Unveiling California’s Rainfall Patterns: A Geographical Perspective
Related Articles: Unveiling California’s Rainfall Patterns: A Geographical Perspective
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling California’s Rainfall Patterns: A Geographical Perspective. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling California’s Rainfall Patterns: A Geographical Perspective
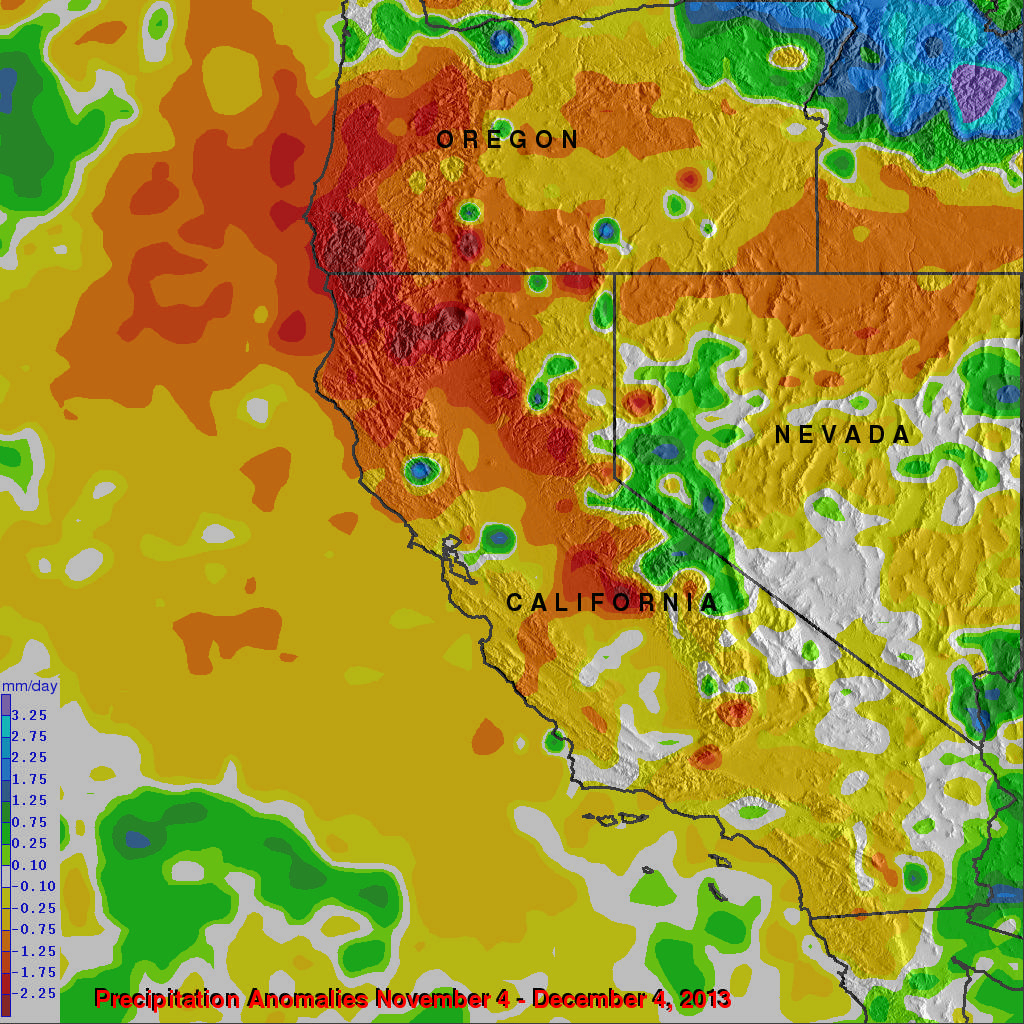
California, a state known for its diverse landscapes and vibrant ecosystems, experiences a wide range of rainfall patterns, shaping its environment and influencing its water resources. Understanding the distribution of rainfall across California is crucial for managing water supply, mitigating drought risks, and preserving the state’s natural beauty.
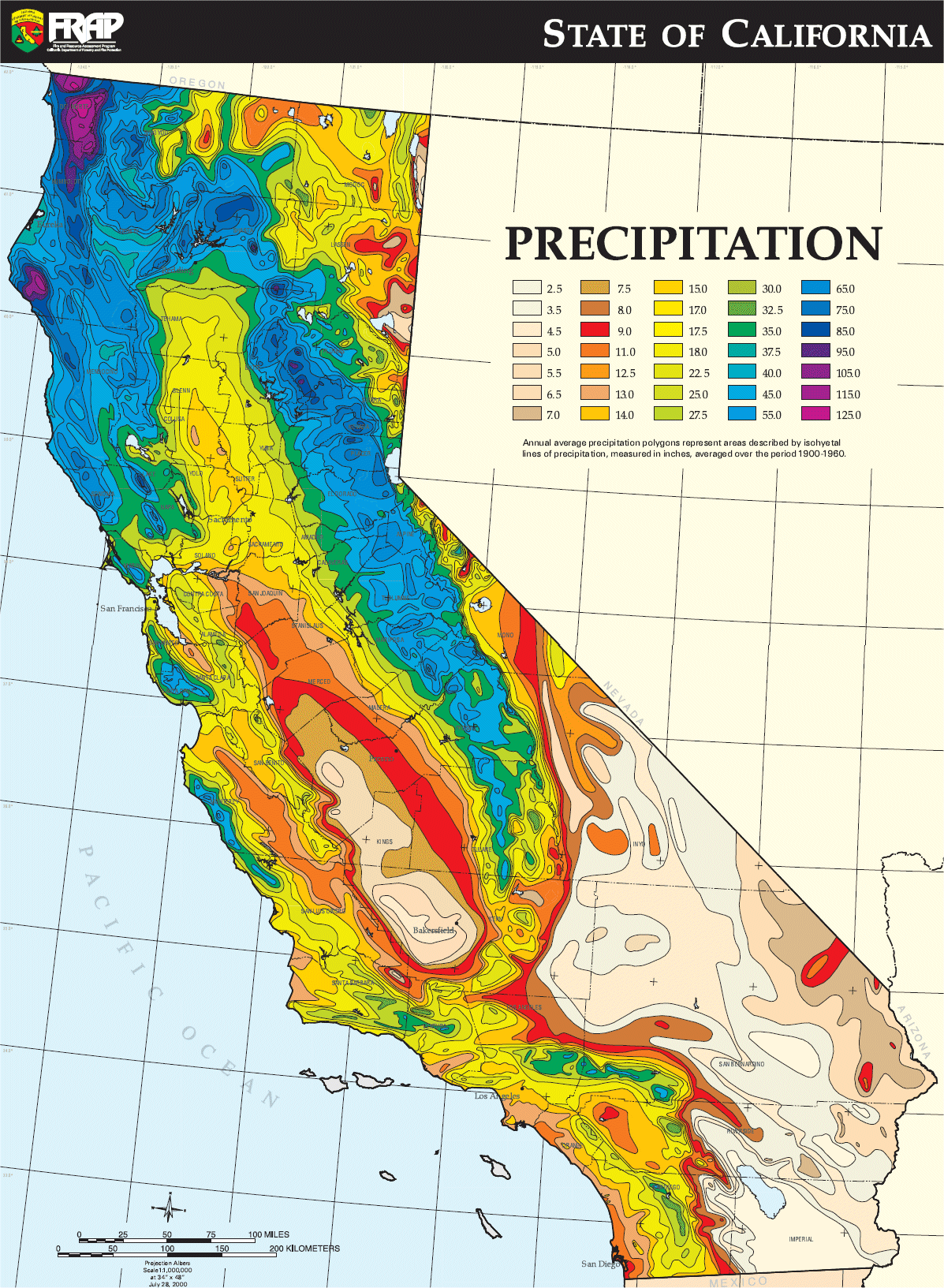
A State of Contrasts: Rainfall Distribution in California
California’s rainfall patterns are far from uniform. The state can be broadly divided into three distinct rainfall zones:
-
Northern California: This region receives the highest rainfall, with an average annual precipitation of 40-60 inches. The Sierra Nevada Mountains play a crucial role in influencing rainfall patterns, as they act as a barrier to moisture-laden winds from the Pacific Ocean. The orographic lift caused by the mountains leads to heavy precipitation on their western slopes, particularly in the winter months.
-
Central California: This region experiences a more moderate rainfall regime, with an average annual precipitation of 20-40 inches. The Central Valley, located between the Sierra Nevada and the Coast Ranges, is generally drier than the coastal areas. Rainfall in this region is influenced by both the Sierra Nevada and the Coast Ranges, with the latter blocking some of the moisture from reaching the valley.
-
Southern California: This region receives the lowest rainfall, with an average annual precipitation of 10-20 inches. The influence of the Pacific Ocean is less pronounced in Southern California, resulting in a drier climate. The Santa Ana winds, which originate in the desert and blow towards the coast, can further exacerbate dry conditions and contribute to wildfires.
The Importance of Rainfall Maps
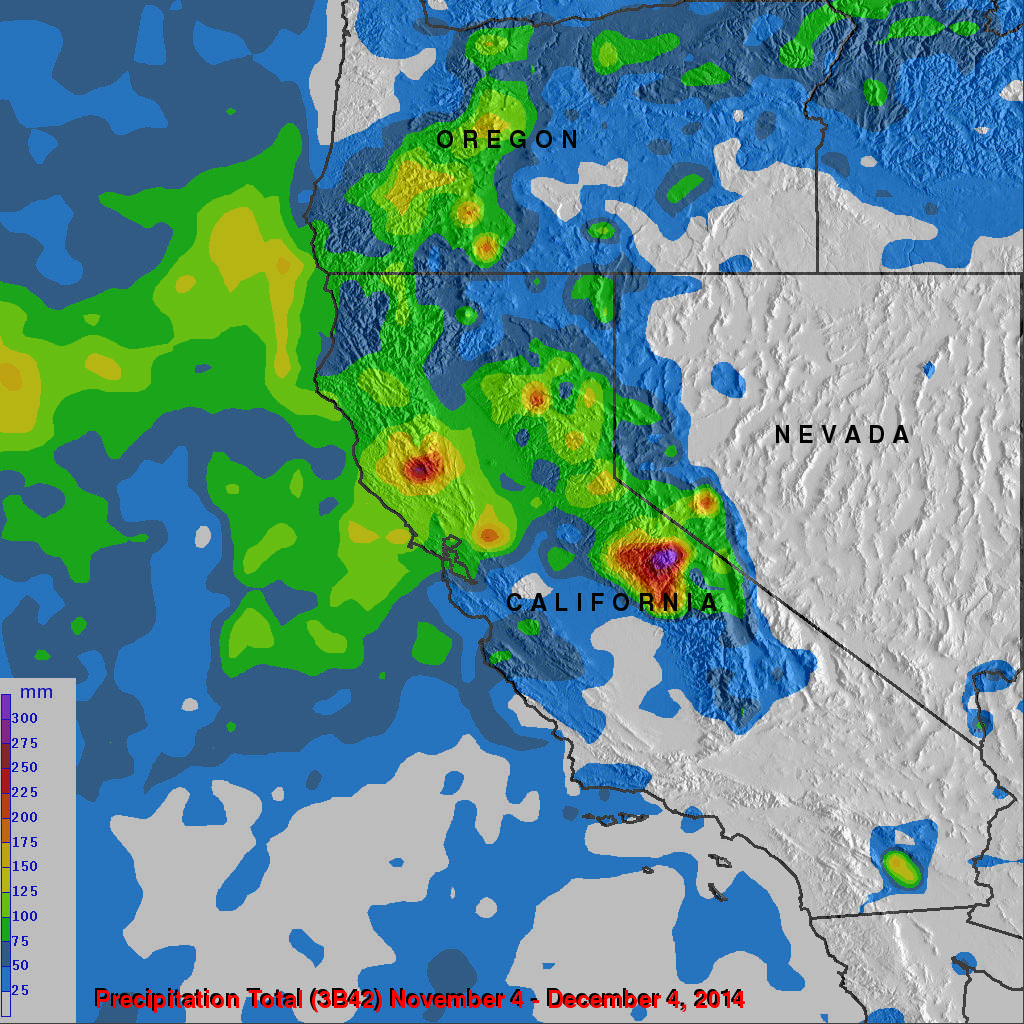
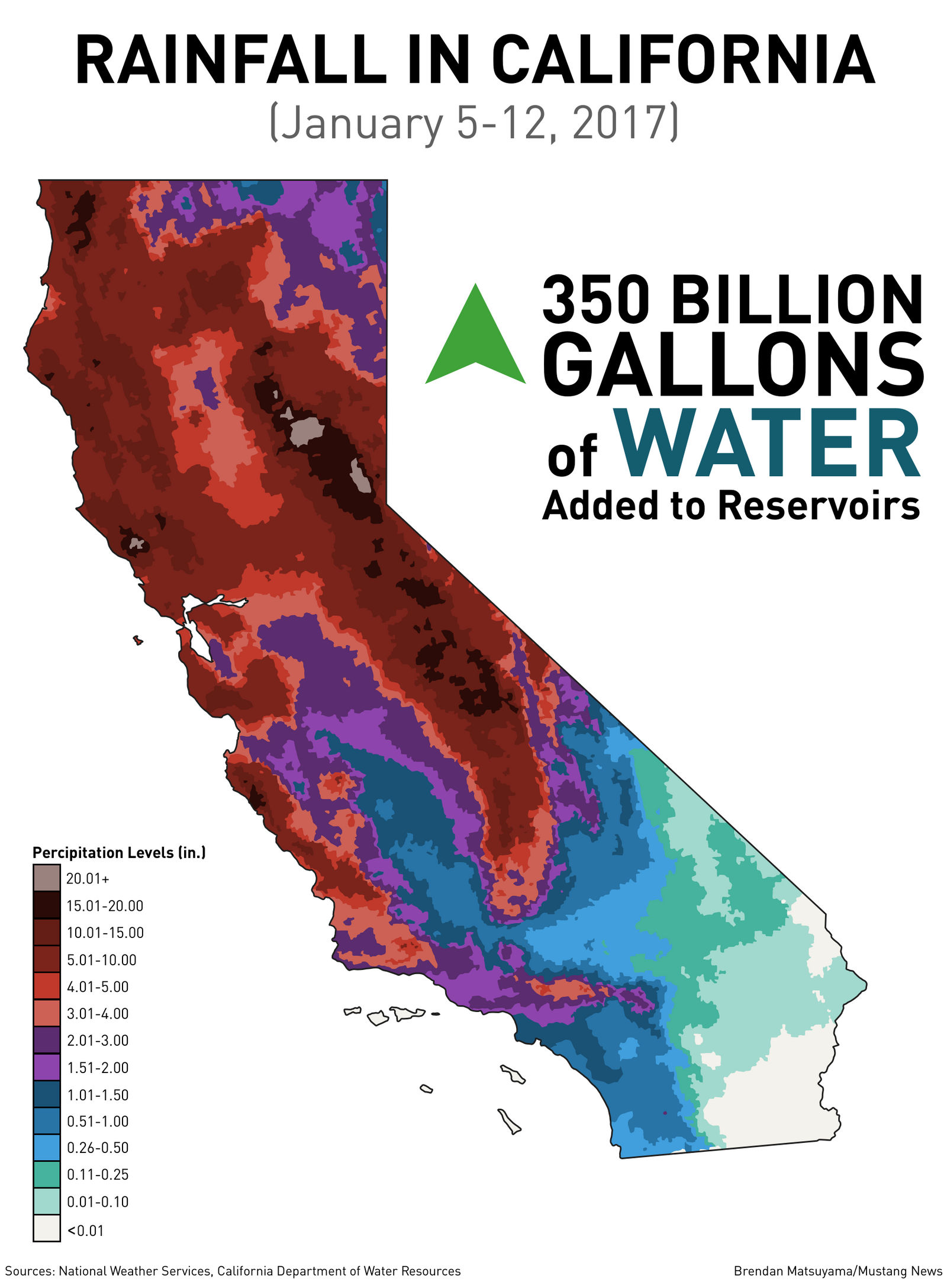
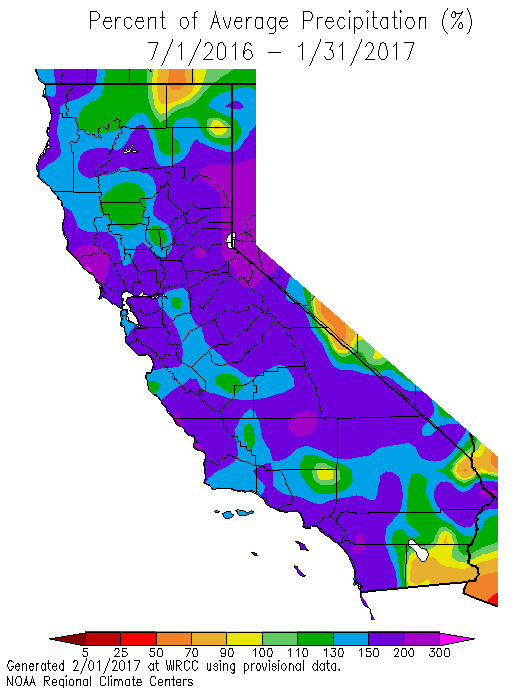
Rainfall maps provide a visual representation of precipitation patterns across California, highlighting areas of high and low rainfall. These maps are essential tools for various purposes, including:
-
Water Resource Management: By understanding rainfall patterns, water managers can effectively allocate water resources to different regions based on their needs. This is particularly crucial during periods of drought, when water scarcity becomes a pressing concern.
-
Drought Monitoring and Prediction: Rainfall maps help track precipitation trends and identify areas most vulnerable to drought. This information is essential for developing drought mitigation strategies and ensuring water security.
-
Agriculture and Irrigation: Farmers rely on rainfall maps to plan their irrigation needs and adjust their planting schedules based on anticipated rainfall patterns.
-
Wildfire Prevention: Rainfall maps are vital for identifying areas prone to wildfires, as dry conditions and low rainfall can increase the risk of ignition and spread.
-
Ecosystem Management: Rainfall patterns play a critical role in shaping the distribution of plant and animal life in California. By understanding rainfall patterns, conservation efforts can be tailored to specific ecosystems and their needs.
Interpreting Rainfall Maps: Key Considerations
When interpreting rainfall maps, it is important to consider several factors:
-
Temporal Variation: Rainfall patterns can vary significantly over time, both seasonally and annually. Maps depicting long-term average rainfall may not accurately reflect current conditions.
-
Spatial Resolution: The resolution of a rainfall map determines the level of detail it provides. High-resolution maps can show rainfall variations within small areas, while low-resolution maps provide a broader overview.
-
Data Sources: Rainfall maps are often based on data collected from various sources, including weather stations, radar systems, and satellite imagery. The quality and reliability of the data can influence the accuracy of the maps.
FAQs about California Rainfall Maps
Q: What is the most common type of rainfall in California?
A: California experiences a Mediterranean climate, characterized by wet winters and dry summers. The majority of rainfall occurs during the winter months, from November to March.
Q: How are rainfall maps created?
A: Rainfall maps are typically created by combining data from various sources, including weather stations, radar systems, and satellite imagery. This data is then processed and analyzed to generate a visual representation of rainfall patterns.
Q: What are the limitations of rainfall maps?
A: Rainfall maps are valuable tools but have limitations. They often represent averages over time and space, and may not accurately reflect localized variations in rainfall. Additionally, the accuracy of maps can be affected by data quality and processing methods.
Tips for Using Rainfall Maps Effectively
-
Consider the time scale: When using rainfall maps, it is important to consider the time period represented by the data. Maps depicting long-term averages may not be relevant for short-term forecasting.
-
Compare multiple sources: It is beneficial to compare rainfall maps from different sources to get a more comprehensive understanding of precipitation patterns.
-
Consult with experts: If you require detailed rainfall information for specific purposes, it is recommended to consult with meteorologists or hydrologists who can provide expert guidance.
Conclusion: A Vital Resource for Understanding California’s Water Landscape
Rainfall maps are an indispensable tool for understanding and managing California’s water resources. They provide valuable insights into precipitation patterns, helping inform water management decisions, mitigate drought risks, and support the state’s diverse ecosystems. By utilizing rainfall maps and incorporating them into planning and decision-making processes, California can better prepare for the challenges and opportunities posed by its unique rainfall patterns.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling California’s Rainfall Patterns: A Geographical Perspective. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!