Unraveling the Geography of South America: A Comprehensive Outline
Related Articles: Unraveling the Geography of South America: A Comprehensive Outline
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Geography of South America: A Comprehensive Outline. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Geography of South America: A Comprehensive Outline
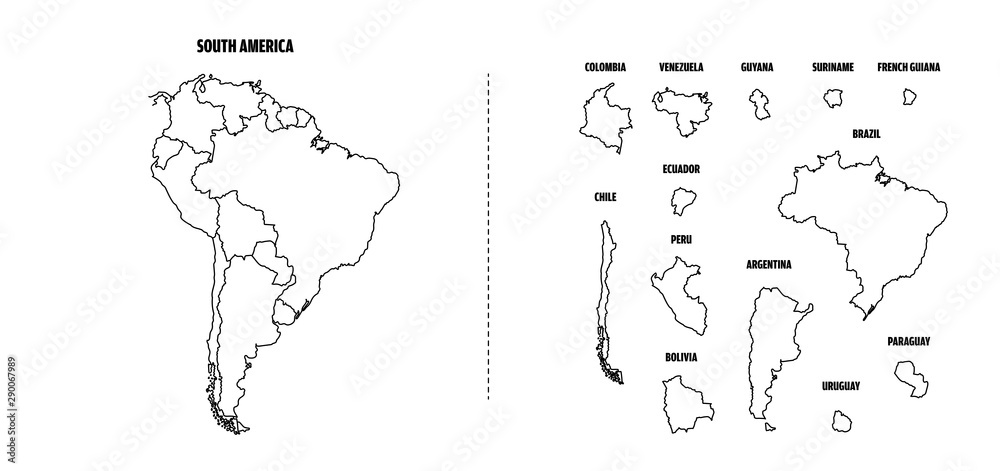
South America, the fourth largest continent, boasts a captivating tapestry of landscapes, cultures, and histories. Understanding its geographic outline is crucial for appreciating its diverse ecosystems, appreciating its cultural tapestry, and comprehending its geopolitical significance. This article delves into the key features of South America’s outline, highlighting its importance in various fields.
A Continent Shaped by Nature:
South America’s outline is a testament to the powerful forces of nature. The continent’s eastern edge is marked by the vast Atlantic Ocean, while the western side is defined by the towering Andes mountain range, the longest mountain chain outside Asia. This cordillera, stretching over 7,000 kilometers, acts as a natural barrier, influencing climate patterns and isolating ecosystems.
The Amazon River, the world’s largest river by discharge, flows through the heart of South America, carving a vast basin that encompasses nine countries. Its tributaries form a complex network, shaping the landscape and supporting a rich biodiversity. The Paraná River, another major waterway, flows south, forming the boundary between Argentina and Paraguay before emptying into the Atlantic. These rivers, along with their tributaries, have historically served as vital trade routes and continue to play a significant role in the continent’s economic and cultural life.
Beyond the Outline: A Closer Look at the Regions:
South America’s outline can be further broken down into distinct regions, each with unique characteristics:
-
The Andean Region: This region, dominated by the Andes, encompasses countries like Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Chile, and Argentina. The Andes create a diverse range of ecosystems, from high-altitude glaciers to lush rainforests, influencing the region’s climate and biodiversity. The Andes also play a vital role in shaping the cultural landscape, with indigenous communities adapting to the challenging terrain and developing unique traditions.
-
The Amazon Basin: This region, encompassing the Amazon River and its tributaries, is a haven of biodiversity, home to a vast array of flora and fauna. The Amazon rainforest, the largest in the world, plays a critical role in regulating global climate and providing essential ecosystem services. The region’s indigenous communities have a deep connection to the rainforest, their cultures and livelihoods intricately intertwined with its natural resources.
-
The Pampas: This vast, fertile grassland region stretches across Argentina, Uruguay, and parts of Brazil. It is characterized by its flat terrain and rich soil, making it ideal for agriculture. The Pampas is known for its cattle ranching industry, contributing significantly to the region’s economy and cultural identity.
-
The Brazilian Highlands: This region, located in eastern Brazil, is characterized by its rolling hills, plateaus, and fertile soils. It is home to a diverse range of ecosystems, including rainforests, savannas, and grasslands. The Brazilian Highlands are a major agricultural region, producing coffee, sugarcane, and other crops.
-
The Caribbean Islands: While not technically part of the mainland, the Caribbean islands are often considered part of the South American cultural sphere. These islands, with their diverse populations and rich history, share a unique cultural identity with South America, influenced by indigenous, European, and African heritage.
The Outline’s Significance:
Understanding South America’s outline is crucial for various reasons:
-
Environmental Conservation: Recognizing the continent’s diverse ecosystems and their interconnectedness is essential for effective environmental conservation efforts. The outline highlights the importance of protecting the Amazon rainforest, the Andes mountain range, and other vital natural resources.
-
Economic Development: South America’s outline reveals its vast natural resources and its potential for economic growth. Understanding the distribution of resources, transportation routes, and potential trade networks is essential for sustainable economic development.
-
Geopolitical Understanding: The continent’s outline provides insights into its geopolitical dynamics. The Andes, for example, have historically acted as a natural barrier, influencing the development of distinct cultural and political identities. The Amazon Basin, with its shared resources, presents challenges and opportunities for regional cooperation.
-
Cultural Appreciation: The continent’s outline reflects the diverse cultures and histories that have shaped South America. Understanding the different regions, their unique landscapes, and their cultural traditions provides a deeper appreciation for the continent’s rich heritage.
FAQs about the Outline of South America:
Q: What are the major physical features that define the outline of South America?
A: The most prominent features are the Andes mountain range, the Amazon River, and the Atlantic Ocean. The Andes run along the western edge of the continent, creating a natural barrier and influencing climate patterns. The Amazon River flows through the heart of South America, forming a vast basin that encompasses nine countries. The Atlantic Ocean borders the eastern edge of the continent, shaping its coastline and influencing its maritime trade.
Q: How does the outline of South America influence its climate?
A: The Andes mountain range plays a significant role in influencing South America’s climate. The mountains act as a barrier, blocking moisture from the Pacific Ocean and creating a rain shadow effect on the eastern side of the Andes. This results in a drier climate in the eastern regions compared to the wetter western regions. The Amazon rainforest, with its vast expanse, also influences regional climate, contributing to the continent’s overall humidity.
Q: What are some of the key challenges facing South America in terms of its geography?
A: One of the major challenges is the vulnerability of the Amazon rainforest to deforestation and climate change. The Andes mountain range faces challenges related to mining and resource extraction, which can have negative environmental impacts. The continent’s diverse ecosystems are also vulnerable to invasive species and pollution.
Q: How does the outline of South America influence its cultural landscape?
A: The continent’s diverse landscape has led to the development of distinct cultures and traditions. The Andean region, with its challenging terrain, has fostered indigenous communities with unique adaptations and cultural practices. The Amazon Basin has a rich cultural heritage, with indigenous groups living in harmony with the rainforest. The Pampas, with its vast grasslands, has influenced the development of a culture centered around cattle ranching.
Tips for Understanding South America’s Outline:
-
Use a physical map: A physical map highlighting the continent’s major features, such as the Andes, the Amazon River, and the Atlantic Ocean, can provide a visual understanding of South America’s outline.
-
Study the regions: Delve into the different regions of South America, focusing on their unique characteristics, landscapes, and cultural traditions.
-
Explore online resources: Websites, documentaries, and online maps can offer detailed information about South America’s geography, including its ecosystems, climate, and cultural diversity.
-
Engage with local communities: If possible, interact with people from different regions of South America to gain firsthand perspectives on their cultural heritage and the challenges and opportunities they face.
Conclusion:
South America’s outline is a powerful tool for understanding the continent’s natural beauty, cultural diversity, and geopolitical significance. From the towering Andes to the vast Amazon Basin, the continent’s geography has shaped its history, its people, and its future. By delving into the intricacies of the outline, we gain a deeper appreciation for this remarkable continent and its vital role in the global landscape.


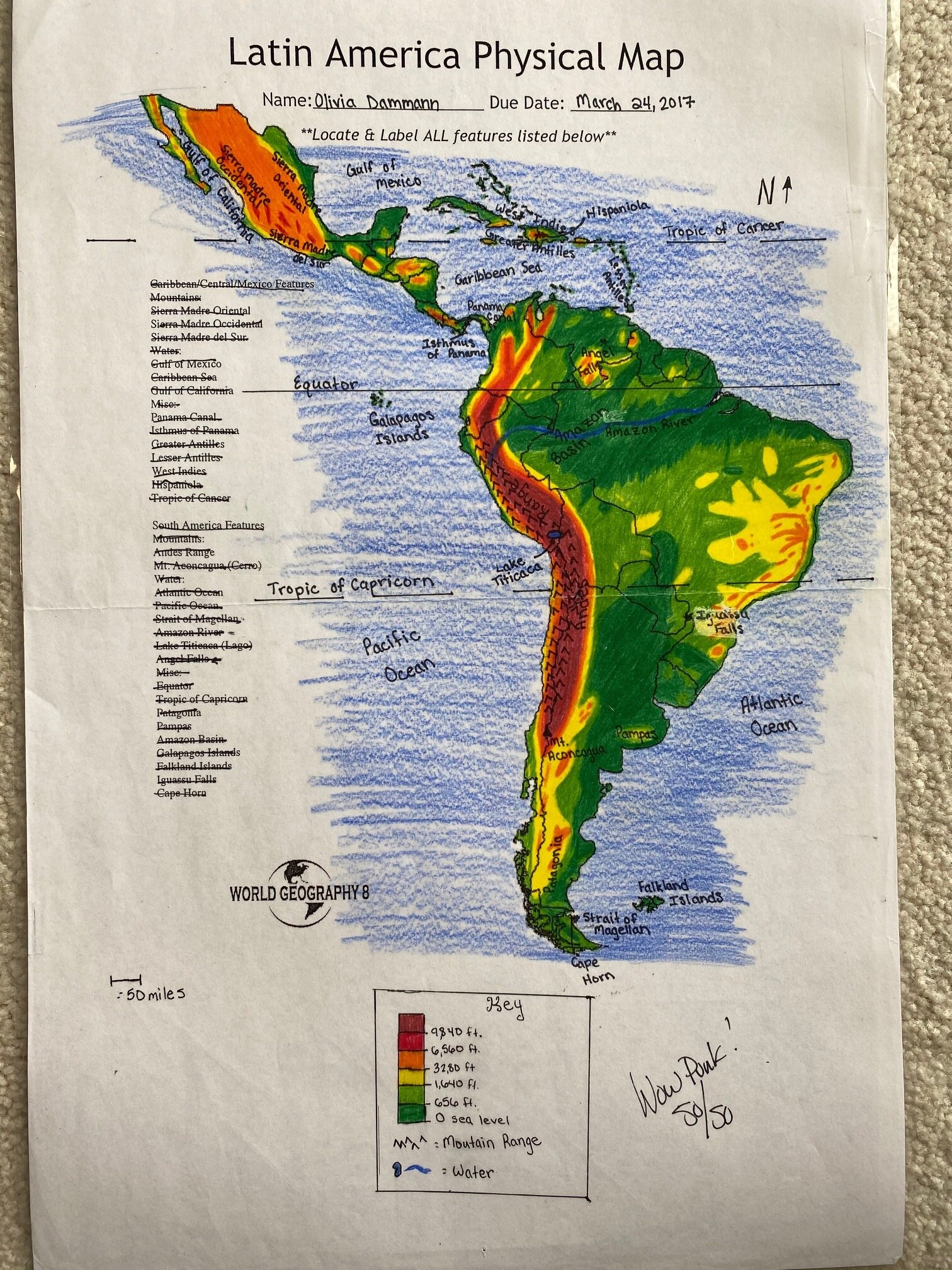
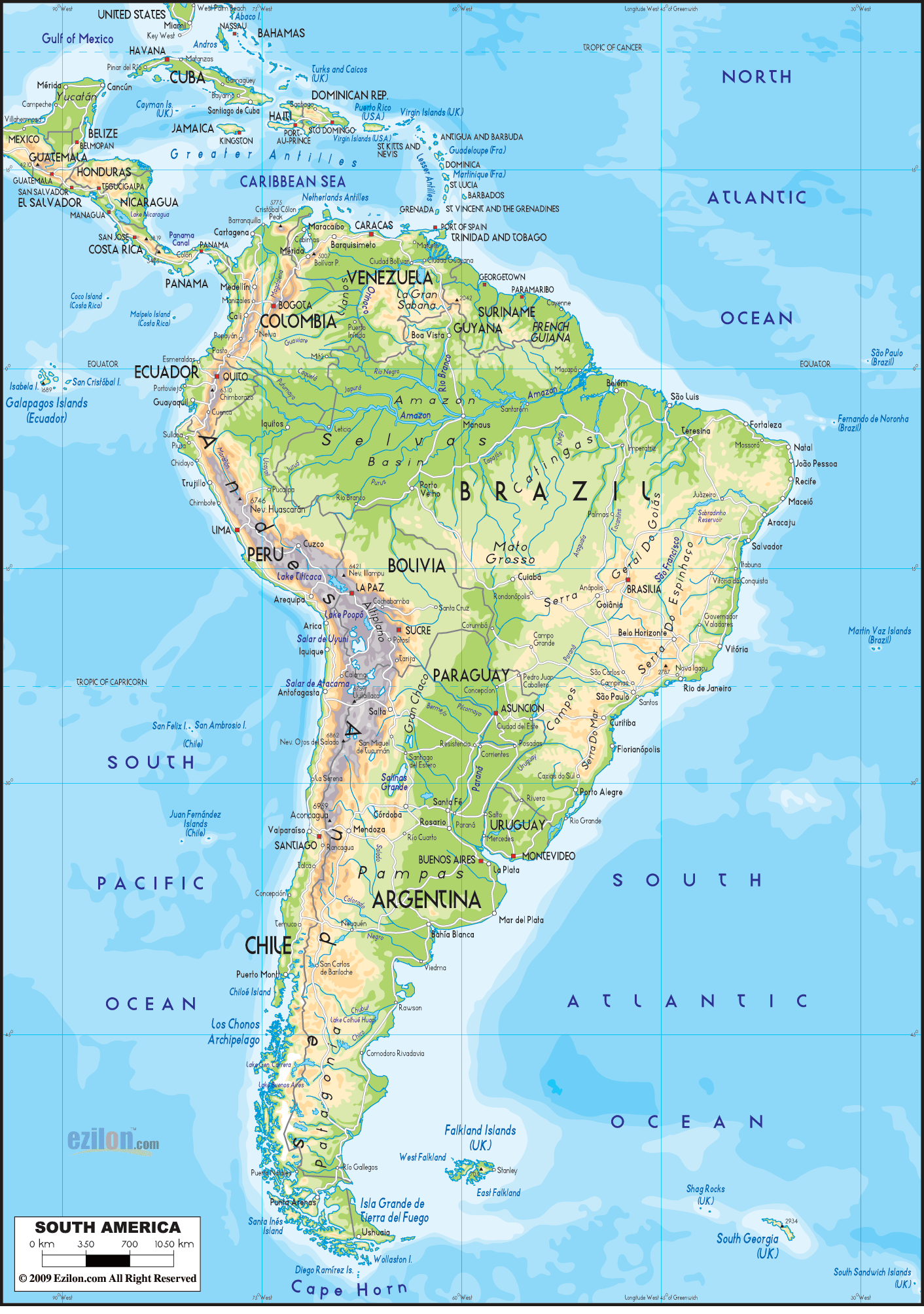


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Geography of South America: A Comprehensive Outline. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!