Unveiling Insights: A Comprehensive Guide to Creating Heat Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling Insights: A Comprehensive Guide to Creating Heat Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Insights: A Comprehensive Guide to Creating Heat Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling Insights: A Comprehensive Guide to Creating Heat Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling Insights: A Comprehensive Guide to Creating Heat Maps
- 3.1 Understanding the Essence of Heat Maps
- 3.2 Diverse Applications of Heat Maps
- 3.3 Essential Steps for Creating a Heat Map
- 3.4 FAQs on Creating Heat Maps
- 3.5 Tips for Creating Effective Heat Maps
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Unveiling Insights: A Comprehensive Guide to Creating Heat Maps
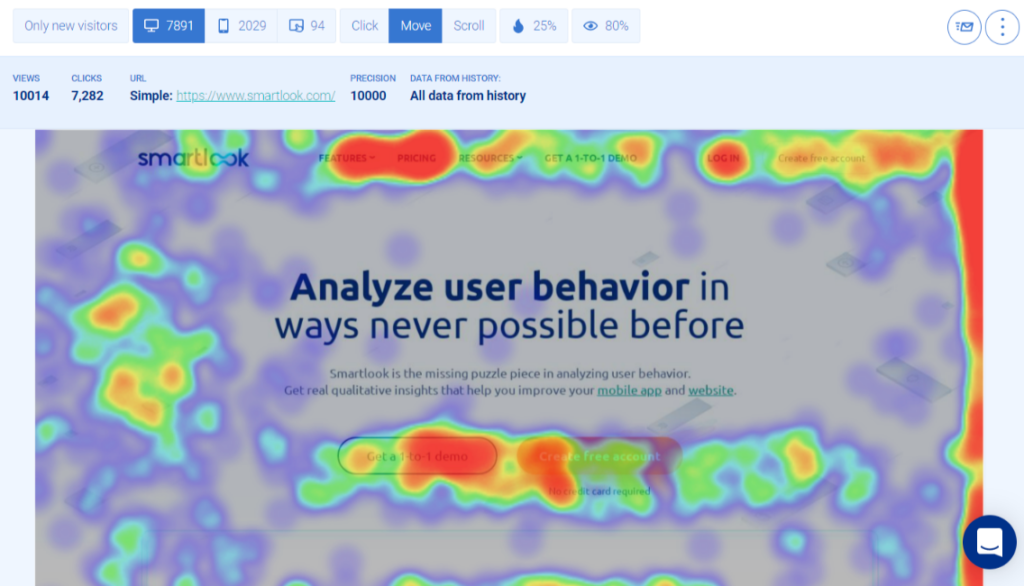
Heat maps, visual representations of data density, are powerful tools for uncovering patterns and insights within datasets. Their ability to translate complex data into easily digestible visual formats makes them invaluable across various fields, from marketing and user experience design to healthcare and finance. This guide provides a comprehensive exploration of heat map creation, encompassing its theoretical foundation, practical applications, and essential steps for successful implementation.
Understanding the Essence of Heat Maps
At its core, a heat map utilizes color gradients to represent the concentration of data points across a defined space. Areas with high data density are depicted in vibrant, "hot" colors, while regions with lower density are represented by cooler, less saturated hues. This visual representation allows for rapid identification of areas of interest, highlighting patterns, trends, and anomalies within the data.
Diverse Applications of Heat Maps
The versatility of heat maps extends across numerous disciplines, each leveraging its unique capabilities to address specific needs.
1. Marketing and Sales:
- Website Analysis: Heat maps track user interactions on websites, identifying areas of high engagement (e.g., buttons, images, text) and revealing areas that require improvement (e.g., low-click areas, abandoned forms).
- Advertising Campaigns: Heat maps analyze the effectiveness of online advertising campaigns, pinpointing the most engaging elements within advertisements and optimizing their design for higher conversion rates.
- Customer Journey Mapping: Heat maps visualize the flow of customer interactions with a brand, identifying pain points and areas for improvement in the customer experience.
2. User Experience (UX) Design:
- Website Usability: Heat maps reveal user behavior on websites, highlighting areas of confusion or frustration. This information helps designers improve navigation, content organization, and overall user experience.
- App Design: Heat maps analyze user interactions within mobile apps, identifying areas of high engagement and areas that need improvement for enhanced usability and user satisfaction.
- Interactive Design: Heat maps provide insights into user behavior on interactive elements, such as sliders, menus, and buttons, guiding design decisions for intuitive and engaging user experiences.
3. Healthcare:
- Medical Imaging: Heat maps are used in medical imaging to highlight areas of abnormal tissue density, aiding in diagnosis and treatment planning.
- Epidemiology: Heat maps visualize the geographical distribution of diseases, enabling public health professionals to identify areas of high risk and implement targeted interventions.
- Patient Monitoring: Heat maps track physiological parameters, such as heart rate and blood pressure, over time, providing visual insights into patient health trends.
4. Finance:
- Stock Market Analysis: Heat maps visualize stock price movements across different sectors and timeframes, revealing market trends and identifying potential investment opportunities.
- Risk Management: Heat maps identify areas of high financial risk, allowing for proactive risk mitigation strategies.
- Financial Reporting: Heat maps provide visual summaries of financial data, making complex information more accessible and understandable.
Essential Steps for Creating a Heat Map
Creating a heat map involves a series of steps, each contributing to the accuracy and effectiveness of the final visualization.
1. Data Collection:
- Identify the Data: Determine the specific data points you wish to visualize and ensure their relevance to the intended analysis.
- Data Source: Choose the appropriate data source, whether it’s a website analytics platform, a customer relationship management system, or a dedicated data collection tool.
- Data Cleaning: Ensure data accuracy and consistency by removing duplicates, correcting errors, and standardizing formats.
2. Defining the Space:
- Spatial Boundaries: Determine the spatial boundaries of the heat map, such as a website page, a geographic region, or a specific area of interest.
- Grid Structure: Choose a suitable grid structure for the heat map, considering the granularity of the data and the desired level of detail.
- Coordinate System: Define the coordinate system for mapping data points within the chosen space, ensuring accurate representation.
3. Data Aggregation:
- Data Grouping: Group data points based on relevant criteria, such as time intervals, user demographics, or specific events.
- Density Calculation: Calculate the density of data points within each grid cell, using methods like kernel density estimation or simple count aggregation.
- Normalization: Normalize the density values to ensure consistent color representation across the heat map.
4. Color Scheme Selection:
- Color Gradient: Choose a color gradient that effectively represents the data density, with vibrant colors for high density and cooler colors for low density.
- Colorblind Accessibility: Consider the accessibility of the color scheme for individuals with colorblindness, ensuring clear visual distinction between different density levels.
- Data Interpretation: Select a color scheme that aligns with the intended interpretation of the heat map, enhancing the clarity and impact of the visualization.
5. Heat Map Visualization:
- Software Options: Utilize specialized software tools like Google Analytics, Hotjar, or Tableau to create heat maps.
- Custom Development: Develop custom heat map visualizations using programming languages like Python or R, offering greater flexibility and control over the final output.
- Visual Clarity: Ensure the heat map is visually clear and easy to interpret, with appropriate labels, legends, and annotations.
FAQs on Creating Heat Maps
Q: What data is suitable for creating heat maps?
A: Heat maps are effective for visualizing data that can be mapped onto a spatial domain, such as website clicks, user interactions within an app, geographic locations, or medical imaging data.
Q: How do I choose the right color scheme for my heat map?
A: Consider the intended interpretation of the heat map and the accessibility of the chosen colors. A common approach is to use a gradient from red (high density) to blue (low density), but other options exist depending on the specific data and visual preferences.
Q: What are the limitations of heat maps?
A: Heat maps provide a valuable overview but may not capture the full complexity of the data. They are best used in conjunction with other data analysis techniques and should not be considered a definitive answer to all data-related questions.
Q: How can I improve the accuracy of my heat map?
A: Ensure accurate data collection, choose an appropriate grid structure, and use robust density calculation methods. Consider the potential for bias in the data and adjust the visualization accordingly.
Tips for Creating Effective Heat Maps
- Keep it Simple: Avoid overcrowding the heat map with too much information, focusing on the key insights you want to communicate.
- Use Clear Labels: Label the axes, grid cells, and legend to provide context and facilitate understanding.
- Highlight Areas of Interest: Use annotations or visual cues to draw attention to specific areas of high or low density.
- Consider Context: Provide relevant background information to help viewers understand the data and its implications.
- Test and Iterate: Experiment with different color schemes, grid structures, and data aggregation methods to optimize the effectiveness of the heat map.
Conclusion
Creating heat maps is a powerful technique for extracting valuable insights from complex data. By understanding the underlying principles, leveraging appropriate tools, and following best practices, individuals across various fields can harness the power of heat maps to uncover patterns, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions. As data continues to grow in volume and complexity, heat maps will remain a valuable tool for visualizing information, enabling deeper understanding and informed action.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Insights: A Comprehensive Guide to Creating Heat Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!