Unveiling the Ocean’s Highway: A Comprehensive Guide to Whale Migration Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Ocean’s Highway: A Comprehensive Guide to Whale Migration Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Ocean’s Highway: A Comprehensive Guide to Whale Migration Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Ocean’s Highway: A Comprehensive Guide to Whale Migration Maps
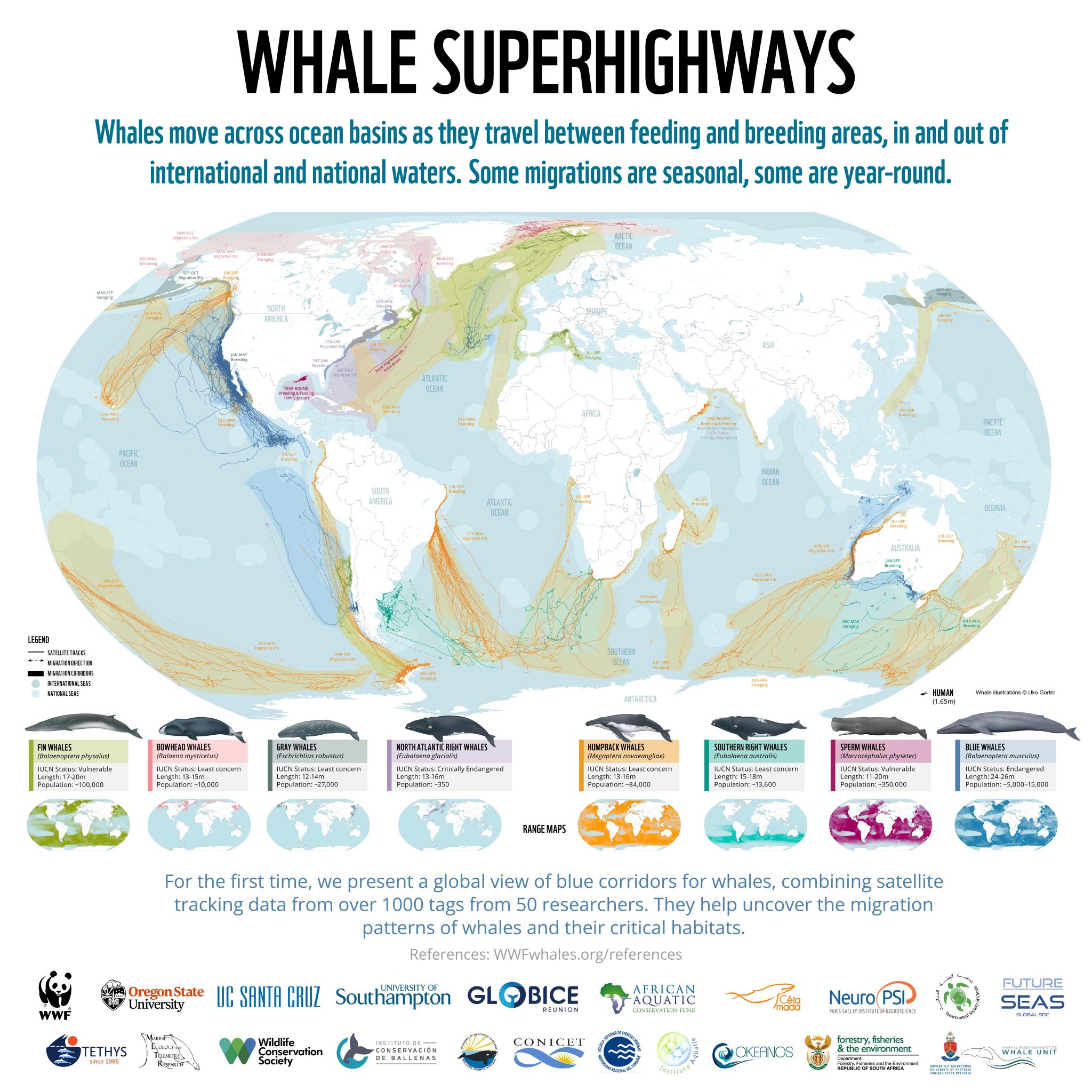
The vast expanse of the ocean, seemingly endless and uniform, harbors intricate patterns of life. Among these, the annual journeys of whales stand out as remarkable displays of instinct, adaptation, and resilience. These journeys, meticulously mapped and studied, reveal a complex network of ocean highways, each with its own unique story of survival and evolution.
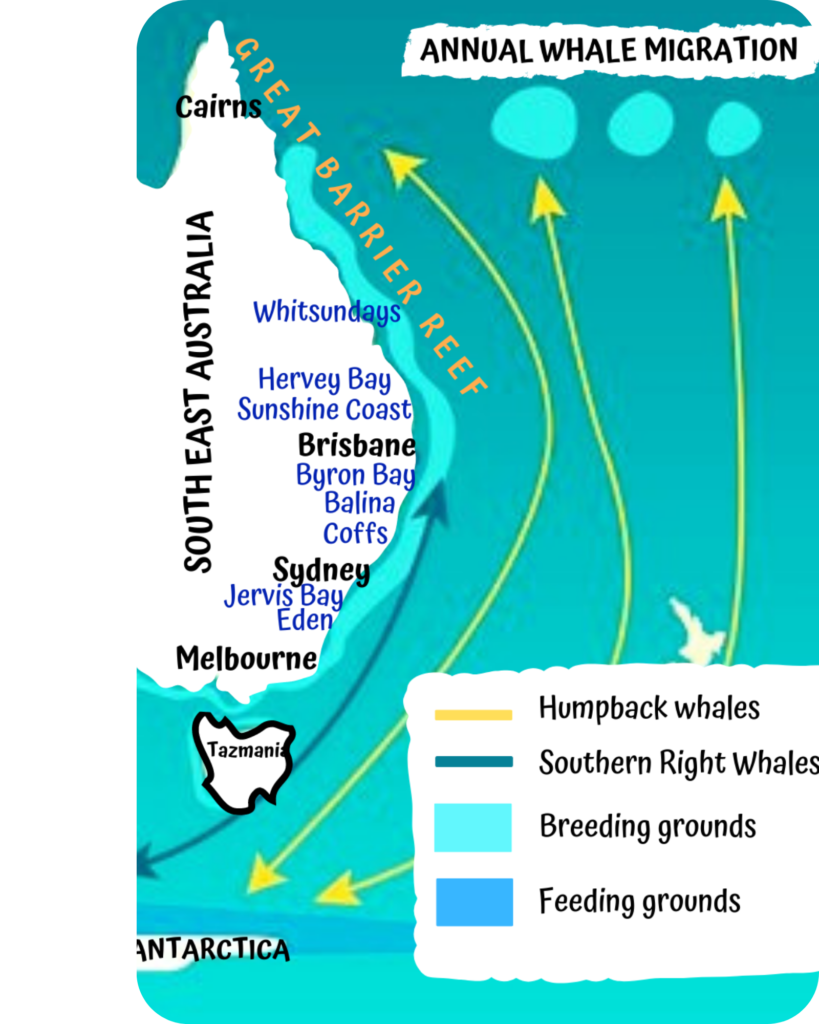
Understanding the Whale Migration Map
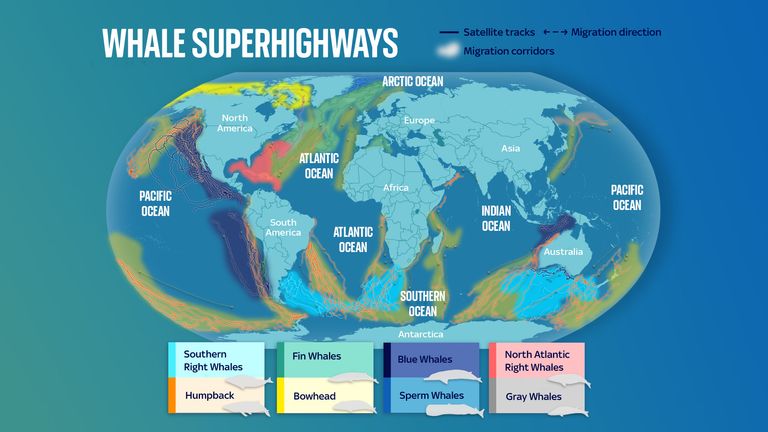
A whale migration map is a visual representation of the seasonal movement patterns of various whale species. These maps depict the routes taken by whales as they travel between their breeding grounds, where they mate and give birth, and their feeding grounds, where they nourish themselves for the demanding journey ahead. These maps are essential tools for scientists, conservationists, and enthusiasts alike, offering valuable insights into the ecology, behavior, and conservation needs of these magnificent creatures.
The Driving Forces Behind Migration
Several factors influence whale migration patterns, each playing a crucial role in ensuring the survival of these marine giants:
- Food Availability: Whales are highly specialized feeders, with diets ranging from tiny krill to massive squid. As their prey migrates seasonally, whales follow suit, seeking out areas of abundant food sources.
- Water Temperature: Whales are sensitive to water temperature, preferring specific ranges for breeding and feeding. Migration allows them to exploit the ideal conditions for each stage of their life cycle.
- Calving Grounds: Warm, sheltered waters are essential for the successful birth and development of whale calves. Breeding grounds provide protection from predators and ample food for nursing mothers.
- Reproduction: The migration routes often lead to specific breeding grounds, allowing whales to congregate and mate, ensuring the continuation of their species.
Mapping the Journey: Methods and Tools
Mapping whale migration relies on a combination of methods, each contributing to a comprehensive understanding of these journeys:
- Satellite Tracking: Advanced satellite tags attached to whales transmit data on their location, depth, and behavior, providing real-time insights into their movements.
- Photo Identification: Distinctive markings on whales, such as fluke patterns or dorsal fin shapes, allow researchers to identify individuals and track their movements over time.
- Acoustic Monitoring: Passive acoustic monitoring uses underwater microphones to detect whale vocalizations, providing information on their presence, distribution, and migration routes.
- Genetic Analysis: Analyzing whale DNA can reveal population structure and migration patterns, helping scientists understand the connectivity of whale populations across different regions.
The Importance of Whale Migration Maps
Whale migration maps serve as crucial tools for conservation efforts, providing valuable data to:
- Identify Critical Habitats: Mapping migration routes helps pinpoint areas of high whale concentration, enabling the establishment of protected areas and marine sanctuaries.
- Monitor Population Trends: By tracking migration patterns, scientists can assess the health and abundance of whale populations, identifying potential threats and implementing conservation measures.
- Minimize Human Impacts: Understanding whale migration routes assists in mitigating human activities that could disrupt their journeys, such as shipping traffic, fishing operations, and offshore development.
- Promote Sustainable Tourism: Whale watching tourism is a growing industry, and migration maps help guide responsible tourism practices, ensuring minimal disturbance to whales and their habitats.
FAQs about Whale Migration Maps
1. What are the longest whale migration routes?
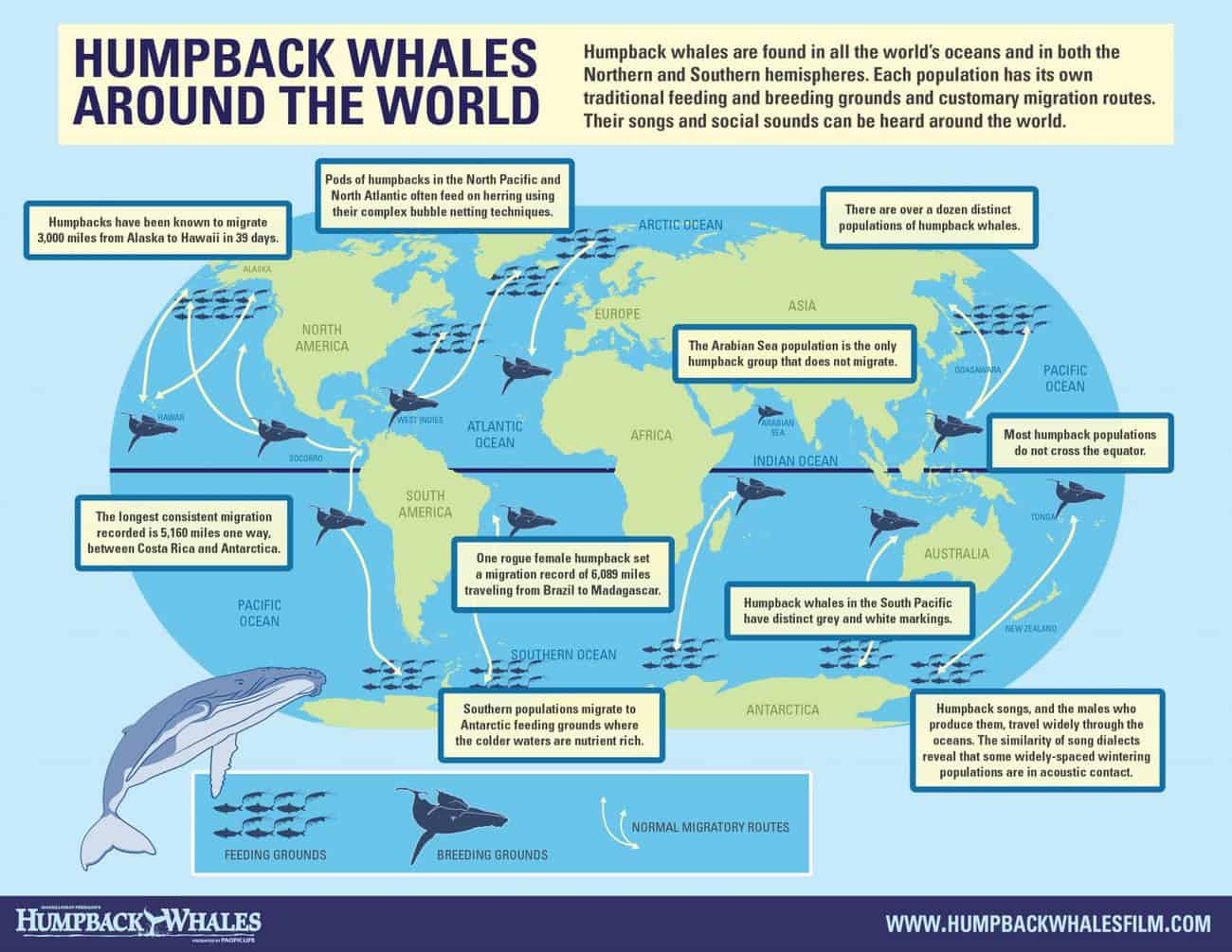
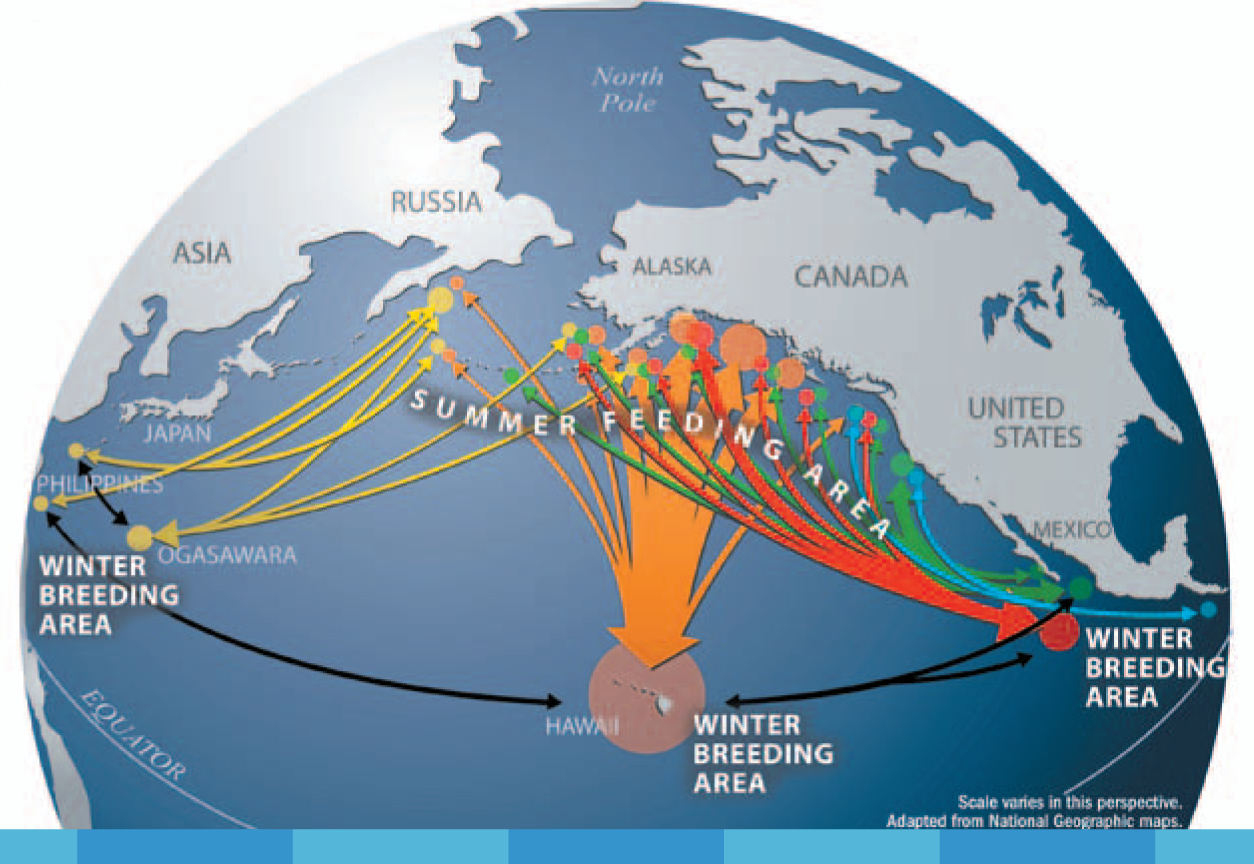
The longest whale migration routes are often attributed to humpback whales, with some individuals traveling over 5,000 miles from their breeding grounds in tropical waters to their feeding grounds in the Arctic and Antarctic.
2. How do whales navigate such vast distances?
Whales navigate using a combination of senses, including:
- Magnetoreception: Detecting Earth’s magnetic field allows whales to orient themselves and maintain a consistent course.
- Echolocation: Using sound waves, whales can map their surroundings and identify objects in their path.
- Visual Cues: Whales rely on visual cues, such as the position of the sun and stars, to navigate during daylight hours.
- Olfaction: Whales may use their sense of smell to detect specific chemical cues associated with their destination.
3. Do all whales migrate?
Not all whale species migrate. Some species, such as gray whales, undertake long-distance migrations, while others, like orcas, exhibit more localized movements.
4. What are the challenges facing whale migration?
Whale migration is threatened by various human activities, including:
- Climate Change: Rising ocean temperatures and changing ocean currents disrupt migration patterns and food availability.
- Pollution: Marine pollution, including plastic debris and chemical contaminants, poses health risks to whales and their offspring.
- Shipping Traffic: Collisions with ships and underwater noise pollution can disrupt whale migration and communication.
- Overfishing: Depletion of whale prey species can negatively impact their food supply and migration patterns.
Tips for Understanding Whale Migration Maps
- Focus on Species: Different whale species have distinct migration patterns, so it’s crucial to identify the specific species being mapped.
- Consider Time of Year: Whale migration is seasonal, so understanding the timing of their journeys is essential.
- Look for Key Locations: Identify breeding grounds, feeding grounds, and potential stopover points along migration routes.
- Recognize Threats: Identify areas where whale migration is threatened by human activities and consider how to mitigate these risks.
Conclusion
Whale migration maps are invaluable tools for understanding the intricate journeys of these majestic creatures. These maps reveal the interconnectedness of ocean ecosystems, highlighting the importance of protecting whale habitats and mitigating threats to their survival. By studying and appreciating these remarkable migrations, we gain a deeper understanding of the ocean’s delicate balance and our role in preserving its wonders.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Ocean’s Highway: A Comprehensive Guide to Whale Migration Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!