us forests map
Related Articles: us forests map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to us forests map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Look at the U.S. Forest Map: Unveiling the Importance of Our Green Heritage

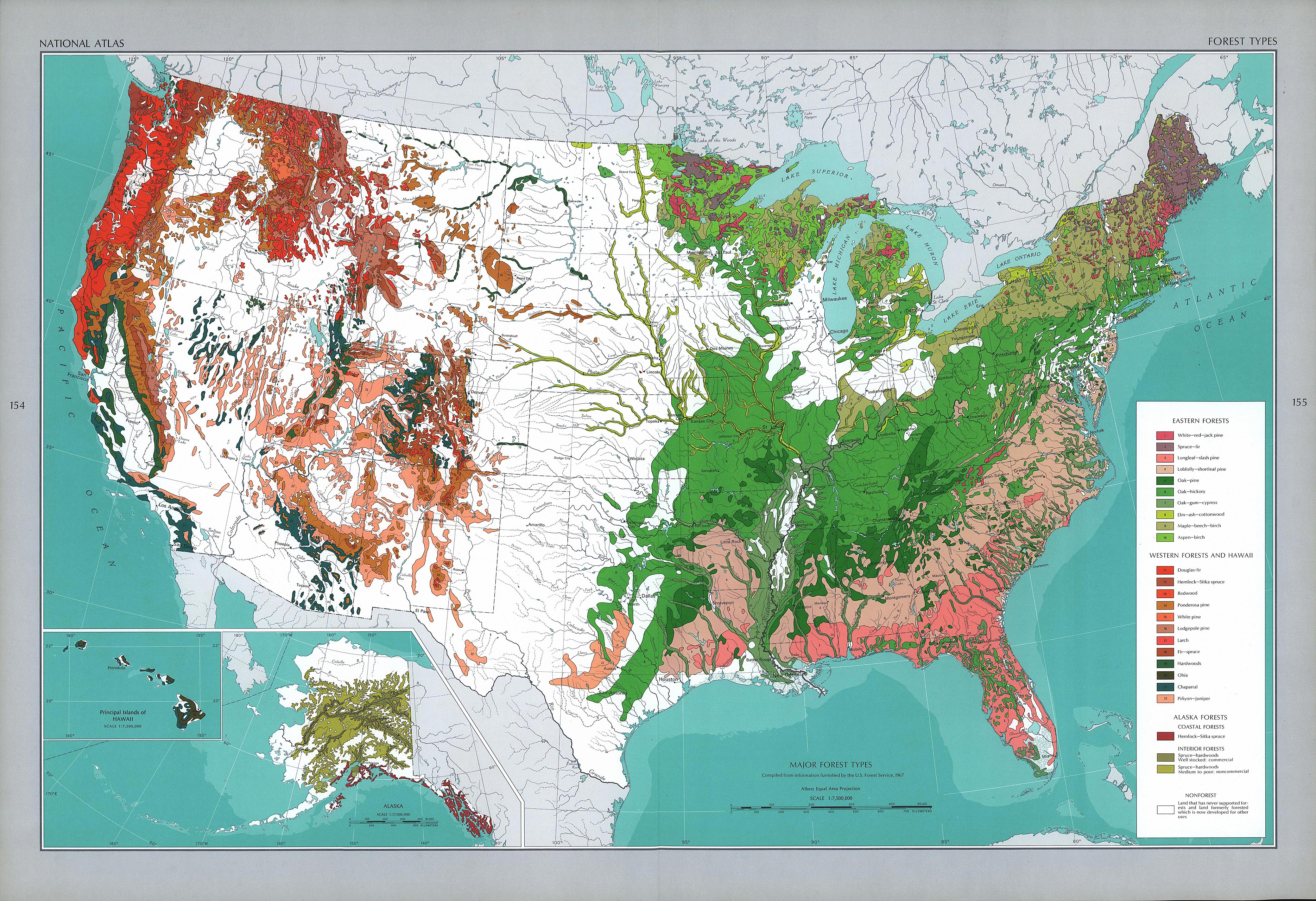
The United States is renowned for its vast and diverse landscapes, and forests play a crucial role in shaping this national identity. From the towering redwoods of California to the dense hardwood forests of the Appalachians, these ecosystems are not merely scenic backdrops; they are vital components of the nation’s environmental, economic, and social fabric. Understanding the distribution and characteristics of these forests is paramount, and the U.S. Forest Map provides a valuable tool for navigating this complex landscape.
Delving into the U.S. Forest Map:
The U.S. Forest Map is a comprehensive cartographic representation of the nation’s forest resources, providing insights into the extent, composition, and condition of these vital ecosystems. It is a dynamic resource, constantly evolving as new data is collected and analyzed. The map is not a static snapshot but a living document reflecting the dynamic nature of forests and their interactions with the environment.
Key Features of the U.S. Forest Map:
- Forest Cover: The map showcases the distribution of forest cover across the United States, delineating areas dominated by trees and distinguishing between different forest types. This information is crucial for understanding the extent of forest resources and their vulnerability to threats like deforestation and climate change.
- Forest Type: The U.S. Forest Map differentiates between various forest types, including deciduous, coniferous, and mixed forests. This classification provides insights into the species composition and ecological characteristics of each forest type, informing management strategies and conservation efforts.
- Forest Condition: The map can also provide information about the health and condition of forests, including factors like tree density, age, and disease prevalence. This data is essential for assessing the resilience of forests to disturbances and for developing effective management practices.
- Ownership: The U.S. Forest Map often includes information about land ownership, distinguishing between public and private forests. This information is vital for understanding the various stakeholders involved in forest management and for coordinating conservation efforts.
The Importance of the U.S. Forest Map:
The U.S. Forest Map serves as a vital tool for a wide range of stakeholders, including:
- Forest Managers: The map provides essential information for developing sustainable forest management plans, ensuring the long-term health and productivity of these ecosystems.
- Researchers: The map facilitates scientific research on forest ecology, biodiversity, and climate change impacts, enabling scientists to develop a deeper understanding of these complex systems.
- Policymakers: The map informs policy decisions related to forest conservation, sustainable forestry, and climate change mitigation, guiding the development of effective regulations and incentives.
- The Public: The map helps raise awareness about the importance of forests and promotes appreciation for these valuable resources, fostering a sense of stewardship and responsibility towards their protection.
Benefits of Utilizing the U.S. Forest Map:
- Enhanced Conservation Efforts: By providing a detailed picture of forest resources, the map enables more targeted and effective conservation efforts, protecting biodiversity and safeguarding vital ecosystems.
- Sustainable Forest Management: The map facilitates sustainable forest management practices, ensuring the long-term health and productivity of forests while minimizing environmental impacts.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Forests play a crucial role in mitigating climate change by absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. The map helps track changes in forest cover and condition, informing efforts to enhance carbon sequestration and climate resilience.
- Economic Development: Forests provide numerous economic benefits, including timber production, recreation, and tourism. The map can support economic development by identifying areas with high forest resource potential and by guiding investment in sustainable forest-based industries.
FAQs about the U.S. Forest Map:
1. Where can I access the U.S. Forest Map?
Various organizations provide access to the U.S. Forest Map, including the U.S. Forest Service, the U.S. Geological Survey, and academic institutions. Online platforms and databases offer interactive maps and downloadable data.
2. What data sources are used to create the U.S. Forest Map?
The map is typically compiled using a combination of satellite imagery, aerial photography, ground-based surveys, and other data sources. These data are analyzed and integrated using sophisticated mapping techniques.
3. How often is the U.S. Forest Map updated?
The frequency of updates varies depending on the specific map and data sources used. Some maps are updated annually, while others may be updated less frequently.
4. What are the limitations of the U.S. Forest Map?
Like any map, the U.S. Forest Map has limitations. Data accuracy can be affected by factors like cloud cover, terrain, and data collection methods. Additionally, the map may not capture all aspects of forest ecosystems, such as soil conditions and biodiversity.
5. How can I contribute to the U.S. Forest Map?
You can contribute to the U.S. Forest Map by participating in citizen science projects, reporting observations of forest conditions, and supporting organizations involved in forest monitoring and research.
Tips for Utilizing the U.S. Forest Map:
- Identify specific areas of interest: Focus on regions or forest types that are relevant to your research, management, or conservation goals.
- Utilize the map’s interactive features: Explore the map’s layers and filters to access specific data sets and customize your view.
- Combine the map with other data sources: Integrate the U.S. Forest Map with other relevant data, such as climate data, soil information, or biodiversity data, to gain a more comprehensive understanding of forest ecosystems.
- Stay informed about updates: Keep abreast of any updates or revisions to the U.S. Forest Map to ensure you are using the most current information.
Conclusion:
The U.S. Forest Map is a vital resource for understanding and managing our nation’s forests. By providing a comprehensive overview of forest cover, type, condition, and ownership, the map empowers stakeholders to make informed decisions about forest conservation, sustainable management, and climate change mitigation. As our forests continue to face a range of challenges, the U.S. Forest Map will remain an indispensable tool for safeguarding these vital ecosystems and ensuring their continued role in supporting our nation’s environment, economy, and well-being.


![[OC] Interactive Map of U.S. National Forests : r/dataisbeautiful](https://i.redd.it/9csm2srgbdy71.png)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into us forests map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!