Unraveling the Political Landscape of Japan: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Unraveling the Political Landscape of Japan: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Political Landscape of Japan: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Political Landscape of Japan: A Comprehensive Guide
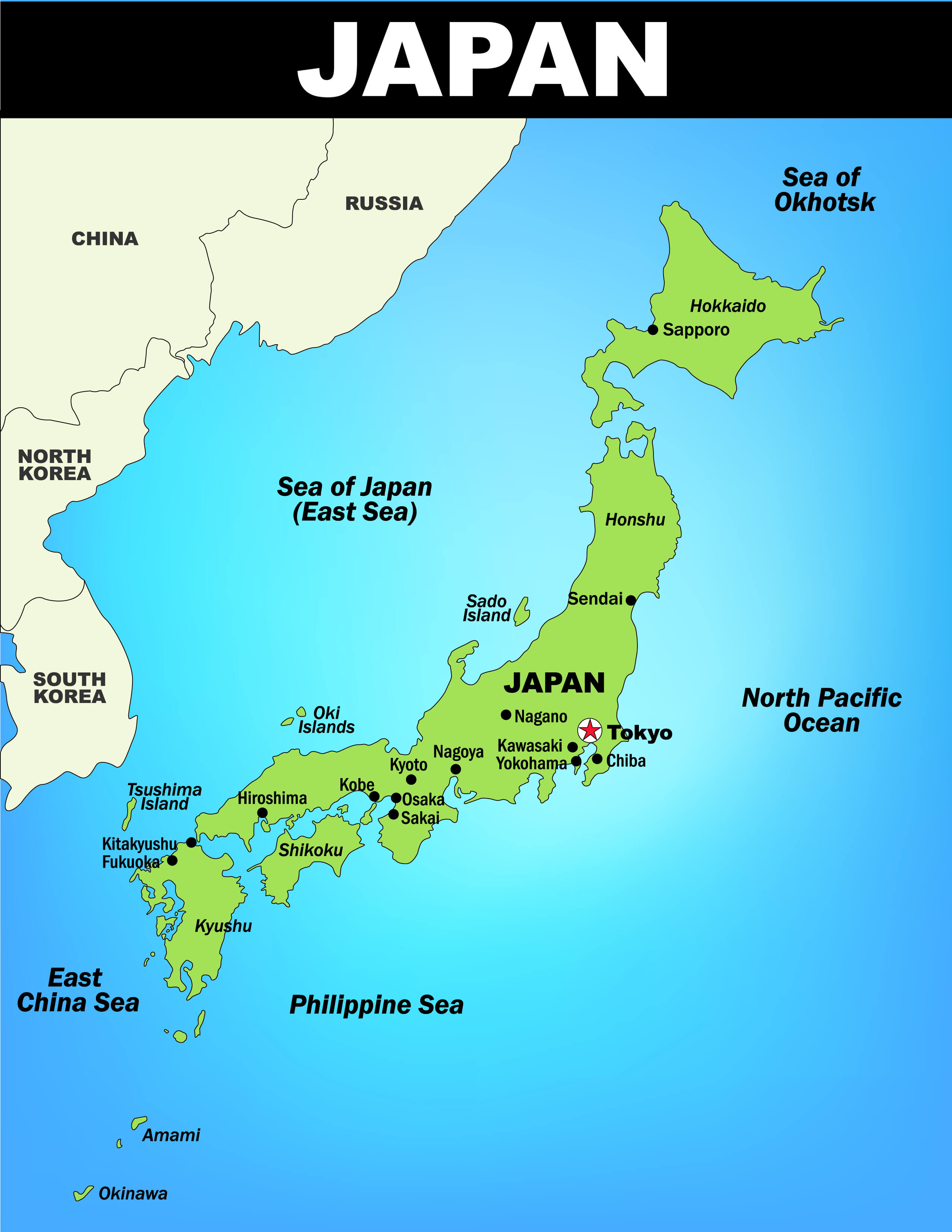
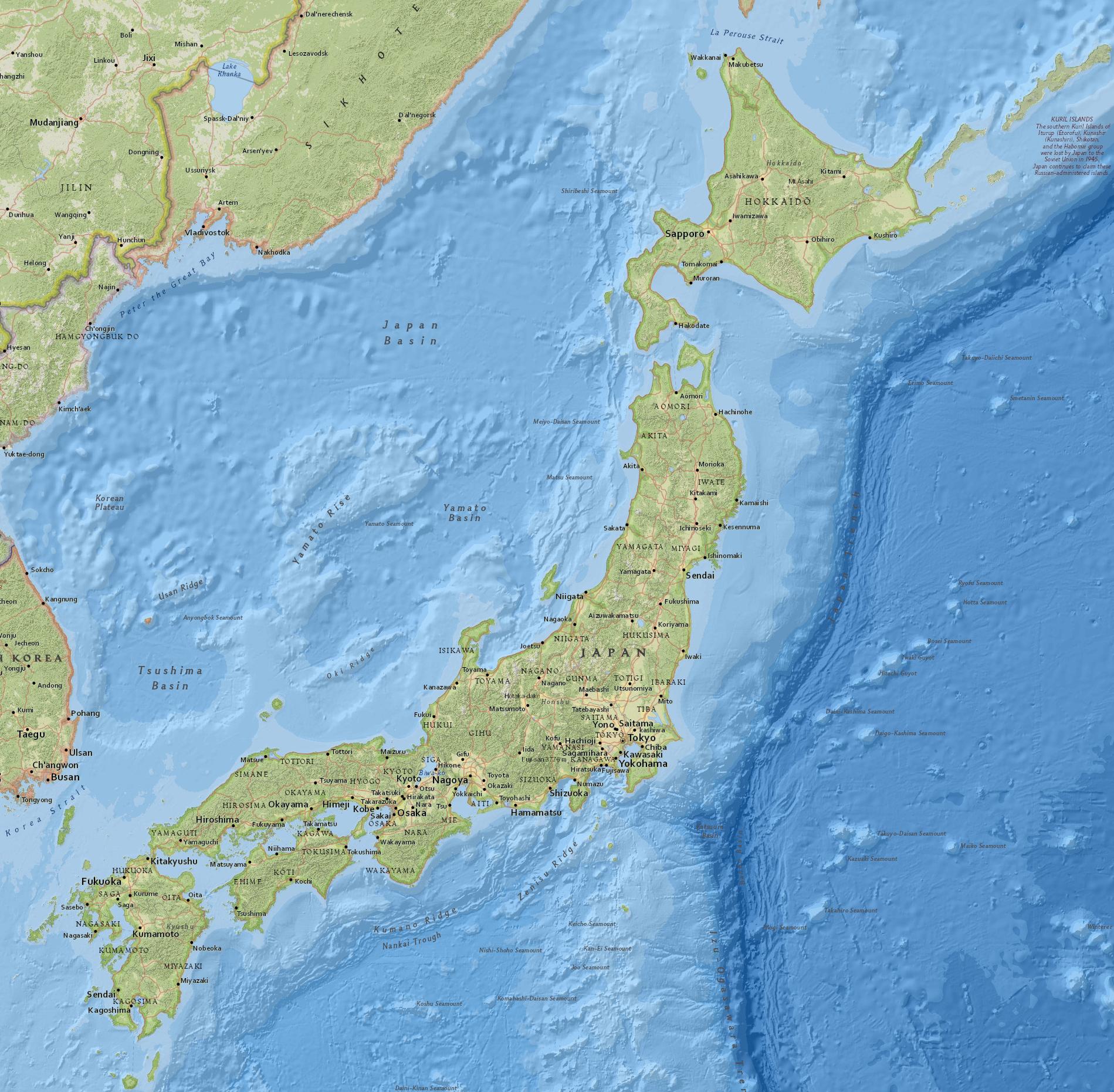
The political map of Japan presents a fascinating tapestry of administrative divisions, each with its unique history, culture, and economic contributions. Understanding this intricate web of governance is crucial for comprehending Japan’s complex political dynamics, its economic powerhouse status, and its role in the global arena.
Administrative Divisions: A Hierarchy of Governance
Japan’s political map is structured in a hierarchical manner, with four distinct levels of administration:
-
Prefectures (ken, do, fu, to): The primary administrative units of Japan, resembling states in the United States. There are 47 prefectures in total, each governed by a prefectural governor and a prefectural assembly. These prefectures are further subdivided into:
- Cities (shi): Urban centers with significant populations and administrative autonomy.
- Towns (machi) and Villages (mura): Smaller, rural communities with less administrative power compared to cities.
- Special Wards (ku): Unique to Tokyo, the capital city, these divisions function similarly to cities but are directly under the control of the Tokyo Metropolitan Government.
- Municipalities (shi, machi, mura): These are the basic units of local government, encompassing cities, towns, and villages.
- Local Government Districts (chiku): Smaller subdivisions within municipalities, primarily for administrative purposes.
A Historical Perspective: The Evolution of Japan’s Political Map
Japan’s political map has undergone significant transformations throughout its history. The current structure emerged following the Meiji Restoration in the late 19th century. Prior to this, Japan was divided into feudal domains (han) ruled by powerful lords (daimyo). The Meiji government centralized power and established a system of prefectures based on the old domains.
The early 20th century saw further refinements, including the creation of special wards in Tokyo and the consolidation of smaller municipalities. Post-World War II, Japan’s political map remained largely unchanged, with the exception of a few minor adjustments.
The Importance of Understanding Japan’s Political Map
Understanding the political map of Japan offers valuable insights into various aspects of the country:
- Decentralization and Local Governance: Japan’s political map highlights the importance of local governance. Prefectures and municipalities have significant autonomy in managing their own affairs, fostering a sense of community and local identity.
- Economic Development and Regional Disparities: The political map reveals the uneven distribution of economic activity across Japan. Major cities like Tokyo, Osaka, and Nagoya are economic powerhouses, while rural areas often face challenges in attracting investment and development.
- Political Representation and Public Policy: Understanding the structure of Japan’s political map is essential for comprehending how policies are formulated and implemented. Local governments play a crucial role in representing the interests of their constituents and influencing national policy decisions.
- Cultural Diversity and Identity: Each prefecture possesses a unique cultural heritage, reflected in local traditions, dialects, and cuisine. The political map provides a framework for understanding the diverse cultural tapestry of Japan.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Why is Tokyo divided into special wards?
A: Tokyo is a sprawling metropolis with a vast population. Dividing the city into special wards allows for more efficient administration and local governance. This system ensures that each ward has its own elected council and mayor, addressing local concerns and needs.
Q: What are the main differences between cities, towns, and villages in Japan?
A: Cities are typically larger and more urbanized, with a greater concentration of population and economic activity. Towns and villages are generally smaller and more rural, often characterized by agriculture and traditional industries. The level of administrative autonomy and funding varies between these categories.
Q: How does Japan’s political map compare to those of other countries?
A: Compared to countries with a federal system, such as the United States, Japan’s political map reflects a more centralized structure. The central government holds significant power, although prefectures and municipalities enjoy a degree of autonomy in local affairs.
Tips for Navigating Japan’s Political Map
- Visualize the map: Use online resources or physical maps to visualize the geographical distribution of prefectures, cities, towns, and villages.
- Focus on key regions: Familiarize yourself with the major economic centers, cultural hubs, and areas of historical significance.
- Explore local government websites: Websites of prefectures and municipalities offer valuable information about local policies, services, and events.
- Engage with local communities: Spending time in different parts of Japan can provide firsthand insights into the unique characteristics and perspectives of local communities.
Conclusion
The political map of Japan is a reflection of its complex history, diverse culture, and dynamic economy. Understanding this map is essential for appreciating the country’s administrative structure, local governance, and the intricate interplay of national and regional forces. By navigating the complexities of Japan’s political landscape, we gain a deeper understanding of this fascinating nation and its place in the world.

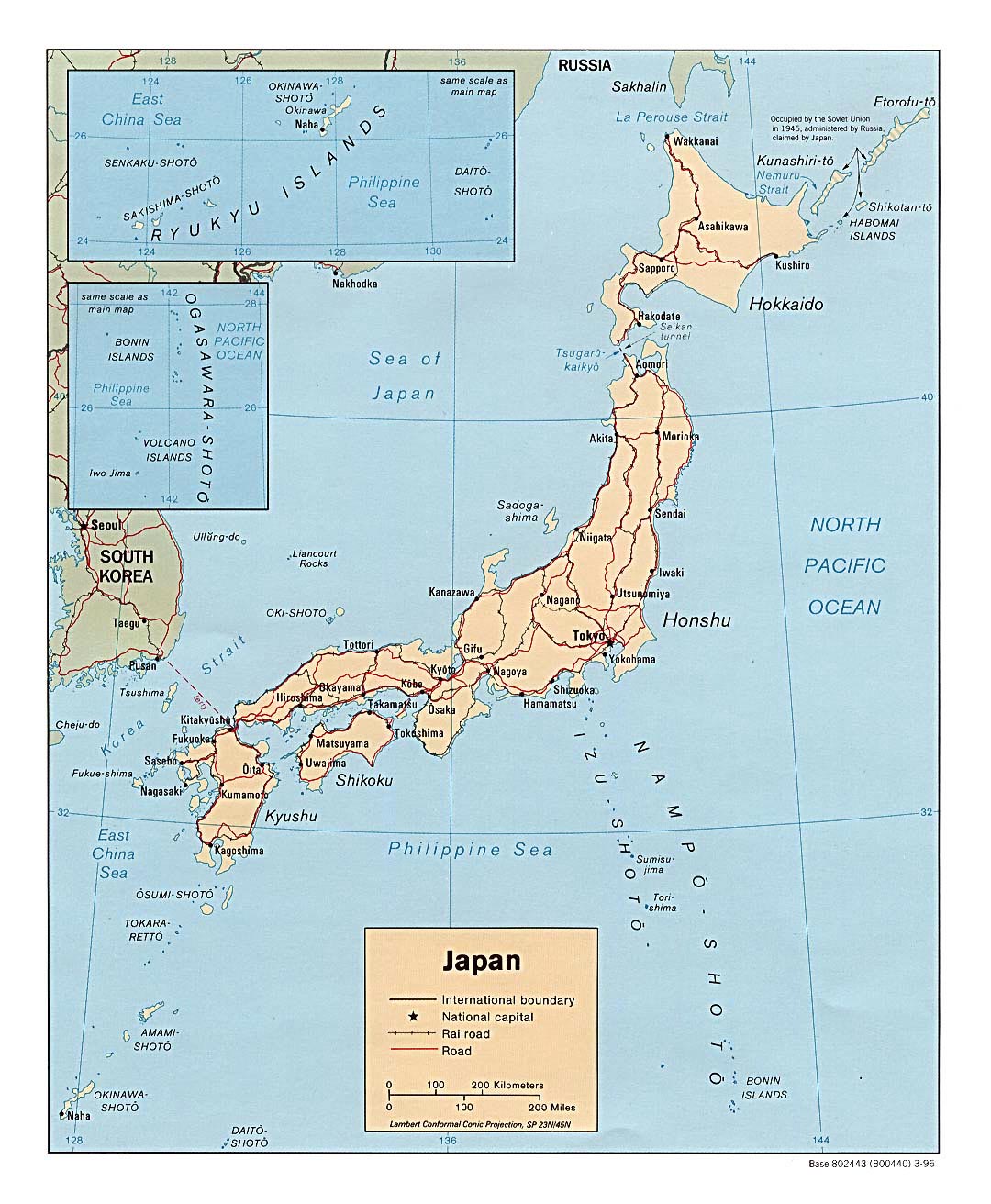
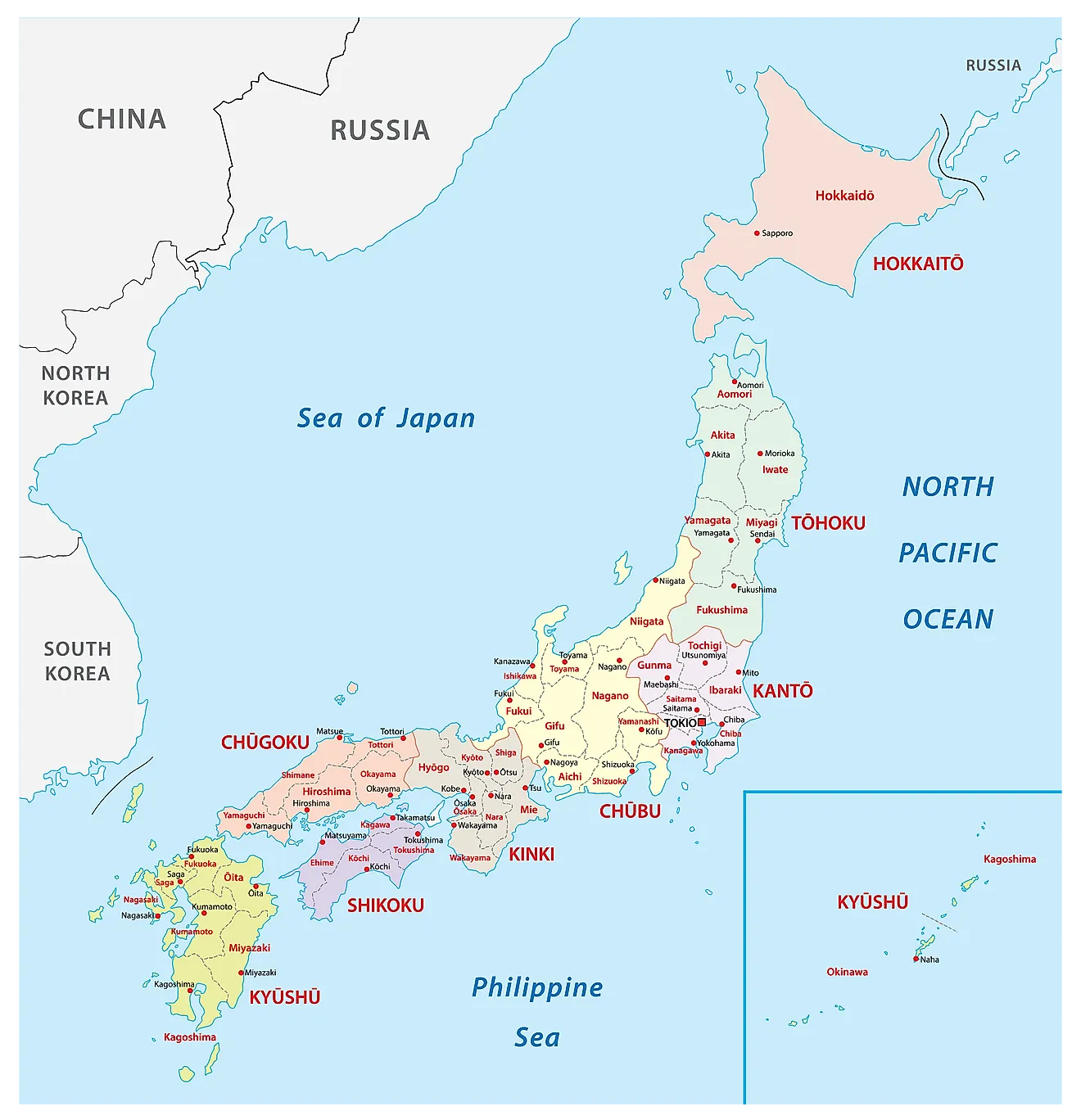

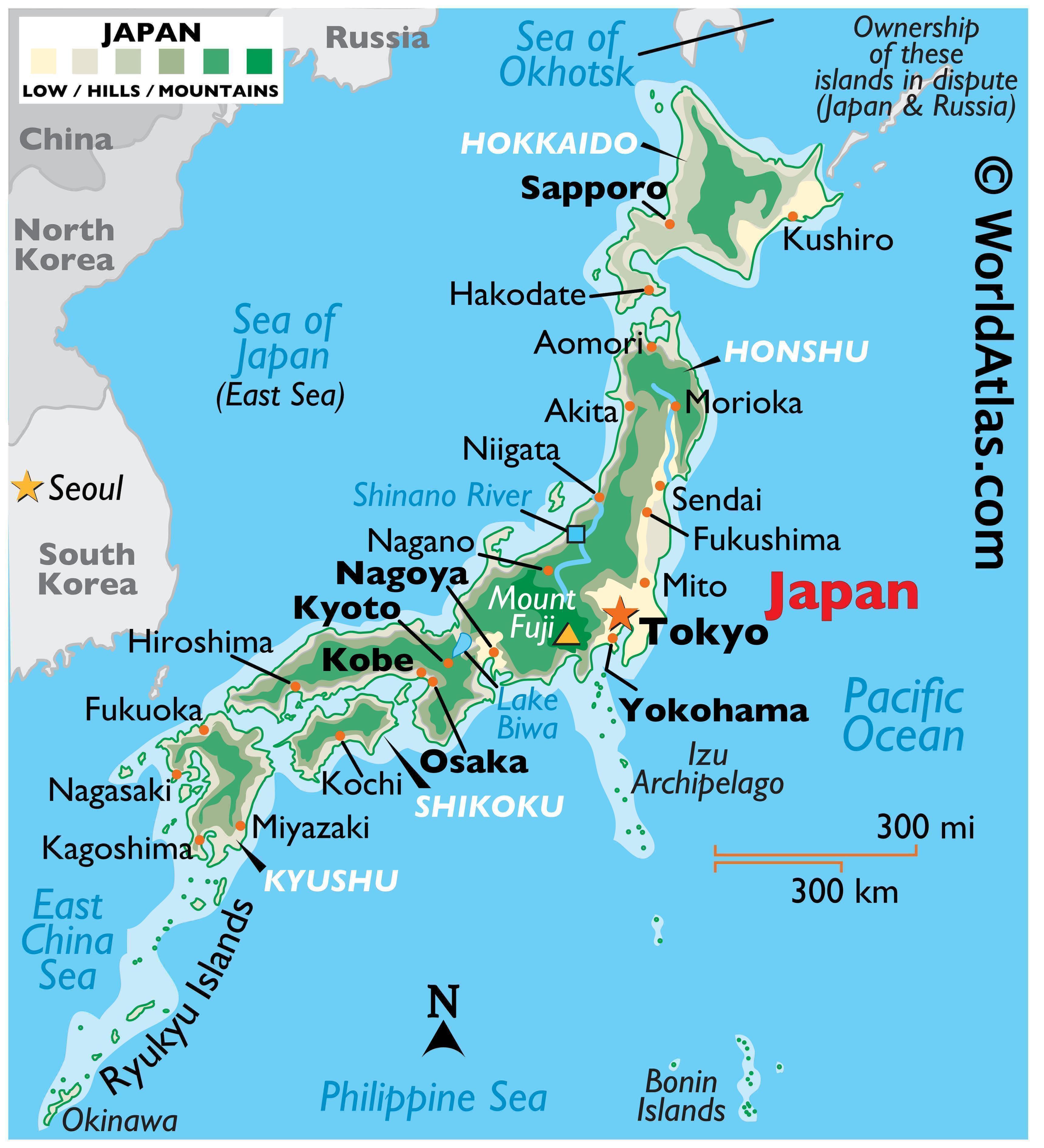


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Political Landscape of Japan: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!