates, known as the World Plate Map, offers a fascinating glimpse into the intricate workings of our planet and reveals the forces that shape its landforms, landscapes, and even its climate.
The Foundation of Plate Tectonics:
The theory of plate tectonics, a cornerstone of modern geology, revolutionized our understanding of the Earth’s history and its present-day features. It explains the formation of mountain ranges, the occurrence of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, and the distribution of continents and oceans.
The Earth’s outer layer, the lithosphere, is not a single, continuous shell but rather a mosaic of giant, rigid plates. These plates, typically 50 to 150 kilometers thick, "float" on a semi-molten layer called the asthenosphere. The asthenosphere’s fluidity allows the plates to move, driven by convection currents within the Earth’s mantle.
Types of Plate Boundaries:
The interactions between these plates, occurring along their boundaries, are categorized into three main types:
-
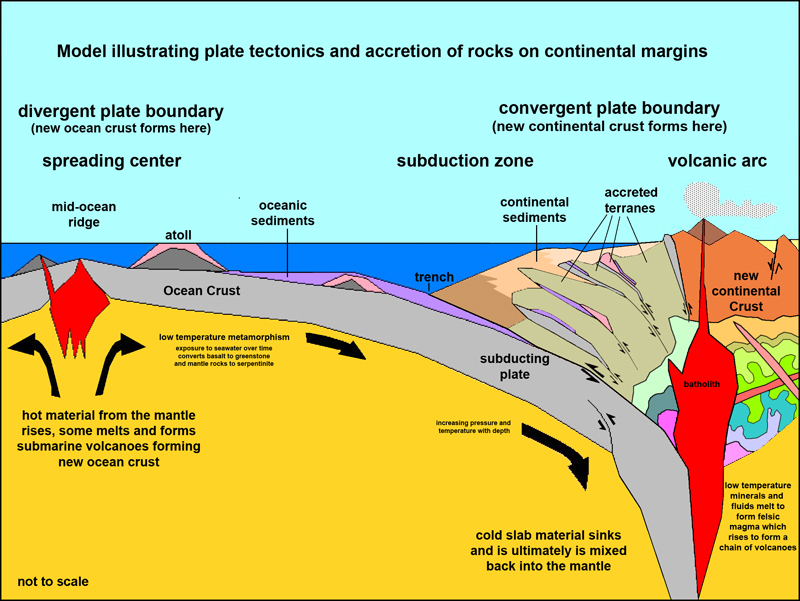
Divergent Boundaries: At these boundaries, plates move apart, allowing molten rock from the mantle to rise and create new crust. This process, known as seafloor spreading, is responsible for the formation of mid-ocean ridges, rift valleys, and volcanic islands. The Mid-Atlantic Ridge, a vast underwater mountain range, is a prime example of a divergent boundary.
-
Convergent Boundaries: Here, plates collide, resulting in dramatic geological events. The denser plate subducts, or dives beneath, the less dense plate, leading to the formation of deep ocean trenches, volcanic arcs, and mountain ranges. The Himalayas, the Andes, and the Japanese archipelago are all products of convergent boundaries.
-
Transform Boundaries: At these boundaries, plates slide past each other horizontally, causing friction and seismic activity. The San Andreas Fault in California, a notorious earthquake zone, is a classic example of a transform boundary.
The World Plate Map: A Window into Earth’s Processes:
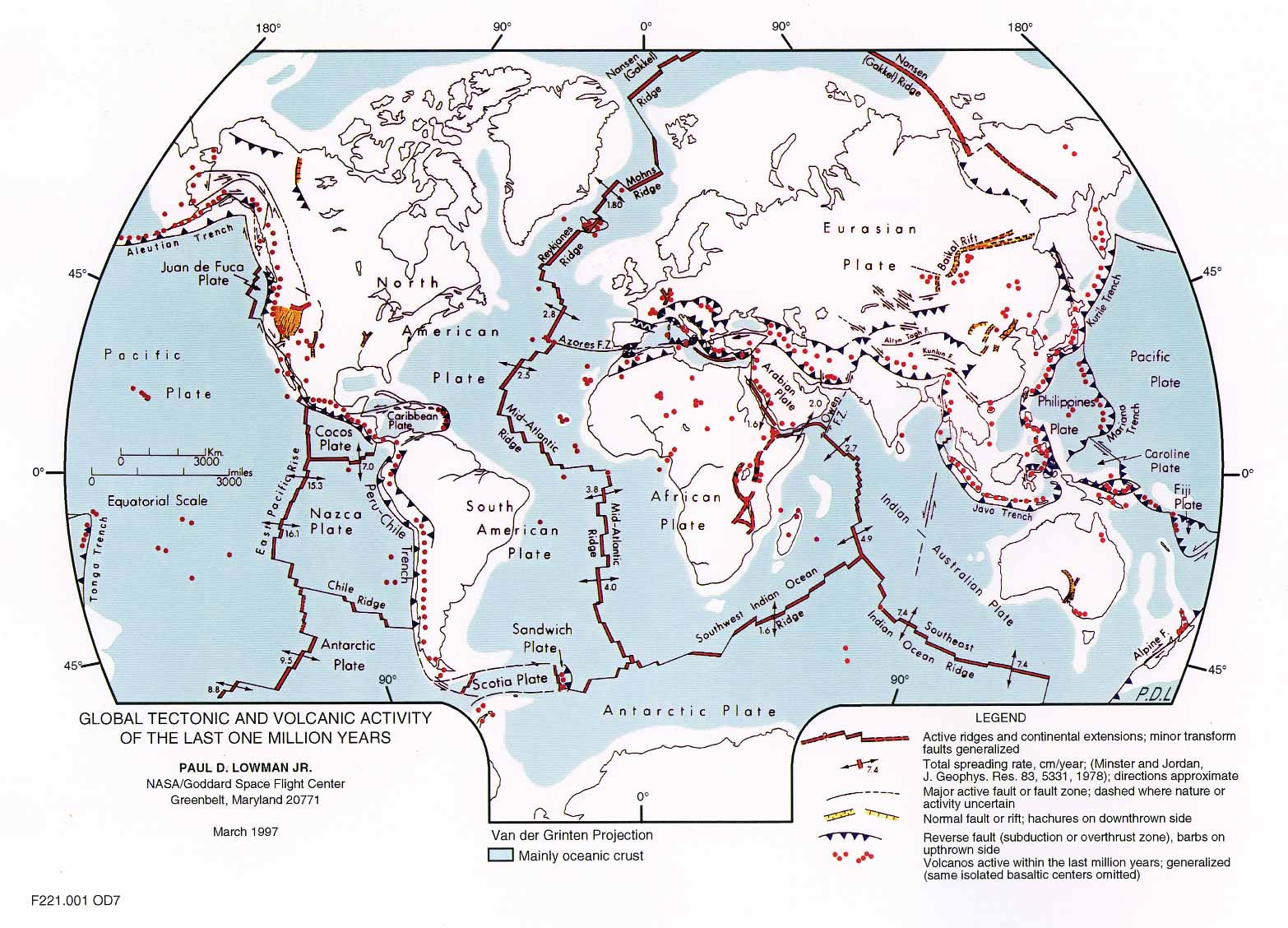
The World Plate Map provides a visual representation of these plate boundaries and their interactions. It highlights the locations of active volcanoes, earthquake zones, and other geologically active areas. This map is an indispensable tool for geologists, seismologists, and other Earth scientists, as it helps them understand the distribution of geological hazards, predict potential future events, and study the Earth’s evolution over millions of years.
Beyond the Map: The Importance of Plate Tectonics:
The significance of plate tectonics extends far beyond the realm of geology. It plays a crucial role in shaping the Earth’s climate, influencing the distribution of life, and even driving the evolution of species.
-
Climate Regulation: Plate movements influence ocean currents, atmospheric circulation, and the distribution of landmasses, which in turn impact global climate patterns. For example, the formation of mountain ranges can create rain shadows, leading to arid regions on one side and lush vegetation on the other.
-
Biodiversity and Evolution: The movement of continents and the formation of new landmasses have played a significant role in shaping biodiversity. As continents drift apart, species evolve in isolation, leading to the development of unique ecosystems and diverse life forms. The separation of the continents, for instance, is responsible for the distinct flora and fauna found in Australia and South America.
-
Resource Distribution: Plate tectonics also influences the distribution of natural resources, such as minerals, oil, and natural gas. Convergent boundaries often lead to the formation of mineral deposits, while divergent boundaries are associated with the formation of oil and gas reserves.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. How do scientists know about plate tectonics?
Scientists have gathered evidence from various sources, including:
- Fossil Distribution: Similar fossils found on continents separated by vast oceans provide evidence of their former connection.
- Geological Features: Matching rock formations and mountain ranges across continents suggest they were once joined.
- Magnetic Stripes: The pattern of magnetic stripes on the ocean floor reveals the process of seafloor spreading.
- Seismic Activity: The distribution of earthquakes and volcanoes along plate boundaries supports the theory of plate movement.
2. What are the consequences of plate movements?
Plate movements can cause:
- Earthquakes: The sudden release of energy along fault lines, where plates slide past each other.
- Volcanic Eruptions: Molten rock, ash, and gases erupt from the Earth’s surface, often near plate boundaries.
- Tsunamis: Large waves generated by earthquakes or volcanic eruptions in the ocean.
- Mountain Formation: Collision of plates forces land upwards, creating mountain ranges.
3. Are the plates still moving today?
Yes, the plates are constantly moving, though at a slow pace, typically a few centimeters per year. This movement is ongoing and continues to shape the Earth’s surface.
4. How does plate tectonics affect humans?
Plate tectonics has a significant impact on human life, both positive and negative:
- Natural Hazards: Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and tsunamis pose significant threats to human populations.
- Resource Availability: Plate tectonics influences the distribution of mineral resources, impacting economies and societies.
- Land Formation: The movement of plates shapes the landforms we live on, influencing human settlements and infrastructure.
Tips for Understanding Plate Tectonics:
- Use a World Plate Map: Visualizing the plates and their boundaries is essential for understanding the concepts.
- Explore Interactive Maps: Online resources offer interactive maps that allow you to zoom in on specific areas and learn more about their geological features.
- Read Books and Articles: Numerous resources are available to delve deeper into the theory of plate tectonics and its implications.
- Visit Geological Sites: Witnessing firsthand the effects of plate tectonics, such as volcanoes, fault lines, and mountain ranges, can enhance your understanding.
Conclusion:
The World Plate Map is a powerful tool for understanding the Earth’s dynamic nature. It unveils the forces that shape our planet, driving geological processes, influencing climate, and shaping the distribution of life. By studying plate tectonics, we gain insights into the Earth’s history, present-day phenomena, and future possibilities. This knowledge is crucial for mitigating geological hazards, managing natural resources, and understanding the interconnectedness of our planet’s systems. As we continue to explore the intricacies of plate tectonics, we unlock deeper understanding of our planet’s past, present, and future.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Earth’s Dynamic Skin: A Guide to World Plate Tectonics. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!