Unpacking the Landscape: A Look at Michigan’s Population Density Map
Related Articles: Unpacking the Landscape: A Look at Michigan’s Population Density Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unpacking the Landscape: A Look at Michigan’s Population Density Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unpacking the Landscape: A Look at Michigan’s Population Density Map
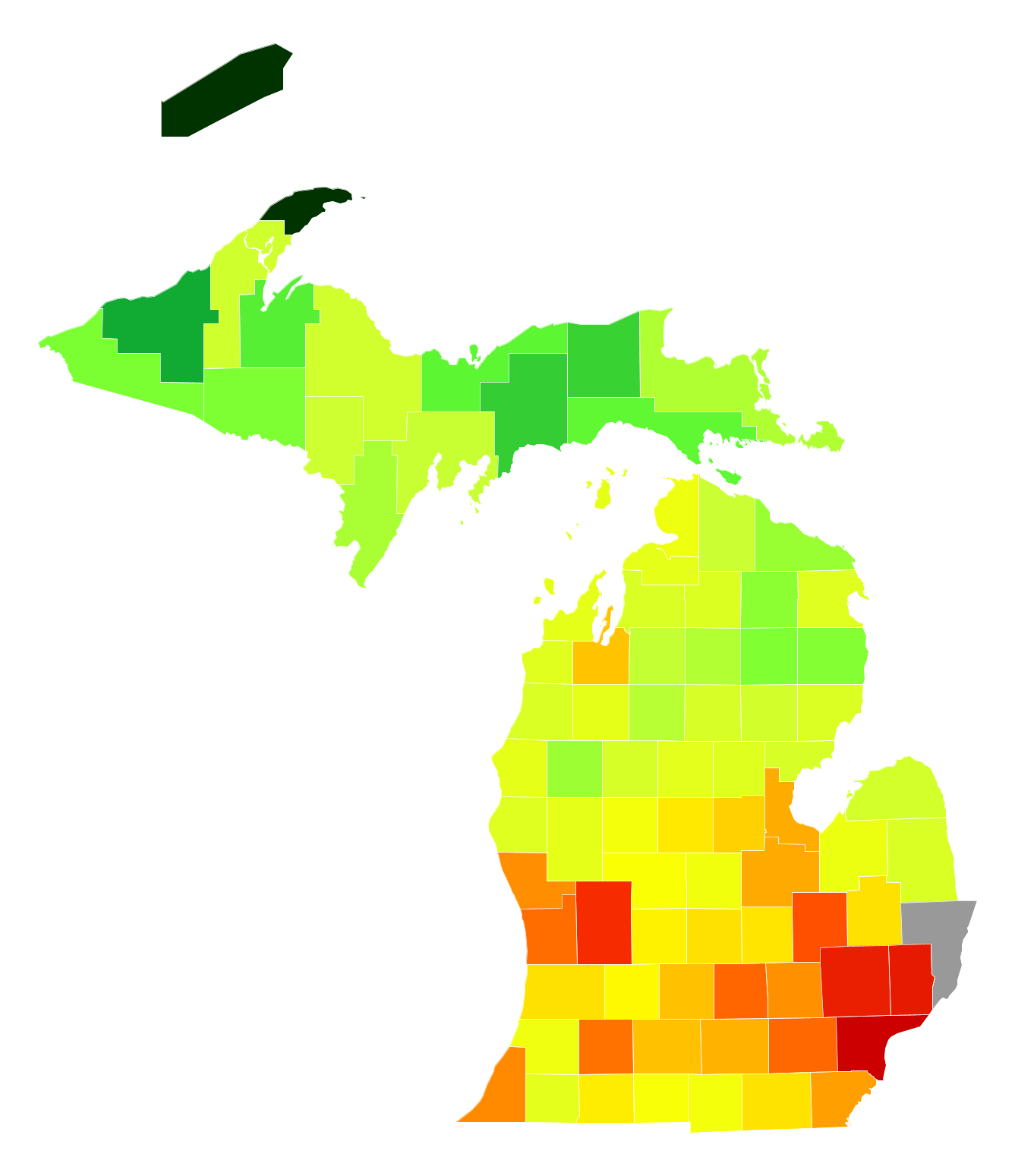
Michigan’s population density map is more than just a visual representation of where people live. It serves as a powerful tool for understanding the state’s demographic makeup, revealing patterns of urban sprawl, rural decline, and the unique distribution of its inhabitants. This map, a visual snapshot of human activity across the state, offers valuable insights into various facets of Michigan’s social, economic, and environmental landscape.
Understanding the Map: A Visual Guide to Michigan’s People
The map utilizes a color gradient to illustrate population density, ranging from low density areas (often depicted in light shades) to high density areas (represented in darker hues). The shades of color represent the number of people per square mile, allowing for a clear visual comparison between different regions. This visual representation makes it easy to identify areas with high population concentration, such as major cities like Detroit, Grand Rapids, and Lansing, and contrast them with sparsely populated regions, such as the Upper Peninsula and the northern Lower Peninsula.
Unveiling Patterns: Insights from the Map
The map reveals several significant patterns in Michigan’s population distribution:
- Urban Concentration: The map vividly highlights the concentration of population in urban areas, particularly in the southeastern region of the state. Detroit, the state’s largest city, stands out as a major population center, with its surrounding metropolitan area experiencing high density.
- Rural Decline: The map also illustrates the trend of population decline in many rural areas, particularly in the Upper Peninsula and the northern Lower Peninsula. This trend is often attributed to factors such as economic decline, limited job opportunities, and outmigration to more densely populated regions.
- Coastal Concentration: Michigan’s coastal areas, especially along Lake Michigan and Lake Huron, demonstrate a higher population density compared to inland regions. This is likely due to factors like tourism, recreational opportunities, and desirable living environments.
- Regional Variations: The map reveals distinct population density variations across different regions of Michigan. The southeastern region boasts the highest concentration, while the northern regions, particularly the Upper Peninsula, exhibit significantly lower density. This reflects diverse economic and geographic factors influencing population distribution.
Beyond the Numbers: The Significance of Population Density
The Michigan population density map is not just a static representation of where people live; it serves as a powerful tool for understanding a multitude of social, economic, and environmental factors.
Social Implications:
- Resource Allocation: The map informs resource allocation decisions, highlighting areas with high population density that might require more resources for infrastructure, public services, and social programs.
- Community Development: Understanding population distribution aids in planning for community development, ensuring equitable access to resources and services across different regions.
- Social Services: The map helps identify areas with high concentrations of vulnerable populations, guiding the allocation of social services and support networks.
Economic Implications:
- Infrastructure Development: The map informs infrastructure development plans, ensuring adequate transportation, utilities, and communication networks are available to meet the needs of diverse populations.
- Economic Development: The map helps identify areas with high growth potential, attracting businesses and investments to create jobs and stimulate economic growth.
- Business Location: The map assists businesses in choosing strategic locations, considering factors like market size, labor availability, and infrastructure access.
Environmental Implications:
- Land Use Planning: The map supports sustainable land use planning, ensuring the preservation of natural resources and the mitigation of environmental impacts associated with population growth.
- Environmental Protection: Understanding population distribution helps identify areas vulnerable to environmental hazards and guide efforts to protect sensitive ecosystems.
- Waste Management: The map informs waste management strategies, ensuring efficient collection and disposal services are available to cater to the needs of diverse populations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Michigan’s Population Density Map
1. How is population density calculated?
Population density is calculated by dividing the total population of a geographic area by the total land area. The resulting figure represents the number of people per square mile.
2. What factors influence population density in Michigan?
Various factors influence population density, including:
- Economic Opportunities: Areas with strong job markets and economic growth tend to attract more residents.
- Natural Resources: The availability of natural resources, such as water, forests, and minerals, can attract populations for resource extraction and related industries.
- Climate: Favorable climate conditions, such as mild temperatures and ample sunshine, can make certain areas more desirable for living.
- Infrastructure: The presence of adequate infrastructure, including transportation, utilities, and communication networks, is crucial for attracting residents.
- Social Factors: Access to quality education, healthcare, and cultural amenities can influence population distribution.
3. How does the population density map contribute to policy-making?
The map serves as a valuable tool for policymakers, providing insights into:
- Resource Allocation: Informing decisions about allocating resources for infrastructure, public services, and social programs based on population needs.
- Economic Development: Identifying areas with high growth potential and guiding investments to stimulate economic activity.
- Environmental Protection: Understanding population distribution to inform strategies for protecting sensitive ecosystems and managing environmental hazards.
4. What are the limitations of the population density map?
While the map provides valuable insights, it has limitations:
- Oversimplification: It presents a simplified view of population distribution, not accounting for variations within specific areas.
- Static Representation: The map captures a snapshot in time and may not reflect dynamic changes in population distribution over time.
- Data Accuracy: The accuracy of the data used to create the map can influence its reliability.
5. How can the population density map be used to improve life in Michigan?
The map can contribute to improving life in Michigan by:
- Promoting Equitable Resource Allocation: Ensuring resources are distributed fairly based on population needs.
- Supporting Sustainable Development: Guiding development plans that consider population density and environmental impacts.
- Facilitating Community Engagement: Providing a visual representation of population distribution to encourage community engagement in planning and decision-making processes.
Tips for Using Michigan’s Population Density Map Effectively
- Consider the Scale: The map’s usefulness depends on the scale of analysis. Zooming in on specific regions provides more detailed insights.
- Compare Data: Combining the population density map with other data sources, such as economic indicators or environmental data, provides a more comprehensive picture.
- Recognize Context: It’s important to consider the historical and social context surrounding population distribution to gain a deeper understanding.
Conclusion: A Vital Tool for Understanding Michigan’s Landscape
Michigan’s population density map is not merely a static representation of where people live; it serves as a vital tool for understanding the state’s demographic makeup, revealing patterns of urban sprawl, rural decline, and the unique distribution of its inhabitants. By providing a visual snapshot of human activity across the state, the map offers valuable insights into various facets of Michigan’s social, economic, and environmental landscape, aiding in informed decision-making and policy development for a more prosperous and sustainable future.


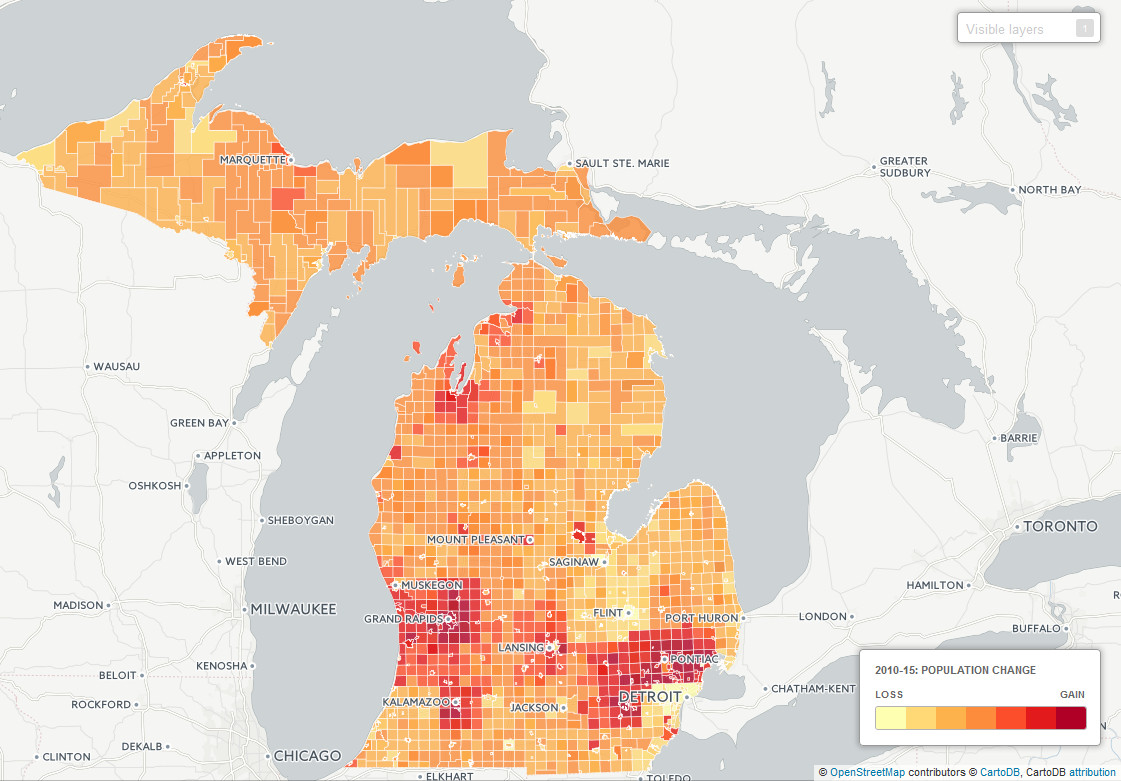

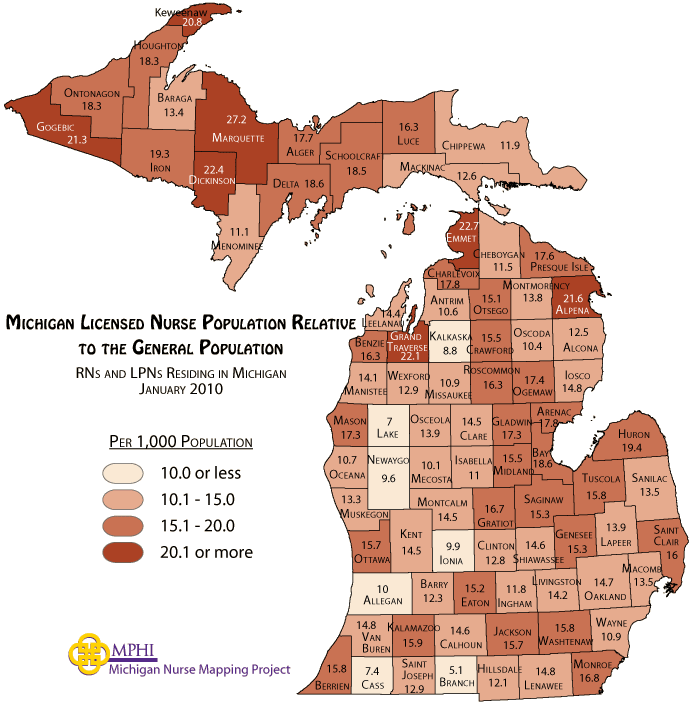
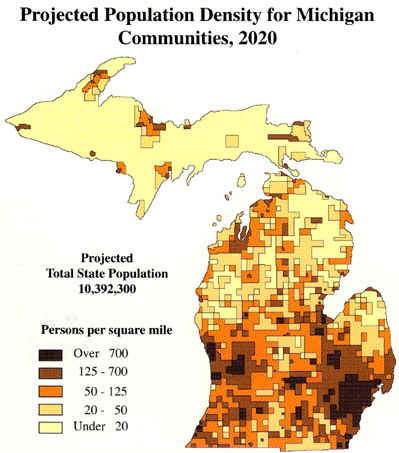
![Michigan population density map [600 x 600]. : r/MapPorn](https://external-preview.redd.it/o35LpzZU8GEp2hOgu4f0ANfkM7--LT4pVo7QHMAHysI.png?auto=webpu0026s=142827eba410cda5554a236d6f71dc5eac16662a)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unpacking the Landscape: A Look at Michigan’s Population Density Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!